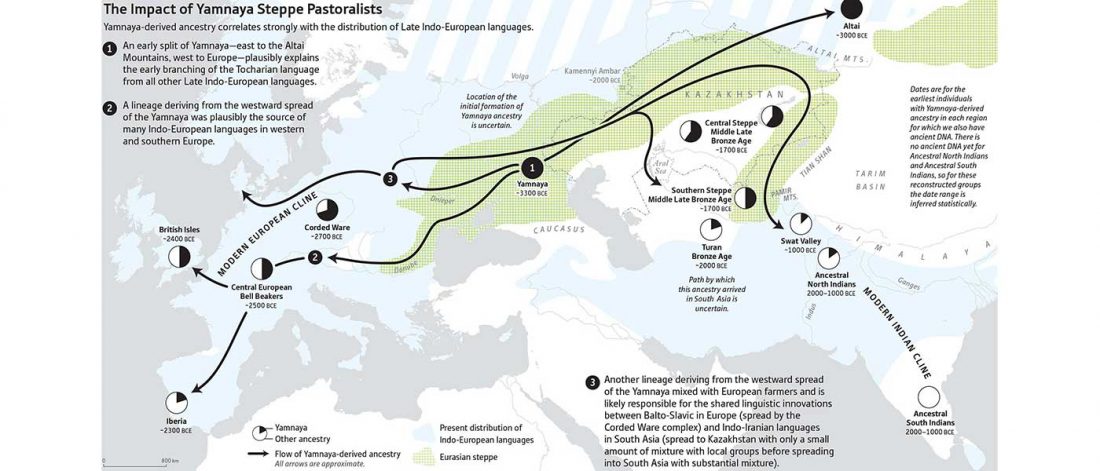
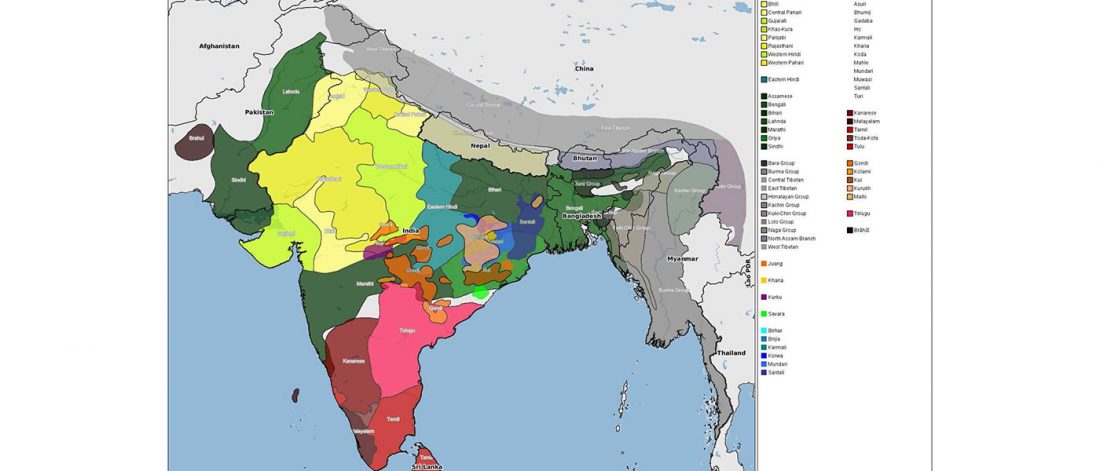
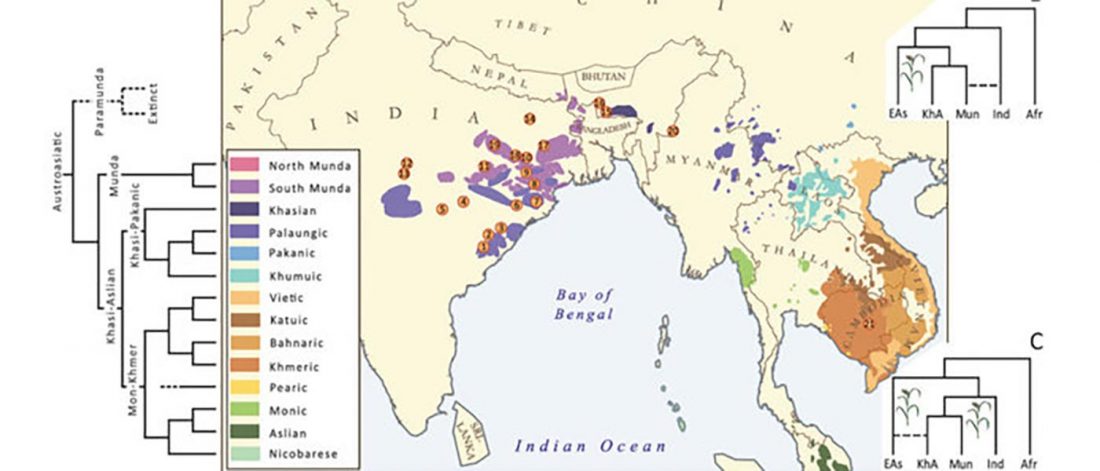
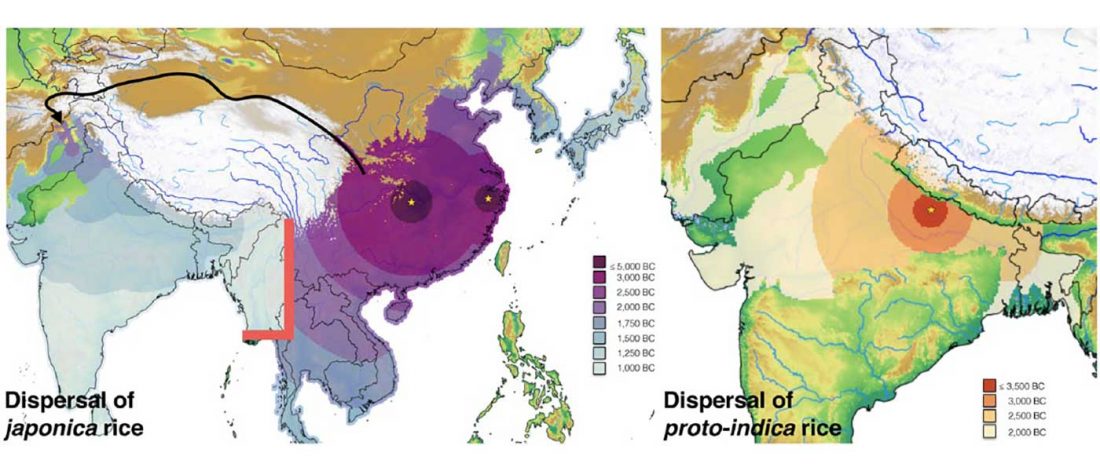
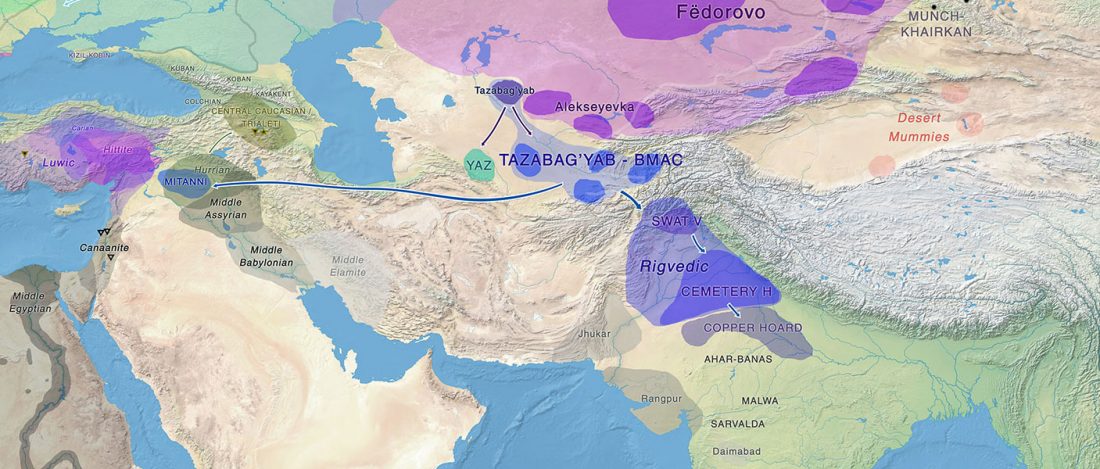
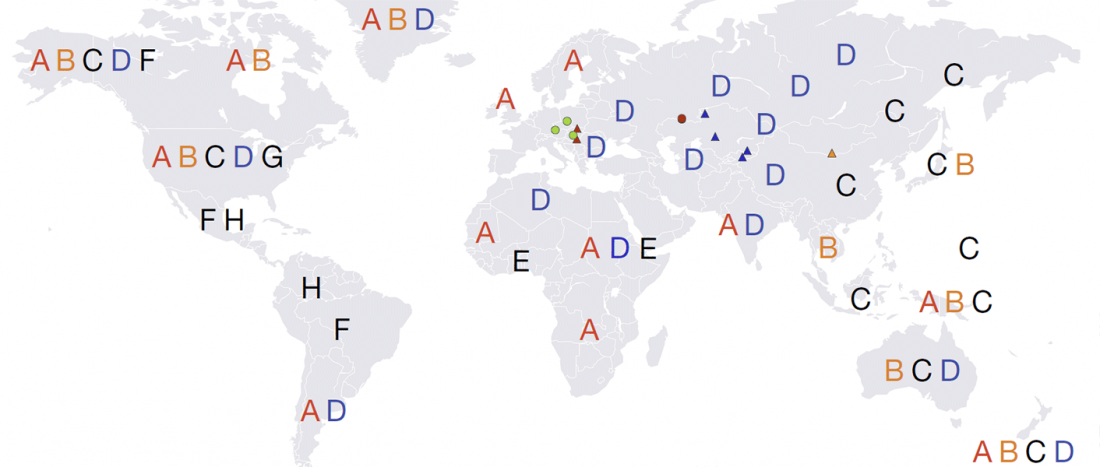
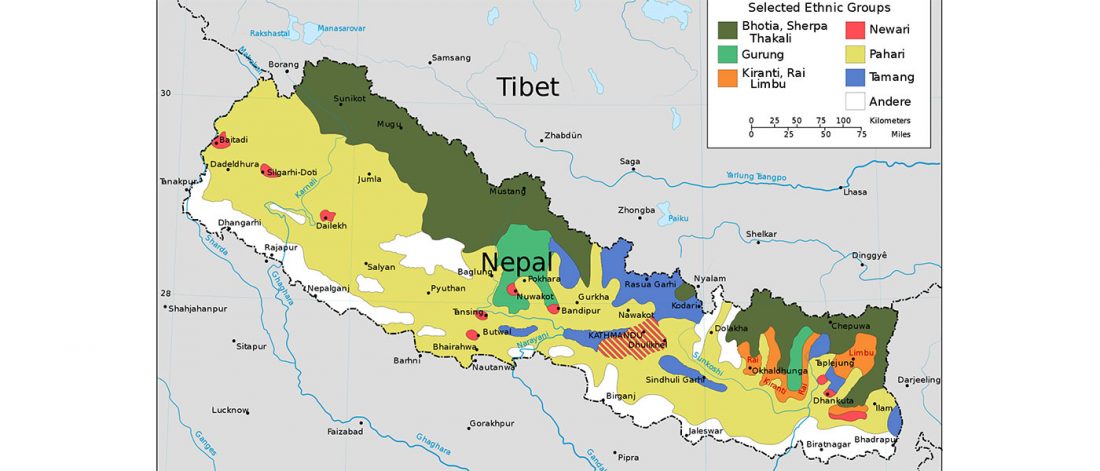
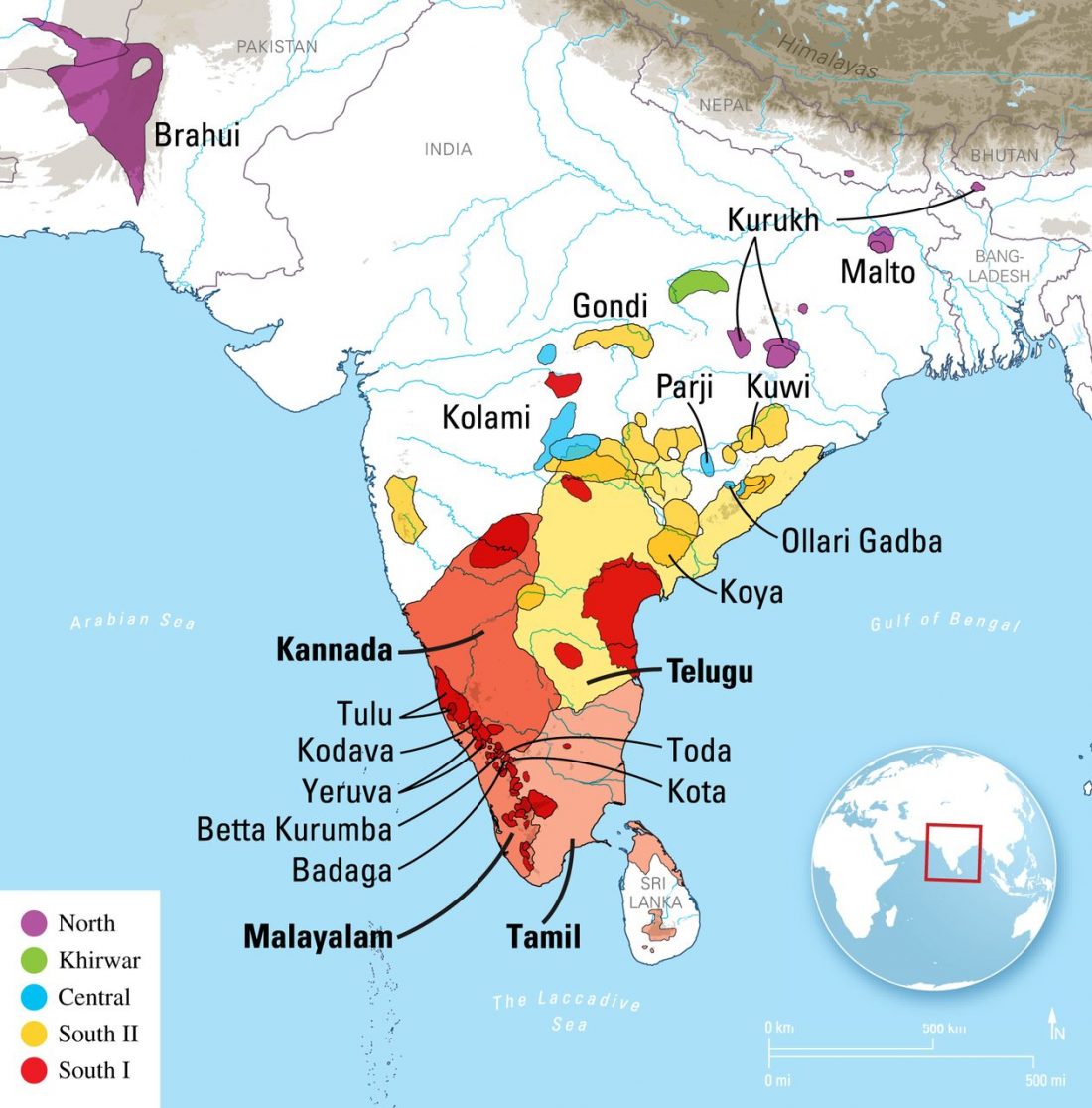
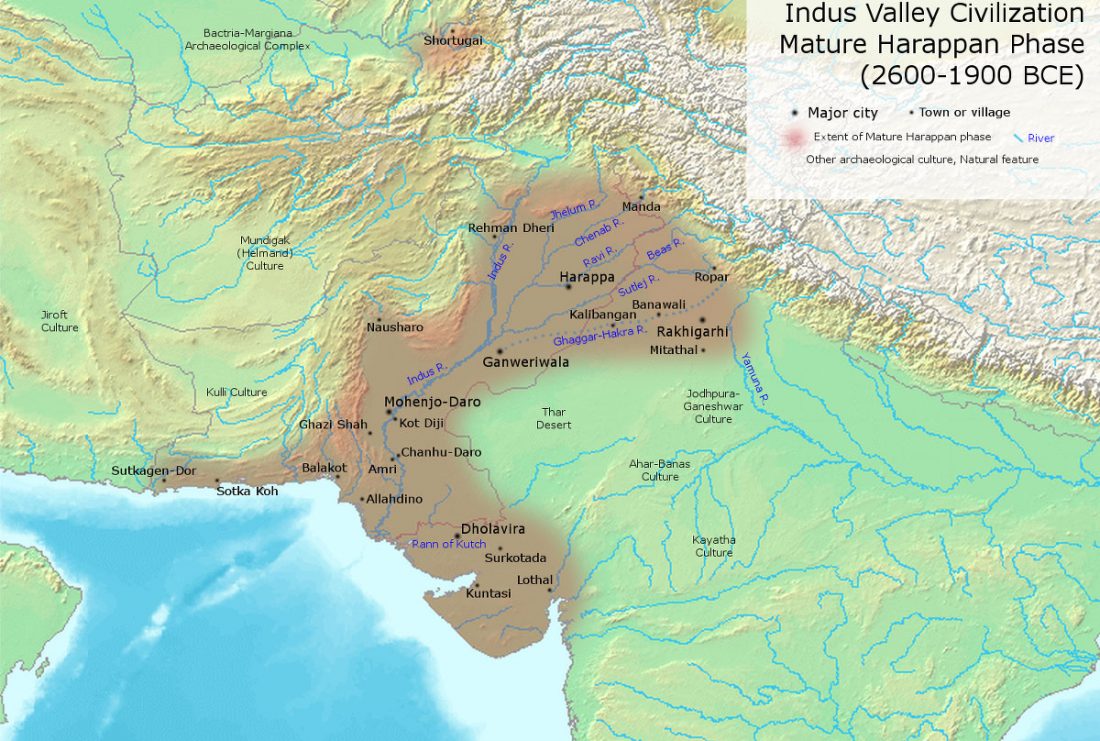
Recent papers The formation of human populations in South and Central Asia, by Narasimhan, Patterson et al. Science (2019) and An Ancient Harappan Genome Lacks Ancestry from Steppe Pastoralists or Iranian Farmers, by Shinde et al. Cell (2019).
NOTE. For direct access to Narasimhan, Patterson et al. (2019), visit this link courtesy of the first author and the Reich Lab.
I am currently not on holidays anymore, and the information in the paper is huge, with many complex issues raised by the new samples and analyses rather than solved, so I will stick to the Indo-European question, … Read the rest “Yamnaya replaced Europeans, but admixed heavily as they spread to Asia”