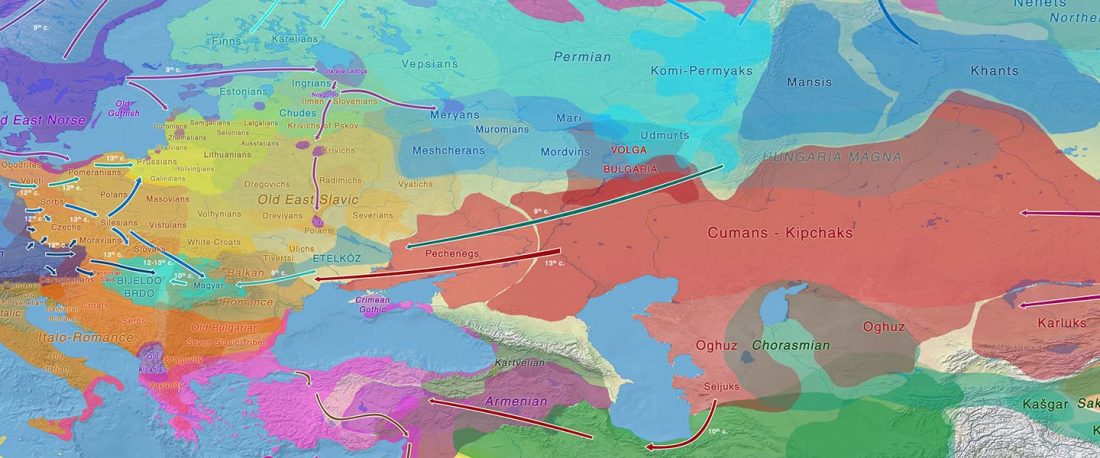
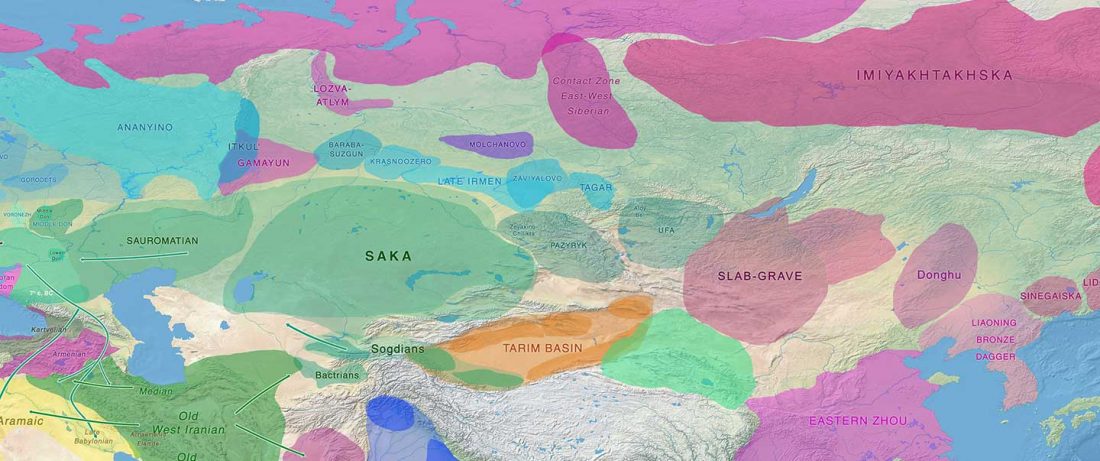
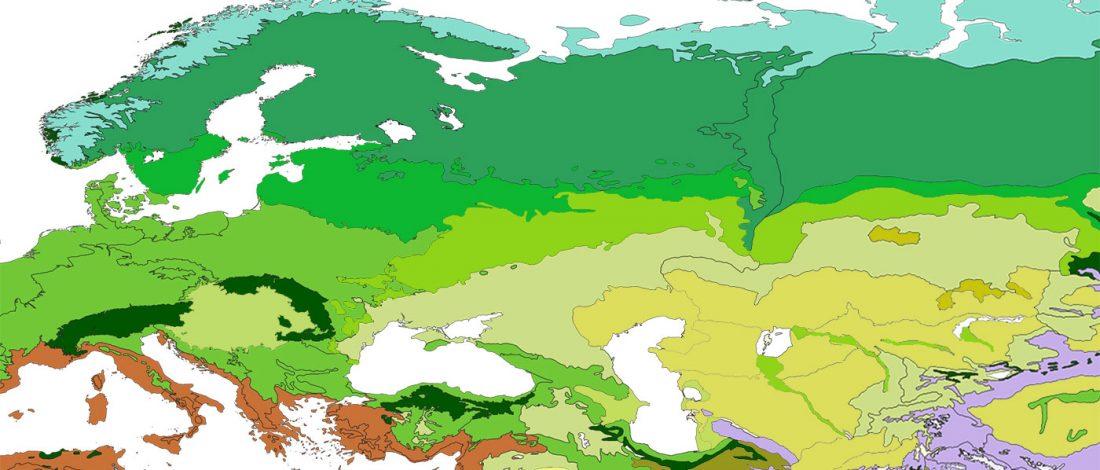
The Nightmare Week of “N1c=Uralic” proponents (see here) continues, now with preprint Y-chromosome haplogroups from Hun, Avar and conquering Hungarian period nomadic people of the Carpathian Basin, by Neparaczki et al. bioRxiv (2019).
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Magyar tribes brought R1a-Z645, I2a-L621, and N1a-L392(xB197) lineages to the Carpathian Basin”Hun, Avar and conquering Hungarian nomadic groups arrived into the Carpathian Basin from the Eurasian Steppes and significantly influenced its political and ethnical landscape. In order to shed light on the genetic affinity of above groups we have determined Y chromosomal haplogroups and autosomal loci, from 49 individuals, supposed to represent military leaders. Haplogroups from the Hun-age are consistent with Xiongnu ancestry of European