Consequences of Damgaard et al. 2018 (II): The late Khvalynsk migration waves with R1b-L23 lineages
This post should probably read “Consequences of Narasimhan et al. (2018),” too, since there seems to be enough data and materials published by the Copenhagen group in Nature and Science to make a proper interpretation of the data that will appear in their corrected tables.
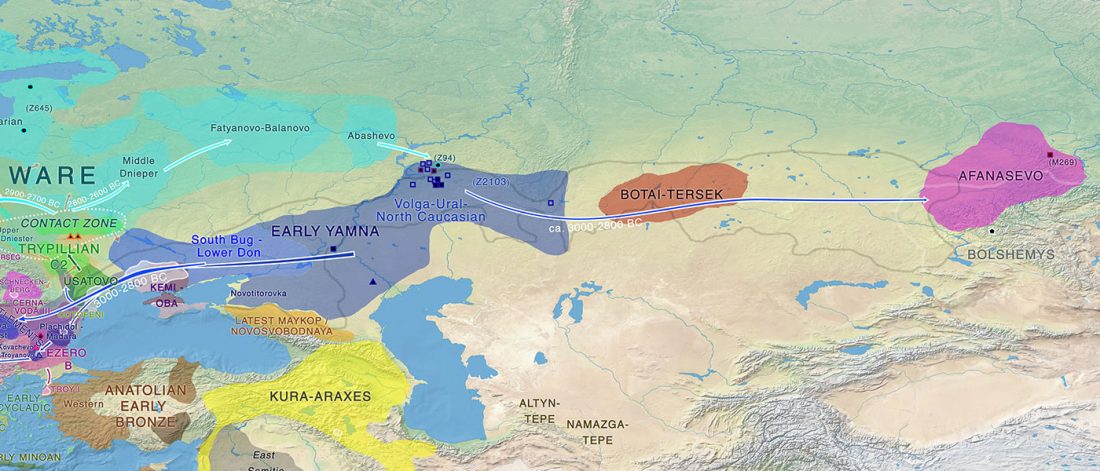
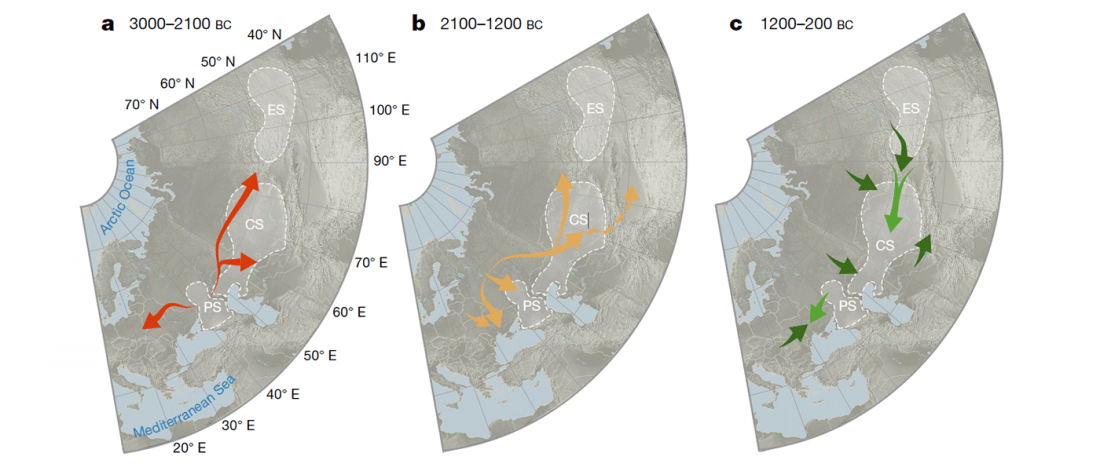
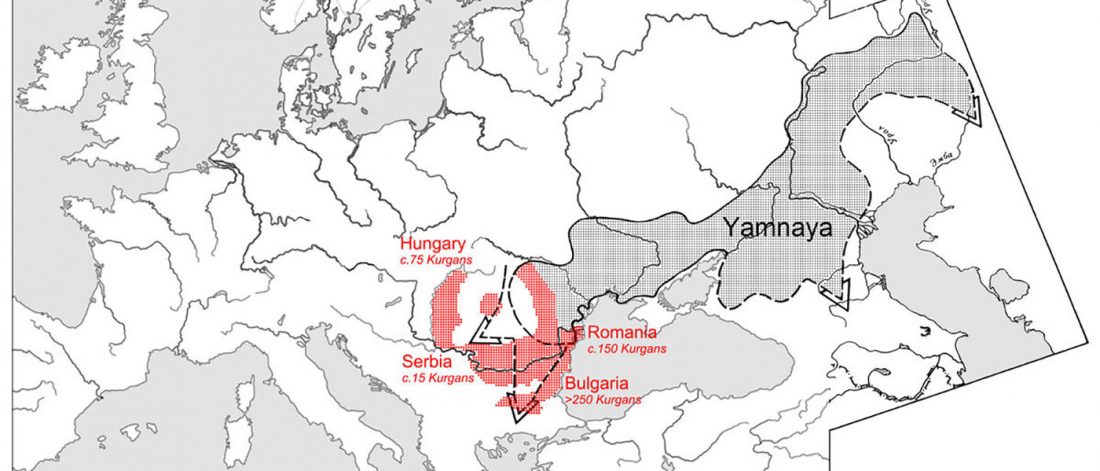
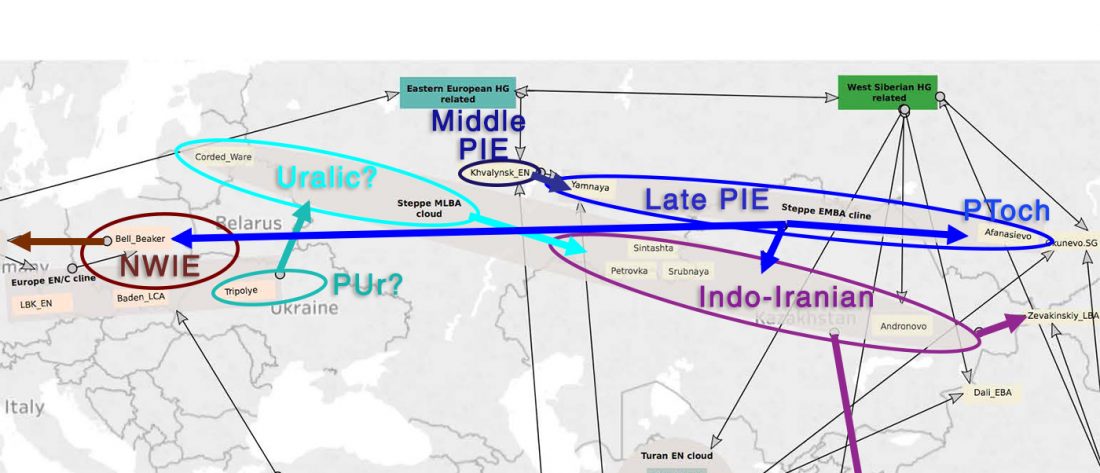
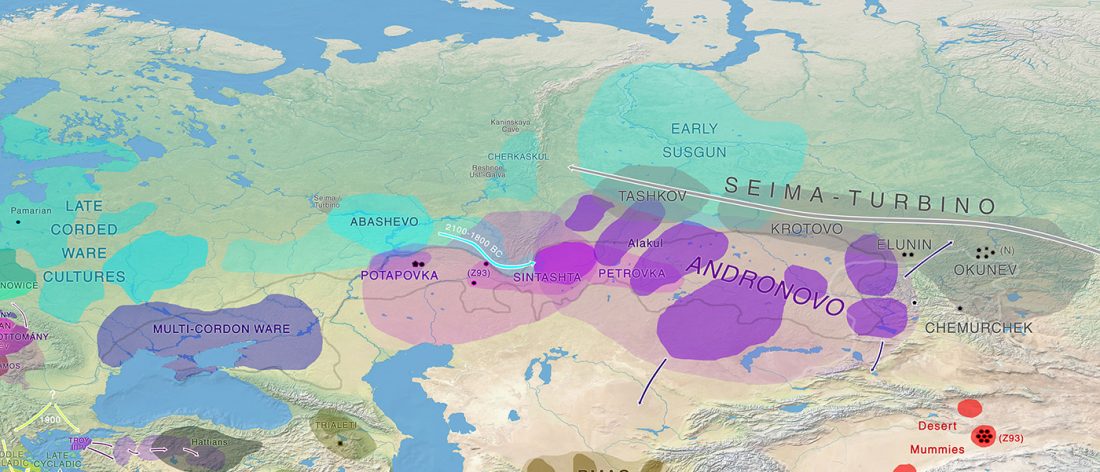
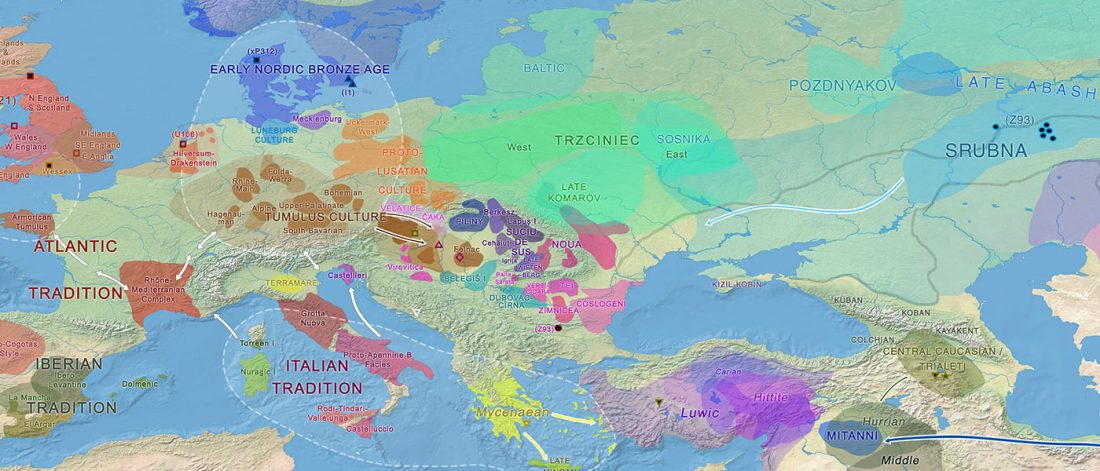
The finding of late Khvalynsk/early Yamna migrations, identified with early LPIE migrants almost exclusively of R1b-L23 subclades is probably one of the most interesting findings in the recent papers regarding the Indo-European question.
Although there are still few samples to derive fully-fledged theories, they begin to depict a clearer idea of waves that … Read the rest “Consequences of Damgaard et al. 2018 (II): The late Khvalynsk migration waves with R1b-L23 lineages”