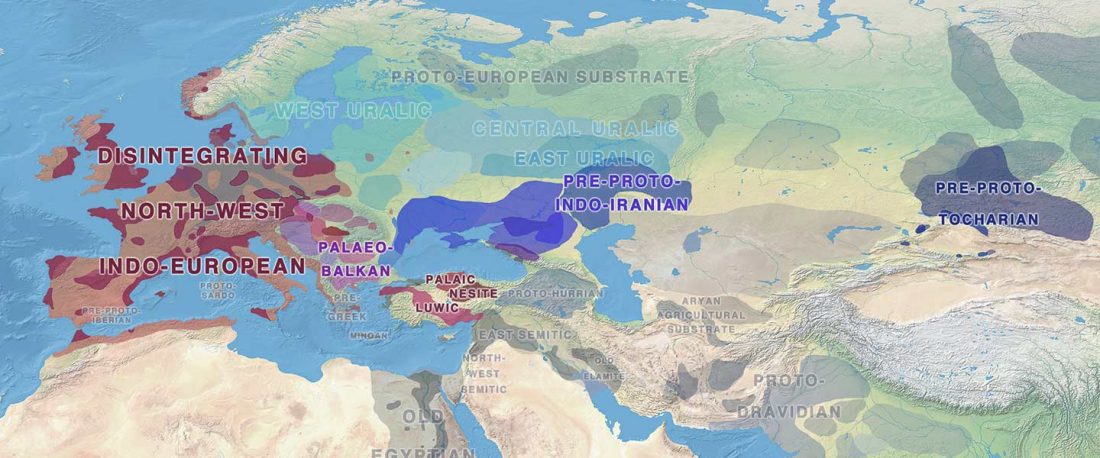
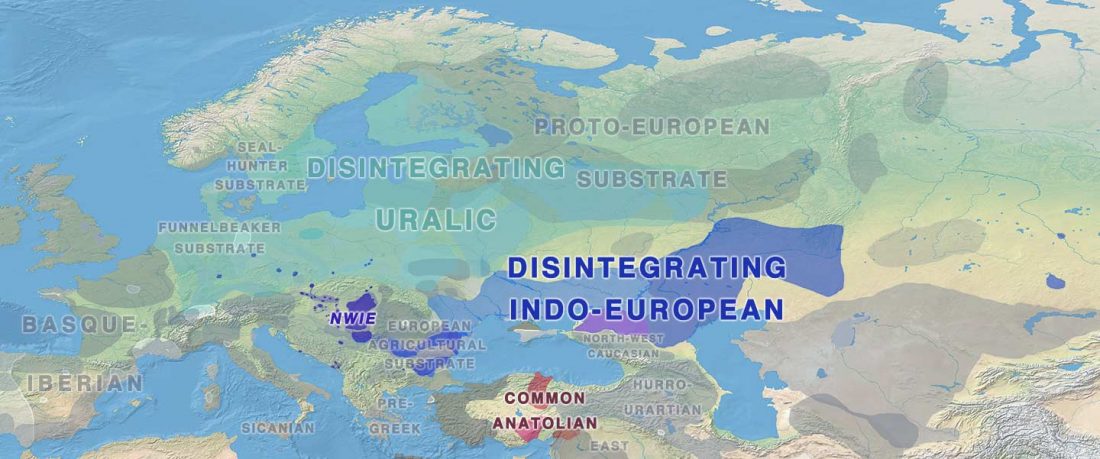
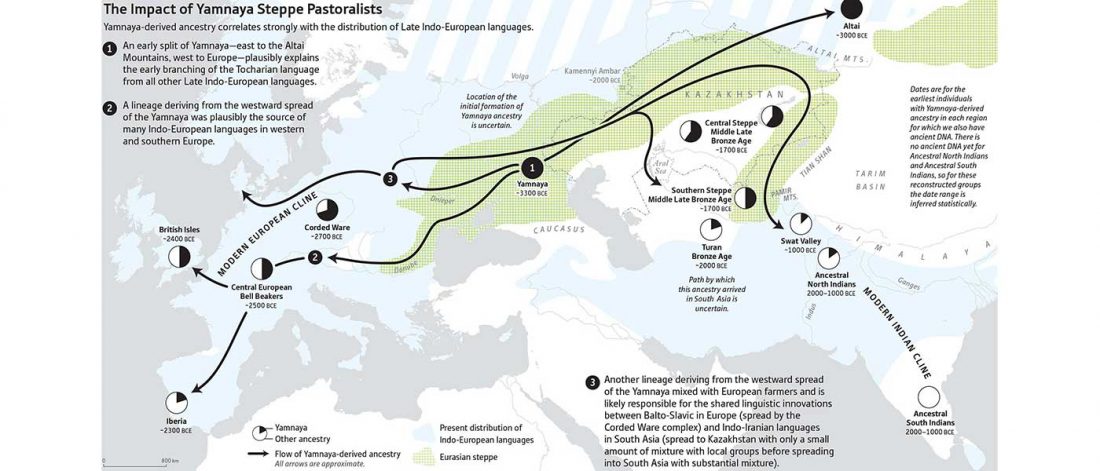
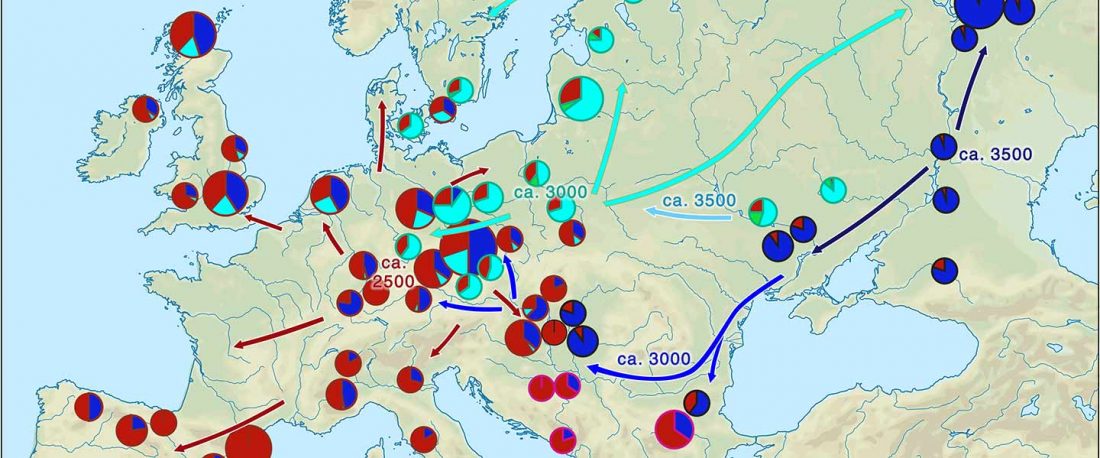
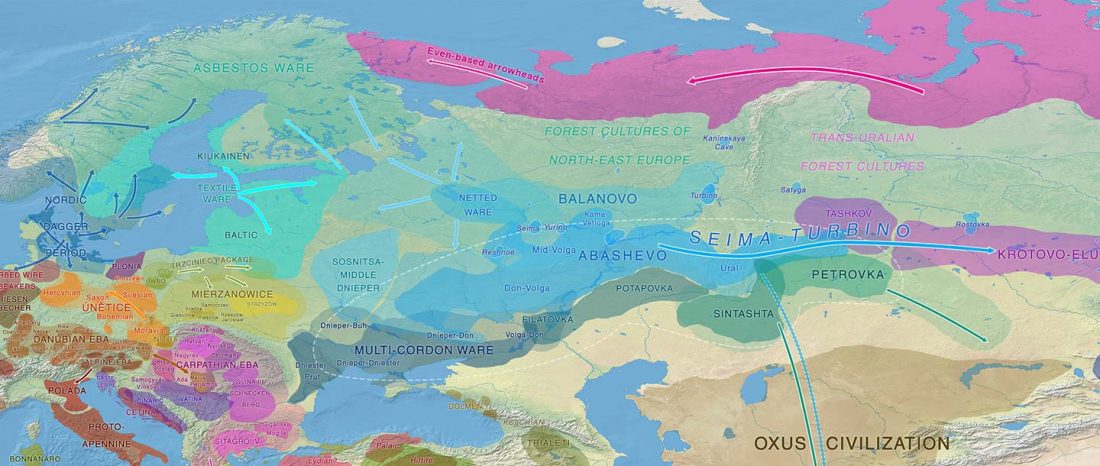
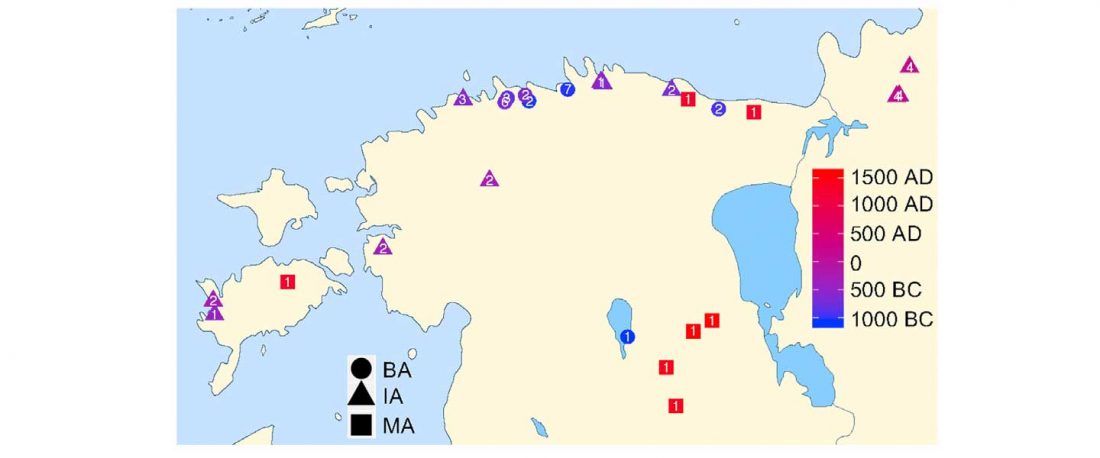
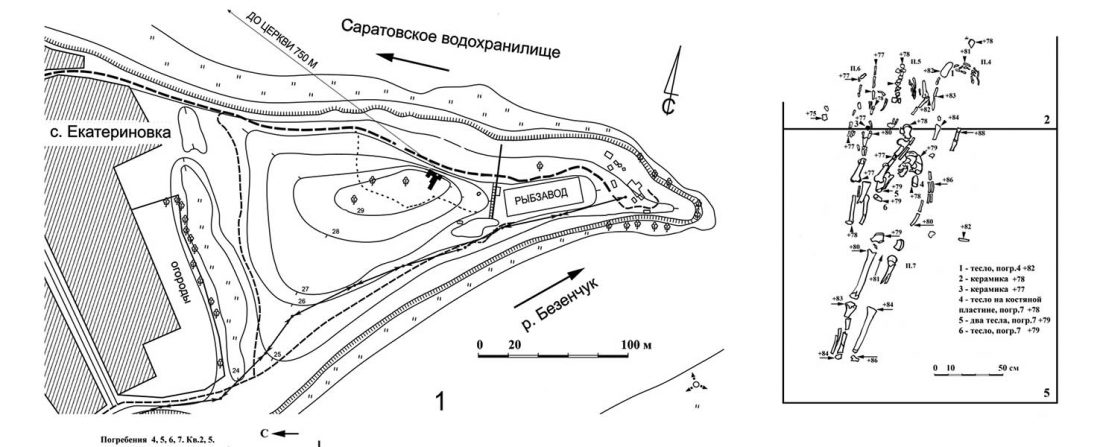
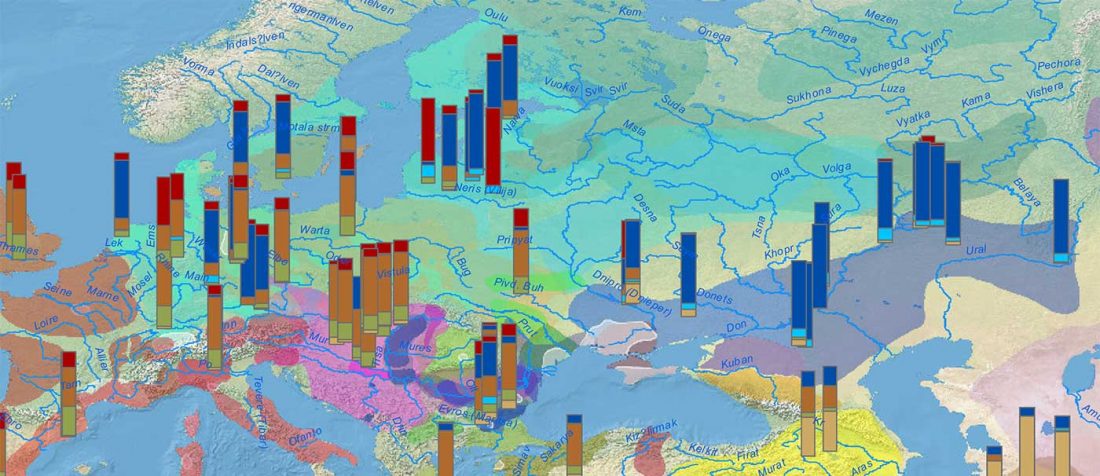
The practice of making inferences about the cultures of language users on the evidence of reconstructed languages is called linguistic palaeontology. These inferences may concern the material culture and geographic location of speakers as well as their social relations, mythology, and beliefs – the notion of ‘archaeological culture’ is used to capture both material culture and behaviour (Mallory 2020).
Proto-Uralic Homeland
This is the introductory post for my draft on the Proto-Uralic Homeland, which I have divided into eight pieces according to semantic fields or chronology, or both. During the following week, you will … Read the rest “Palaeolinguistics: The Homeland Problem”