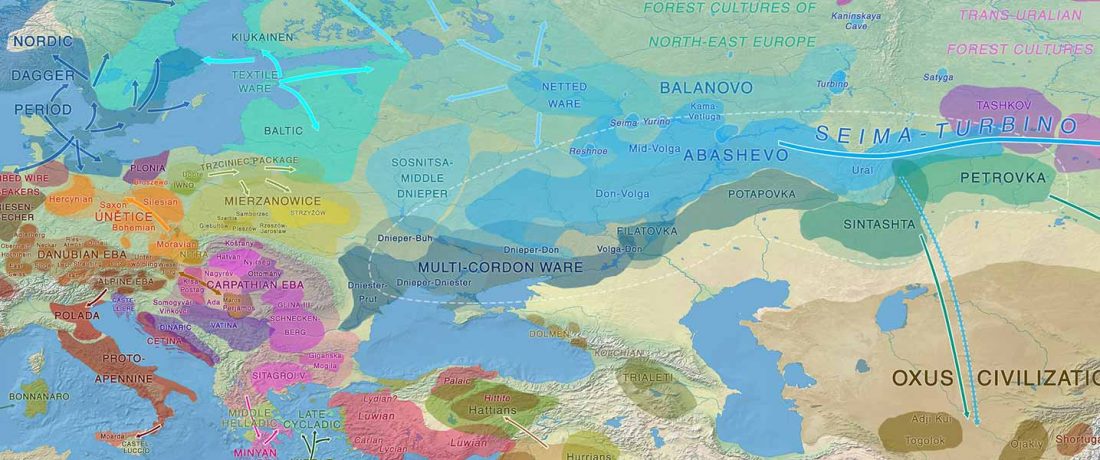
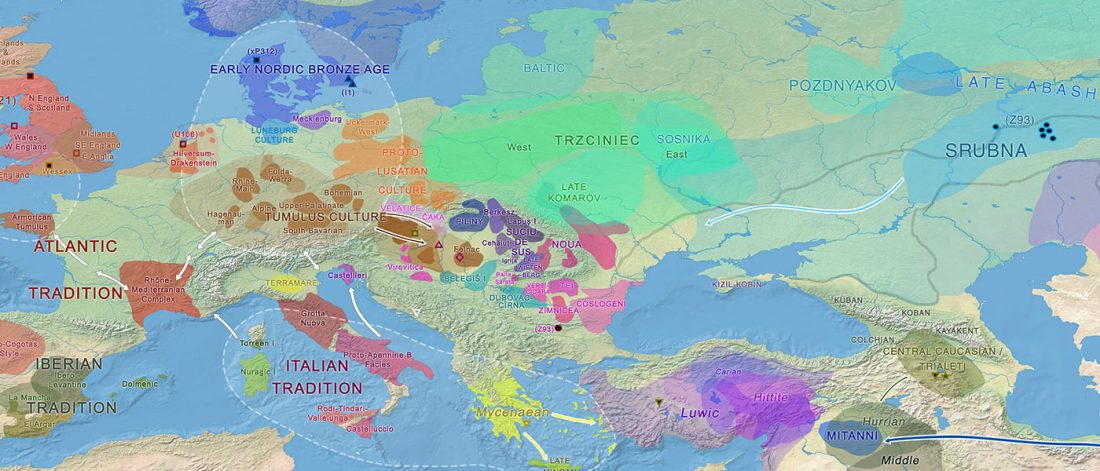
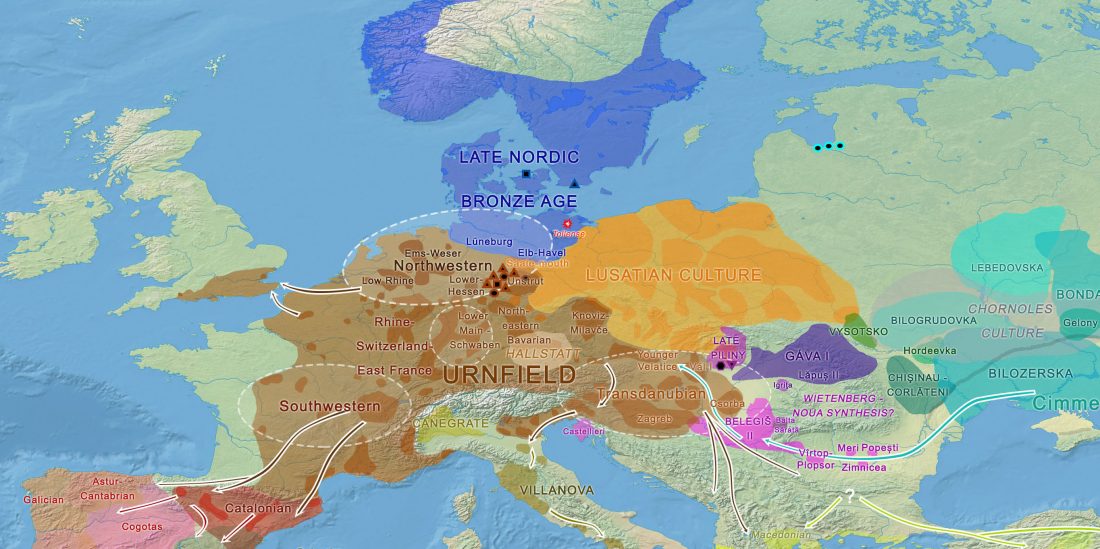
Recent paper (behind paywall) Runes from Lány (Czech Republic) – The oldest inscription among Slavs. A new standard for multidisciplinary analysis of runic bones by Macháček et al. J. Archaeol Sci (2021).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
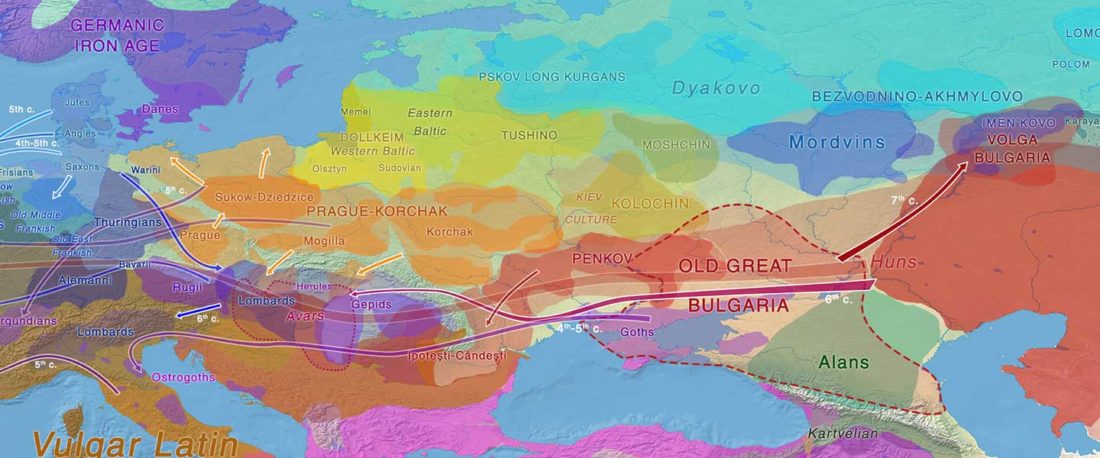
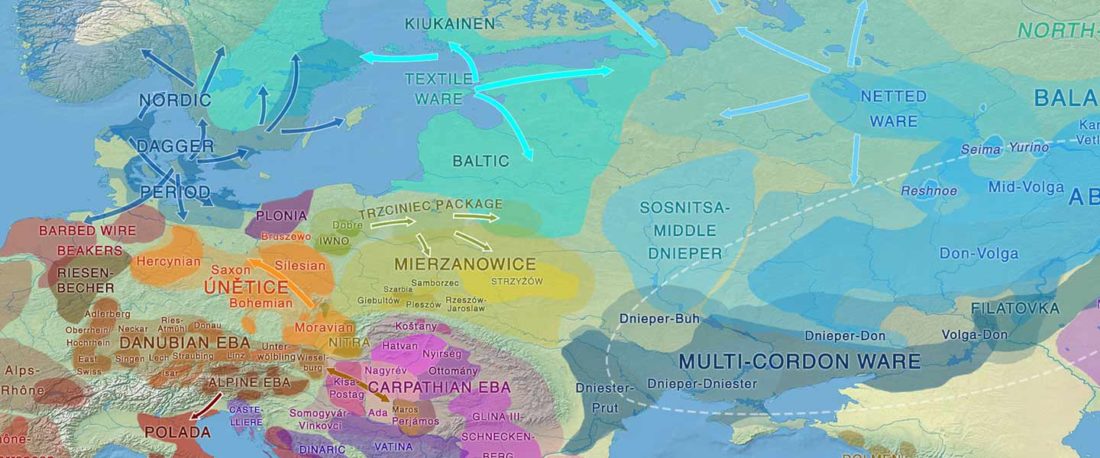
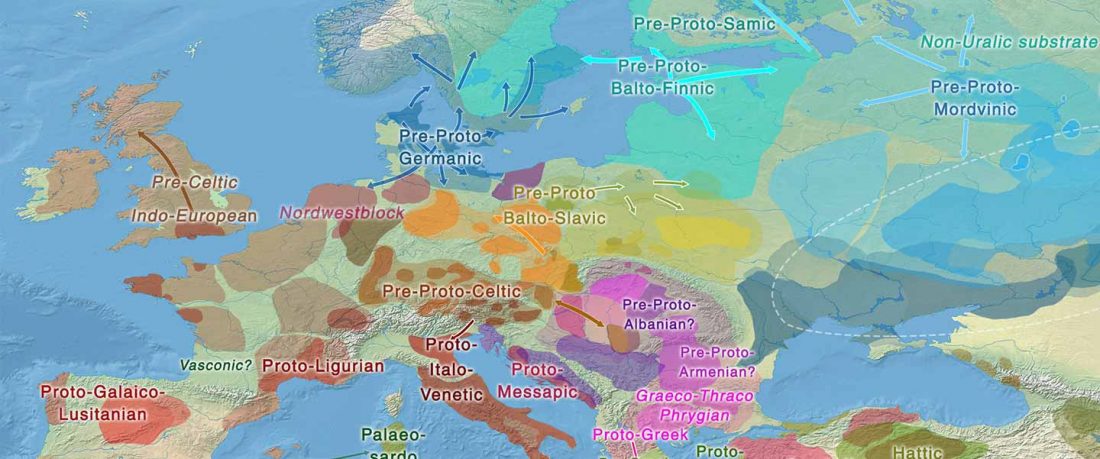
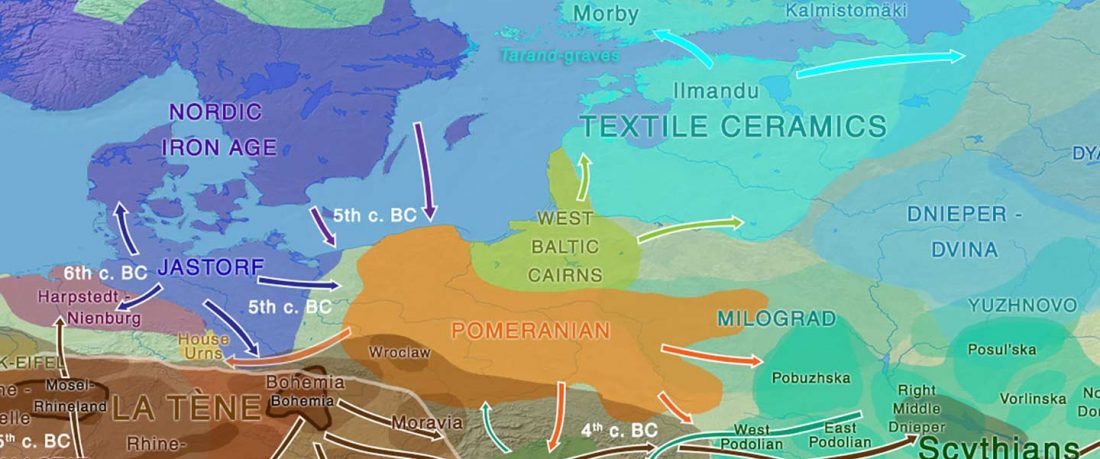
… Read the rest “Germanic runes in the Prague-Type Pottery culture”To date no archaeological find is generally accepted as evidence for a direct contact between Germanic tribes and Early Slavs in Central Europe (Brather, 2004). Here we report a novel archaeological find in support of a direct contact: a rune-inscribed fragment of a bone from the late 6th century found in a Slavic settlement. Runes are an alphabetic script, called fuþark,