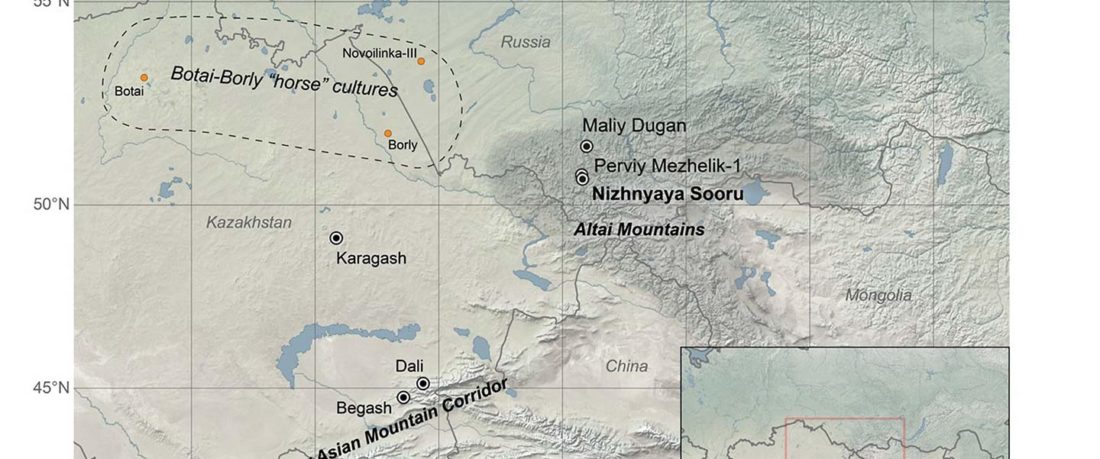
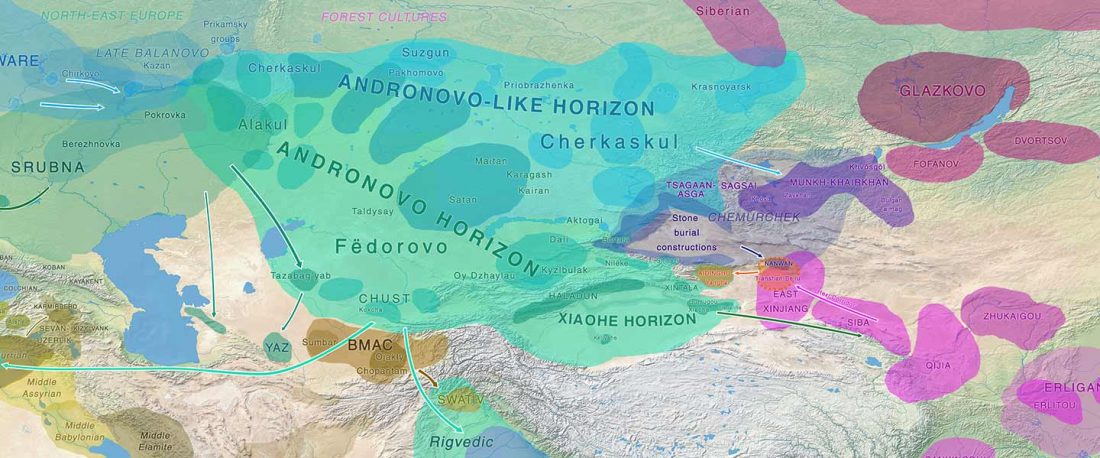
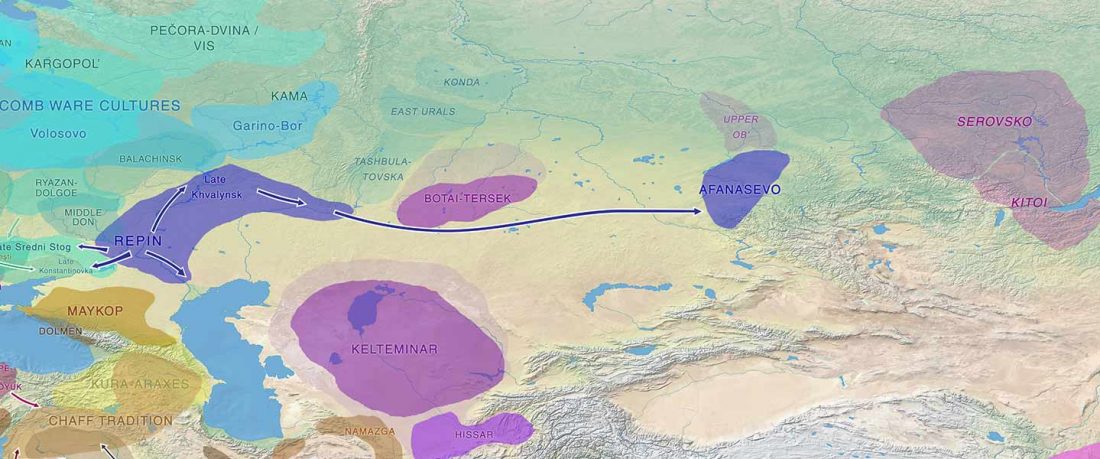
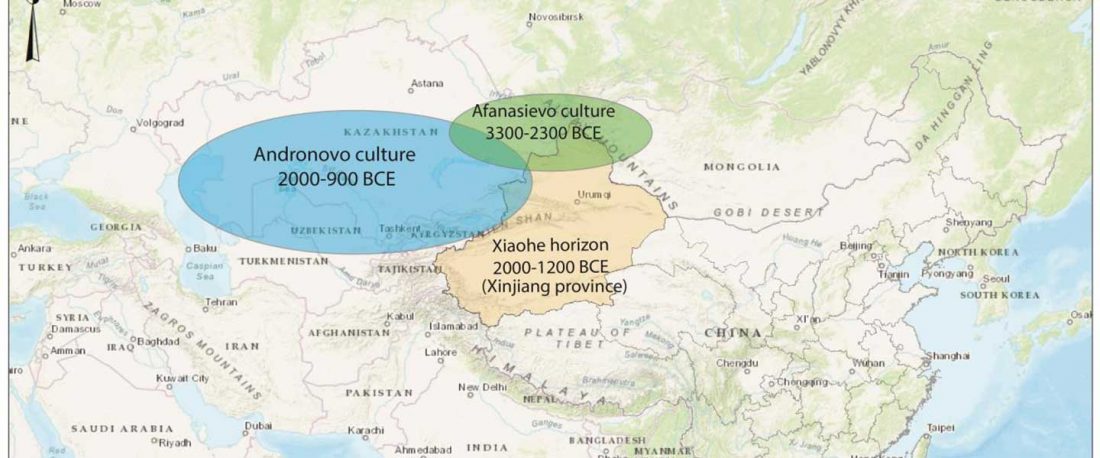
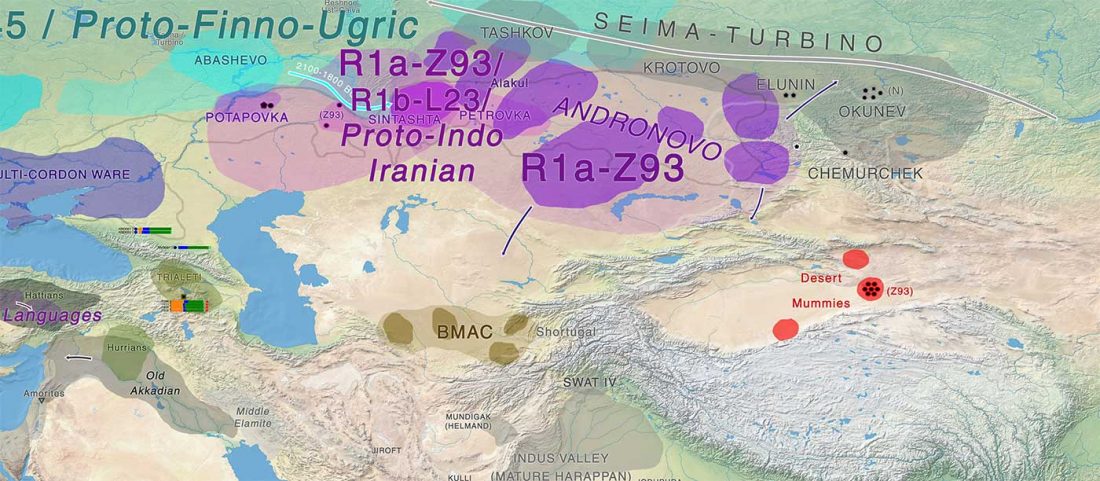
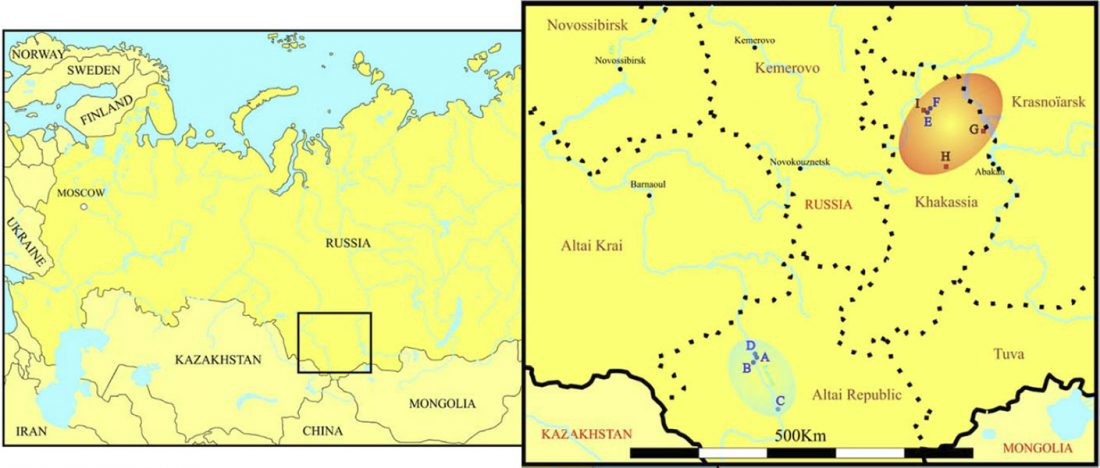
Article in press (behind paywall) Mitochondrial DNA of domesticated sheep confirms pastoralist component of Afanasievo subsistence economy in the Altai Mountains (3300–2900 cal BC), by Hermes et al. Archaeological Research in Asia (2020).
Interesting excerpts:
… Read the rest “Afanasievo brought domesticated bovids to the Altai; new Tianshanbeilu chronology”Previous zooarchaeological research at Afanasievo settlement and mortuary sites argues for the exploitation of both domesticated and wild cattle, sheep, and goats (Derevianko and Molodin, 1994; Gryaznov, 1999; Kosintsev, 2005; Kosintsev and Stepanova, 2010; Pogozheva, 2006). However, the biogeographic distribution of Siberian ibex (Capra sibirica) and argali sheep (Ovis ammon) includes the Altai (Baskin and Danell, 2003), while aurochsen (Bos primigenius) were also likely