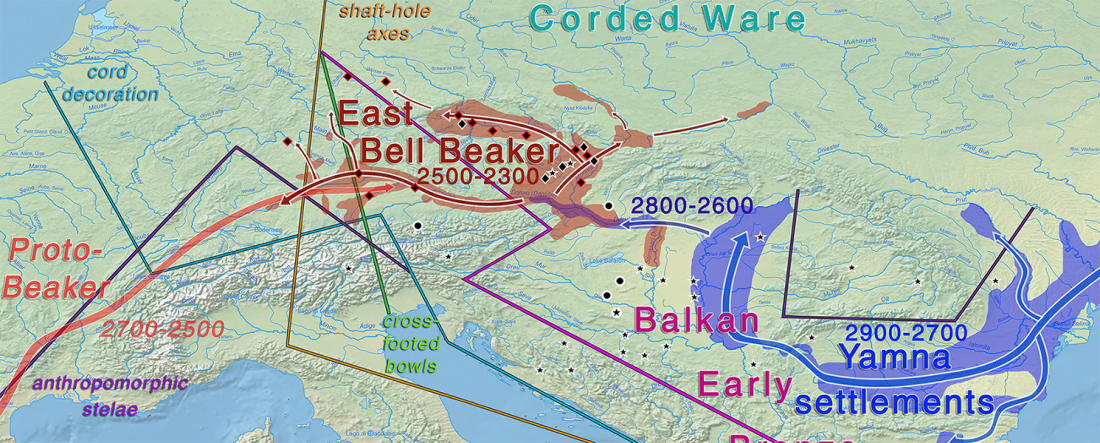
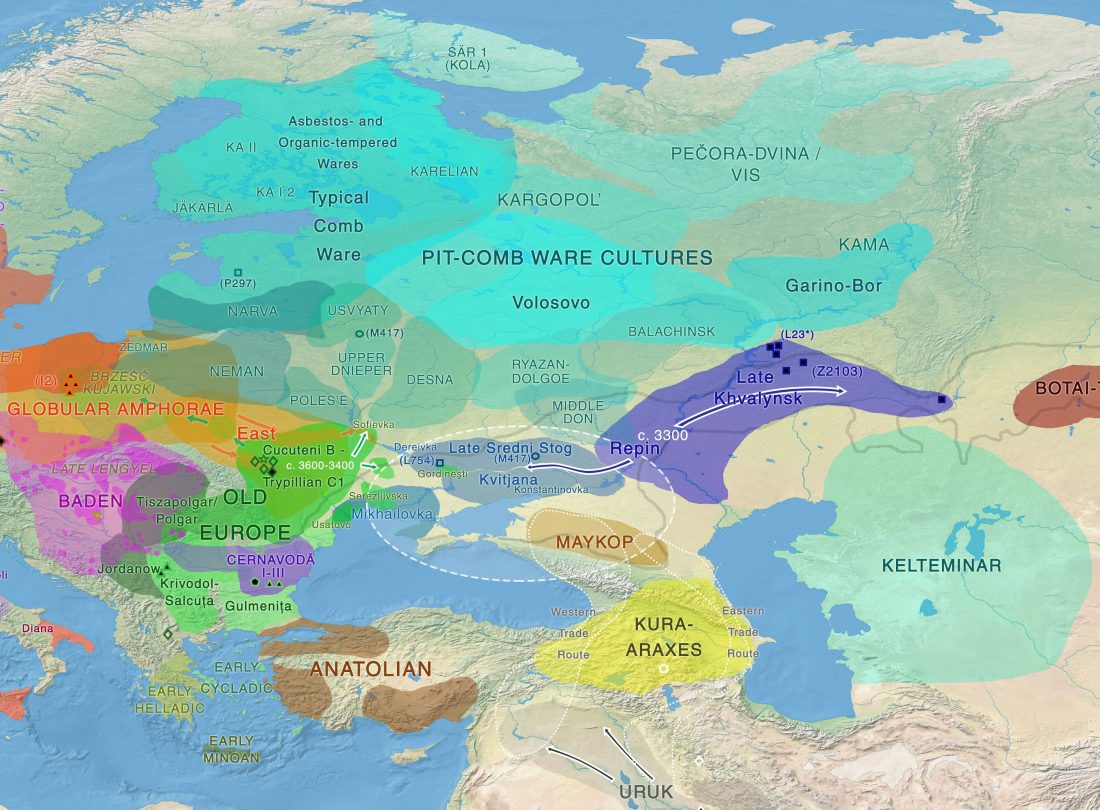
Ancient genomes document multiple waves of migration in south-east Asian prehistory
Open access preprint at bioRxiv Ancient genomes document multiple waves of migration in Southeast Asian prehistory, by Lipson, Cheronet, Mallick, et al. (2018).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
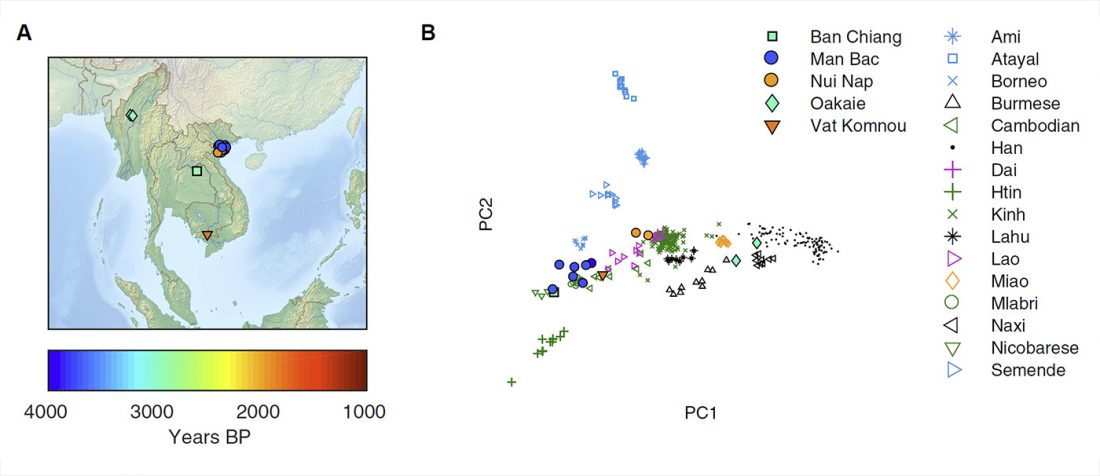
… Read the rest “Ancient genomes document multiple waves of migration in south-east Asian prehistory”Southeast Asia is home to rich human genetic and linguistic diversity, but the details of past population movements in the region are not well known. Here, we report genome-wide ancient DNA data from thirteen Southeast Asian individuals spanning from the Neolithic period through the Iron Age (4100-1700 years ago). Early agriculturalists from Man Bac in Vietnam possessed a mixture of East Asian (southern Chinese farmer) and deeply diverged eastern Eurasian (hunter-gatherer) ancestry characteristic