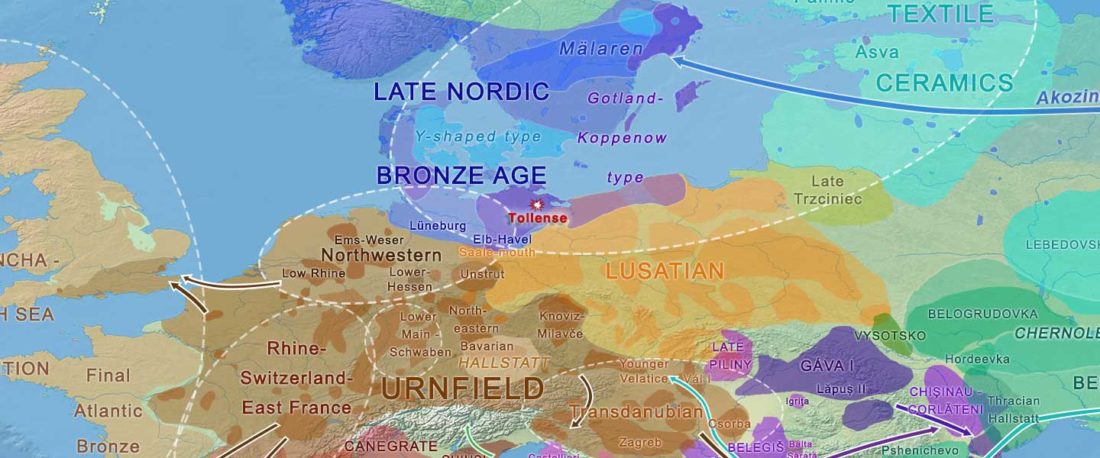
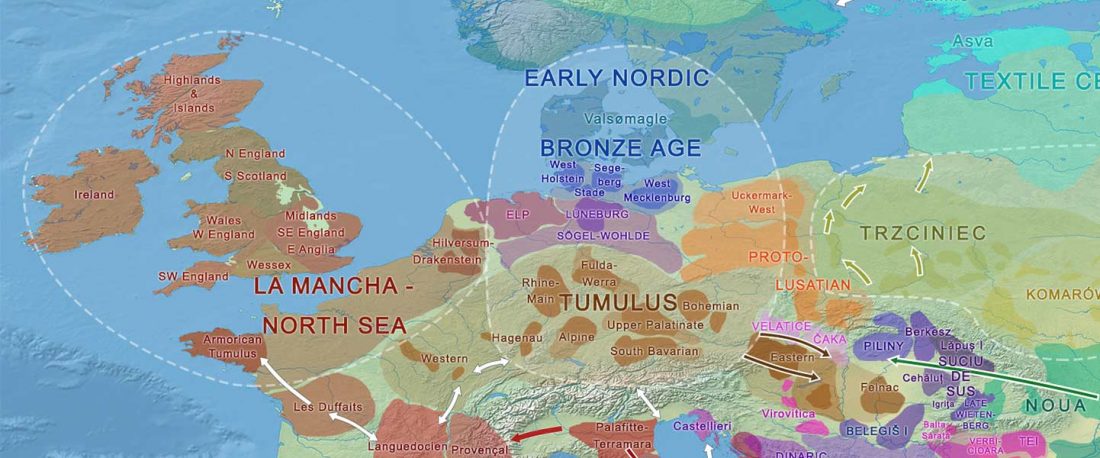
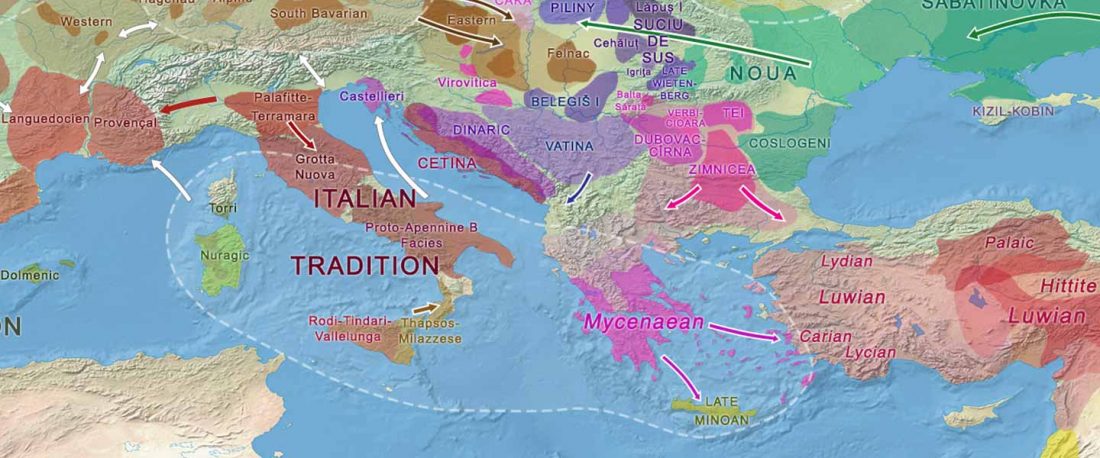
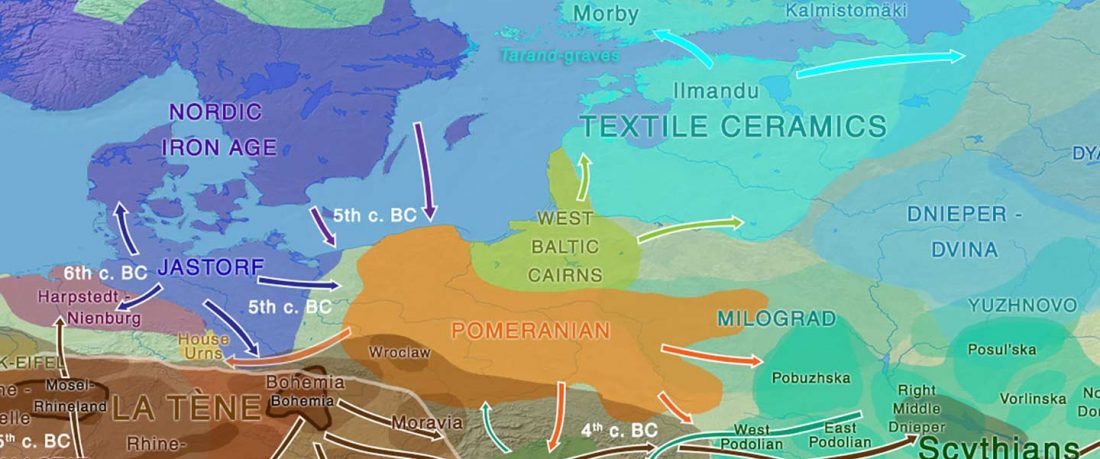
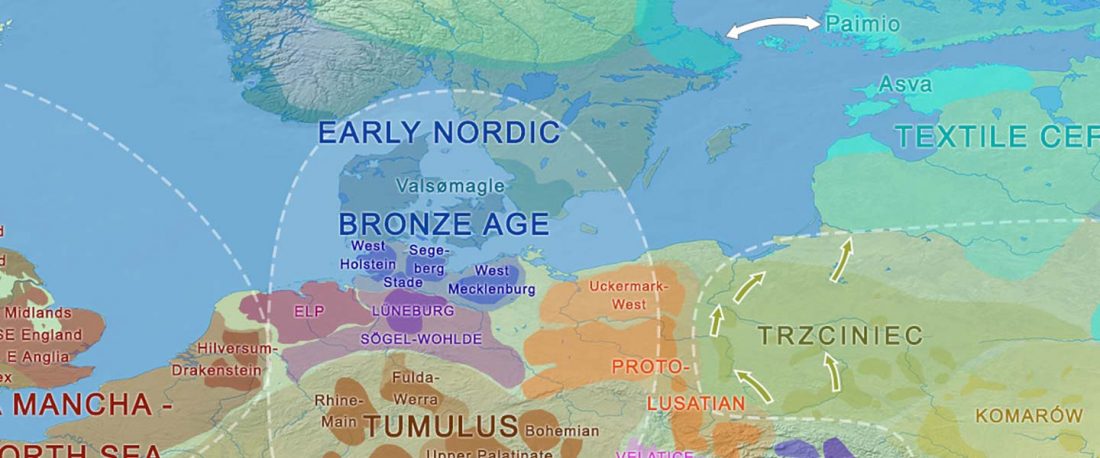
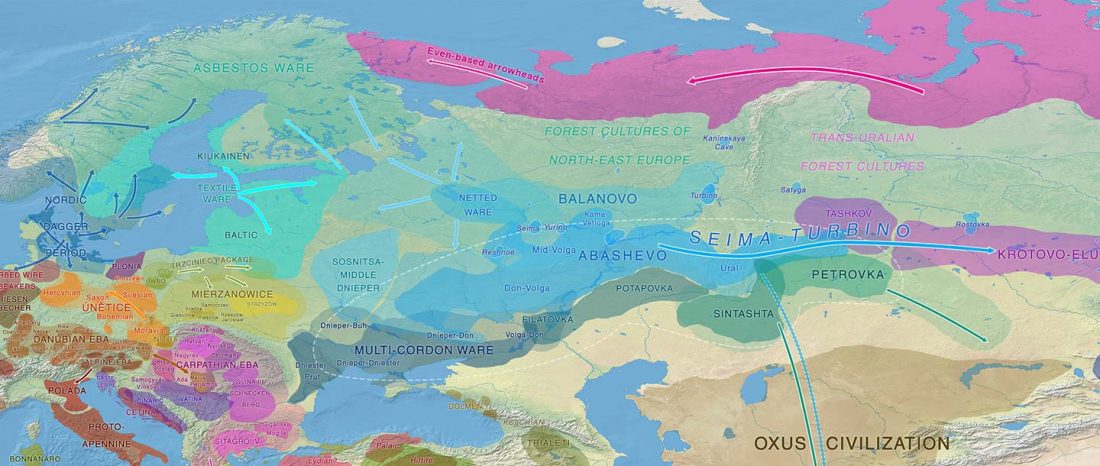
This post is part of a draft on palaeolinguistics and the Proto-Uralic homeland. See below for the color code of protoforms.
3. Forests
3.1. Regular terms
PU (Saa.? Fi., Md., Ma., Ms., Hu.? Smy.) *kojwa ‘birch’ (UEW Nº 334).
PU (Saa., Fi., Ma., P, Kh., Ms.) *ćänä ‘bracket fungus’ (UEW Nº 995; Aikio 2020: 115 with references).
PU (Md., Ma., Hu.) *ćalV/*će̮li/*ćälV ‘elm’ (UEW Nº 926), from PMd. *śäľǝŋ, PMa. *šolǝ, Hu. szil (Aikio 2020: 101 with references).
PU (Saa., Fi., Md., Ma., P, Kh., Ms., Smy.) *kowsi/*kusa ‘spruce; fir’ (UEW Nº … Read the rest “Proto-Uralic Homeland (II): Forests & Climate”