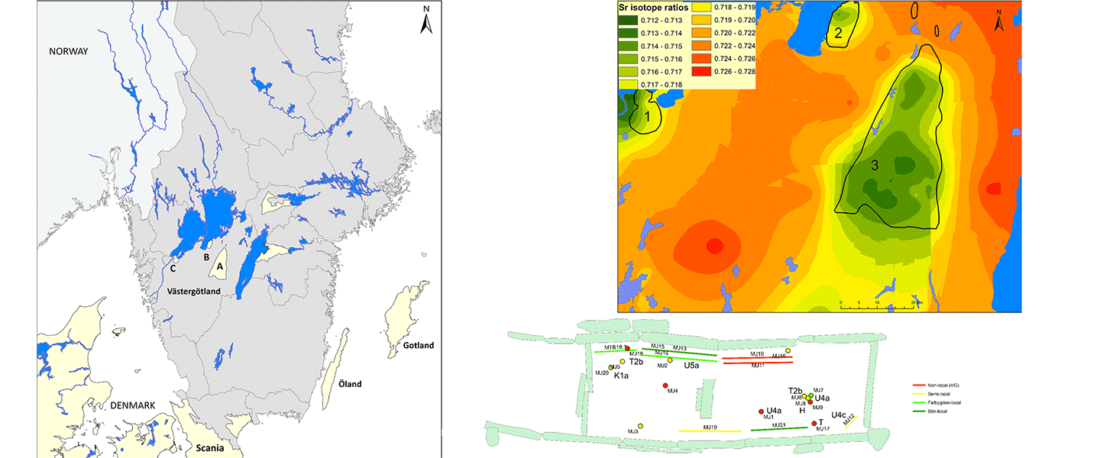
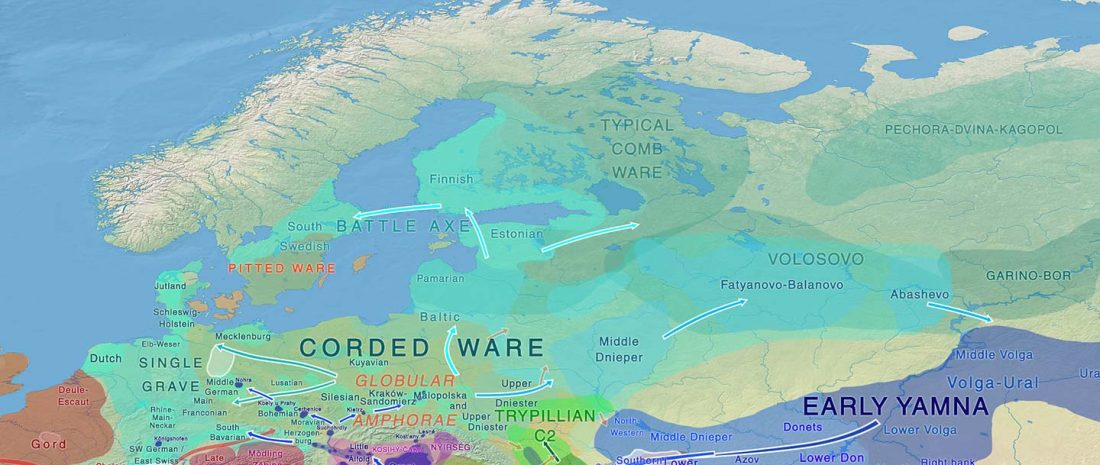
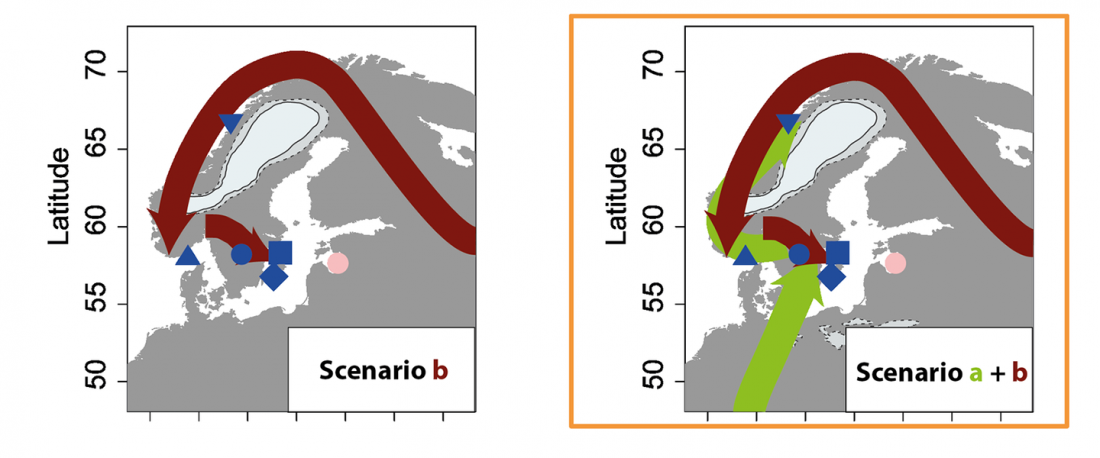
Open access Mobility patterns in inland southwestern Sweden during the Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, by Blank, Sjögren, Knipper, et al. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 13, 64 (2021).
NOTE. For a full archaeological description of the area of study, refer to the related paper Old bones or early graves? Megalithic burial sequences in southern Sweden based on 14C datings, by Blank, Sjögren, & Storå, Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 12, 89 (2020).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Increased mobility in the Nordic Late Neolithic/Bronze Age”The sampling from megalithic graves shows a chronological gap of at least 400 years (2600–2200 cal BC), when no megalithic graves were constructed or used