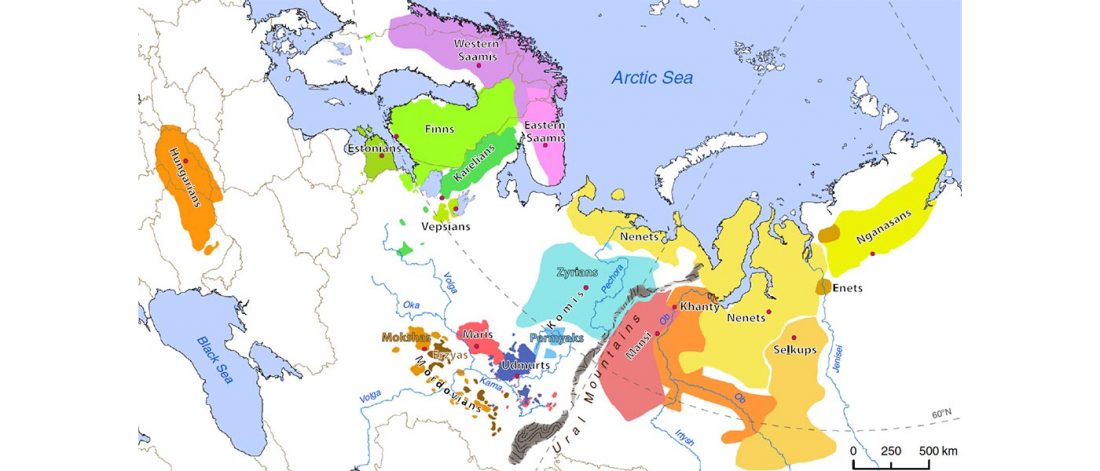
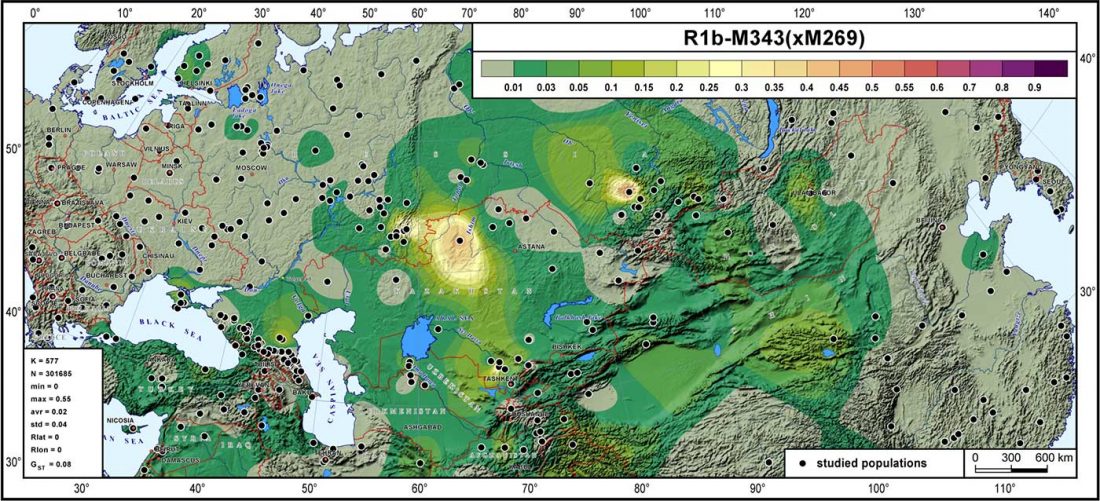
Open access Genes reveal traces of common recent demographic history for most of the Uralic-speaking populations, by Tambets et al. Genome Biology (2018).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Methods
A total of 286 samples of Uralic-speaking individuals, of those 121 genotyped in this study, were analysed in the context of 1514 Eurasian samples (including 14 samples published for the first time) based on whole genome single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (Additional file 1: Table S1). All these samples, together with the larger sample set of Uralic speakers, were characterized for mtDNA and chrY markers.
… Read the rest “Haplogroup R1a and CWC ancestry predominate in Fennic, Ugric, and Samoyedic groups”The question as which material cultures may