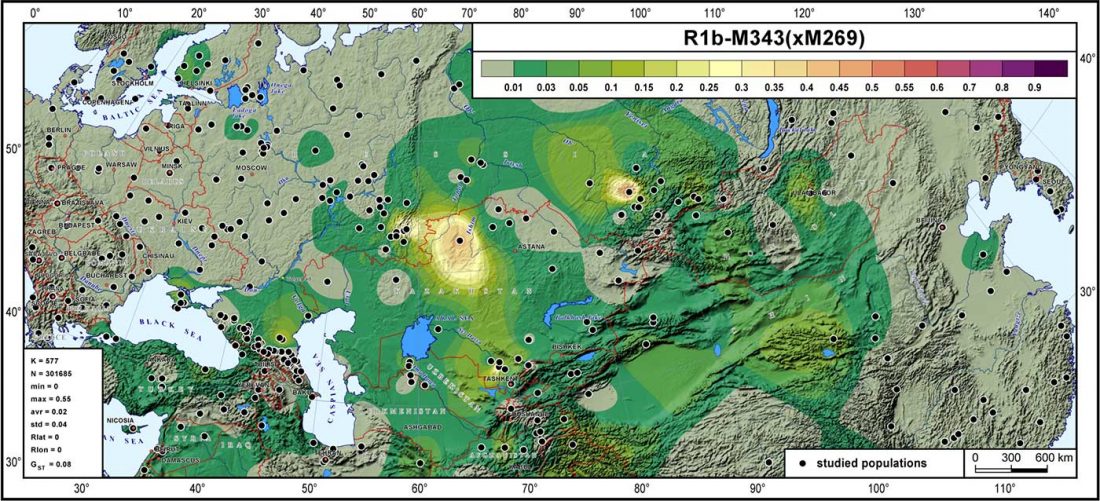
Open access Characterizing the genetic history of admixture across inner Eurasia, by Jeong et al. (2018).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Genetic history of admixture across inner Eurasia; Botai shows R1b-M73”The indigenous populations of inner Eurasia, a huge geographic region covering the central Eurasian steppe and the northern Eurasian taiga and tundra, harbor tremendous diversity in their genes, cultures and languages. In this study, we report novel genome-wide data for 763 individuals from Armenia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Moldova, Mongolia, Russia, Tajikistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. We furthermore report genome-wide data of two Eneolithic individuals (~5,400 years before present) associated with the Botai culture in northern Kazakhstan. We find that inner Eurasian populations