New paper (behind paywall) The Production of Thin‐Walled Jointless Gold Beads from the Maykop Culture Megalithic Tomb of the Early Bronze Age at Tsarskaya in the North Caucasus: Results of Analytical and Experimental Research, by Trifonov et al. Archaeometry (2018)
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
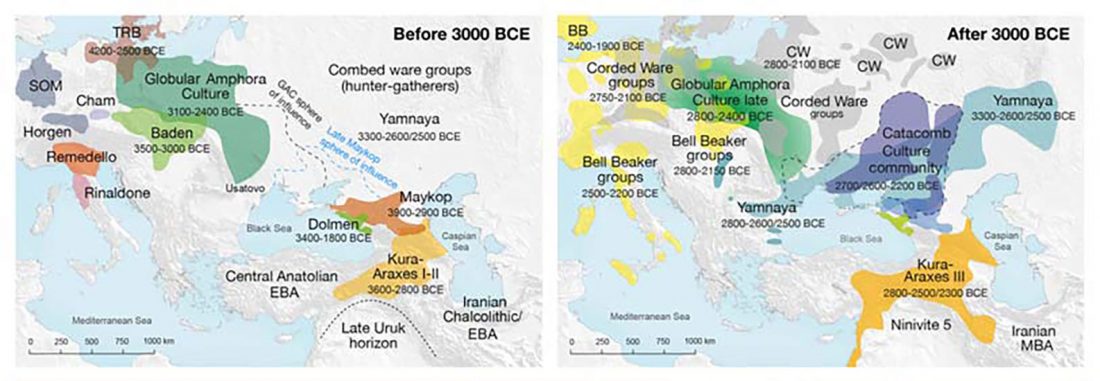
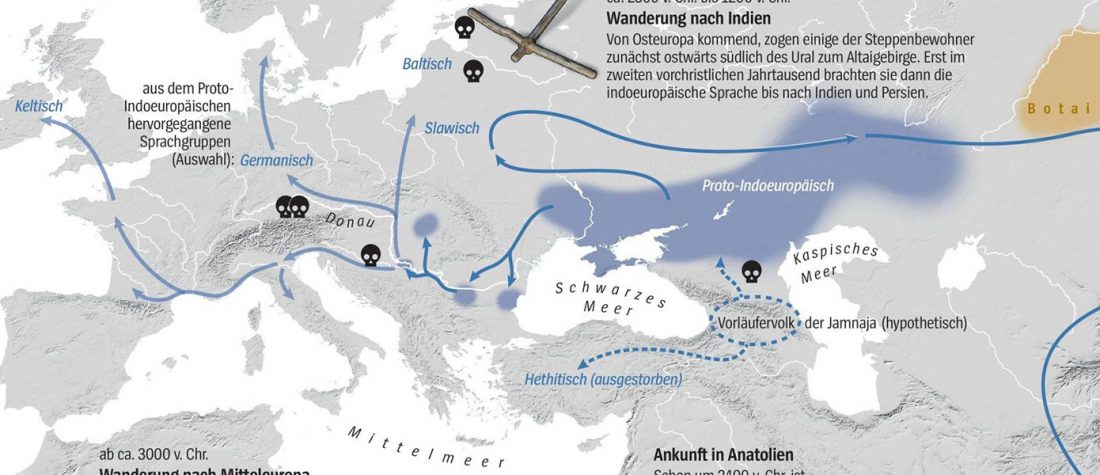
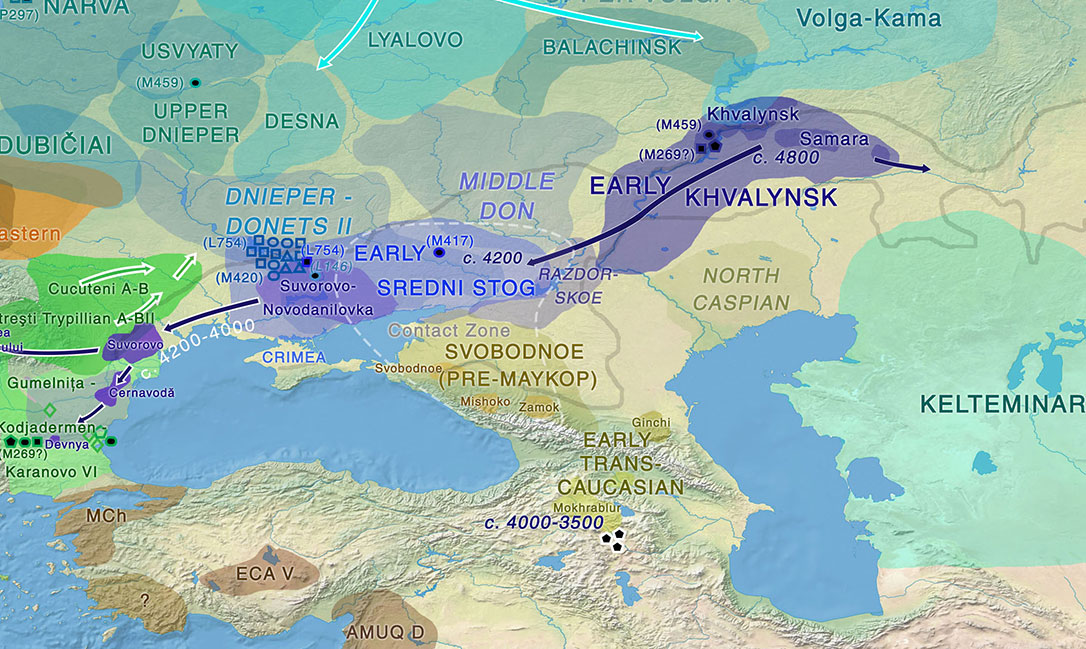
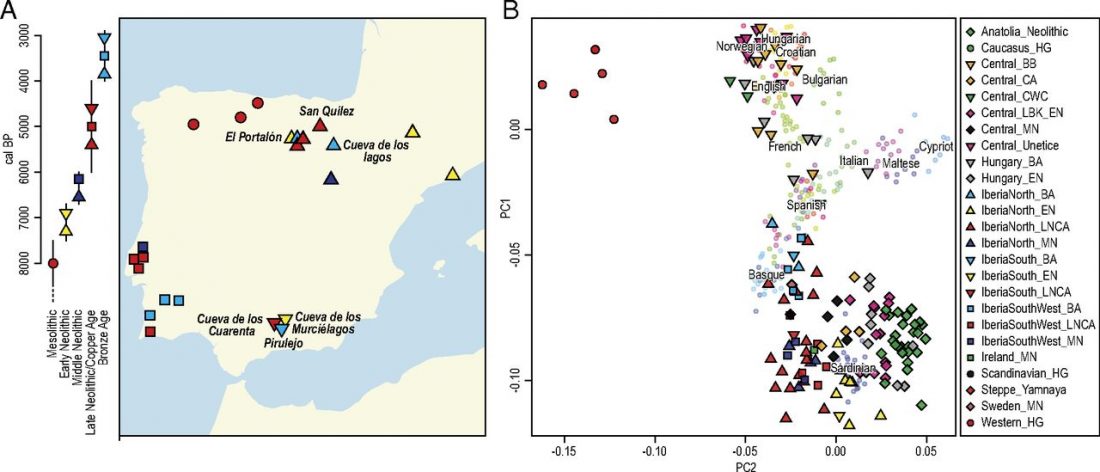
… Read the rest “On the Maykop – Upper Mesopotamia cultural province, distinct from the steppe”In 1898, two megalithic tombs containing graves of a local social elite dated to the Early Bronze Age were discovered by N. I. Veselovsky near the village of Tsarskaya (modern Novosvobodnaya, Republic of Adygeya) (Fig. 1 (a)) (Baye 1900, 43–59; IAC 1901, 33–8; Sagona 2018, 281–97).
Radiocarbon dates place both tombs within the Novosvobodnaya phase