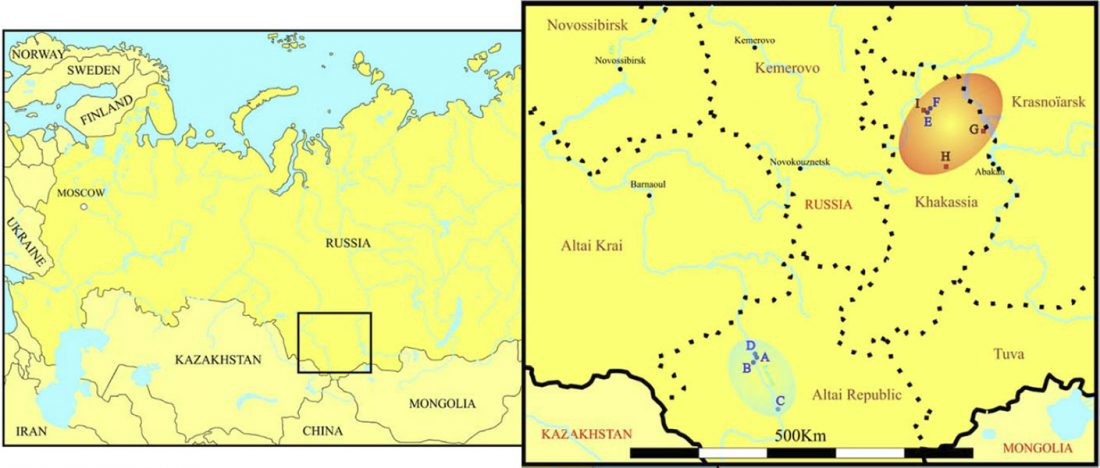
Open access paper New genetic evidence of affinities and discontinuities between bronze age Siberian populations, by Hollard et al., Am J Phys Anthropol. (2018) 00:1–11.
NOTE. This seems to be a peer-reviewed paper based on a more precise re-examination of the samples from Hollard’s PhD thesis, Peuplement du sud de la Sibérie et de l’Altaï à l’âge du Bronze : apport de la paléogénétique (2014).
Interesting excerpts:
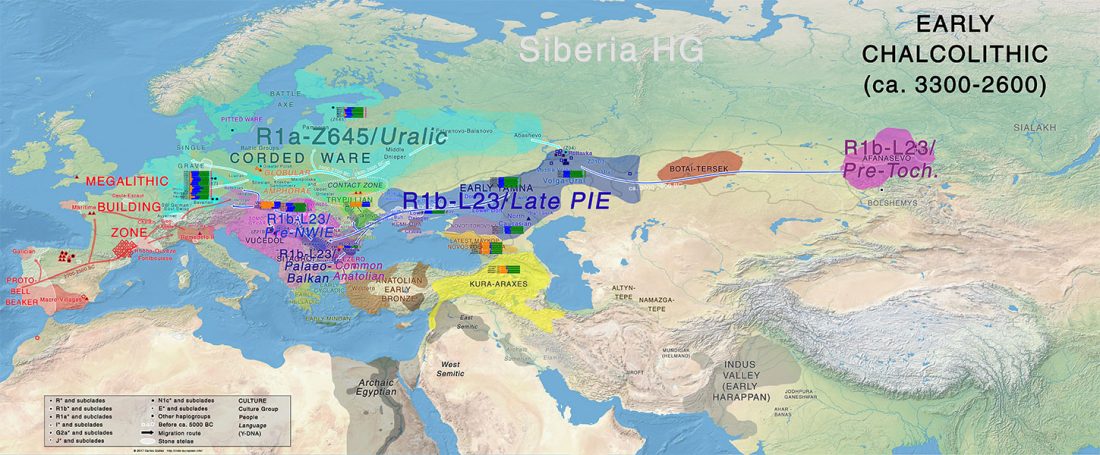
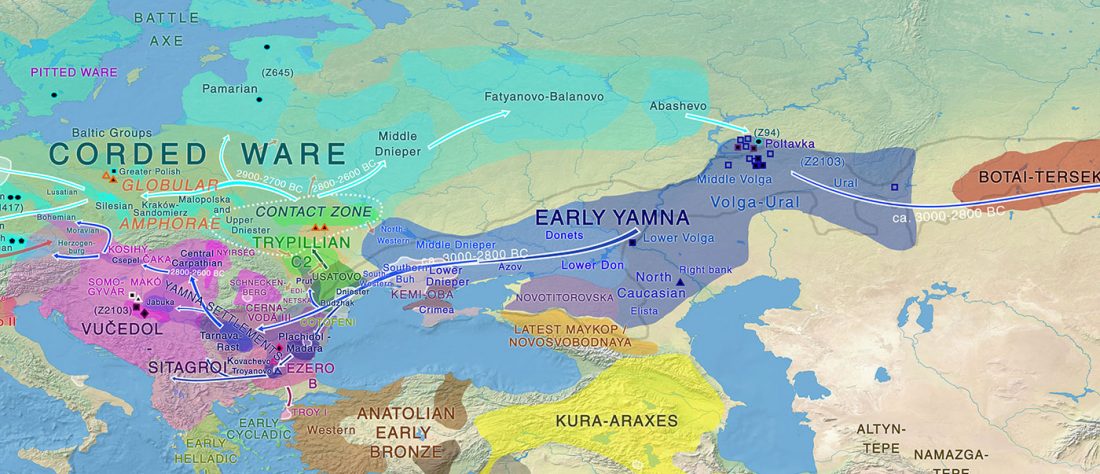
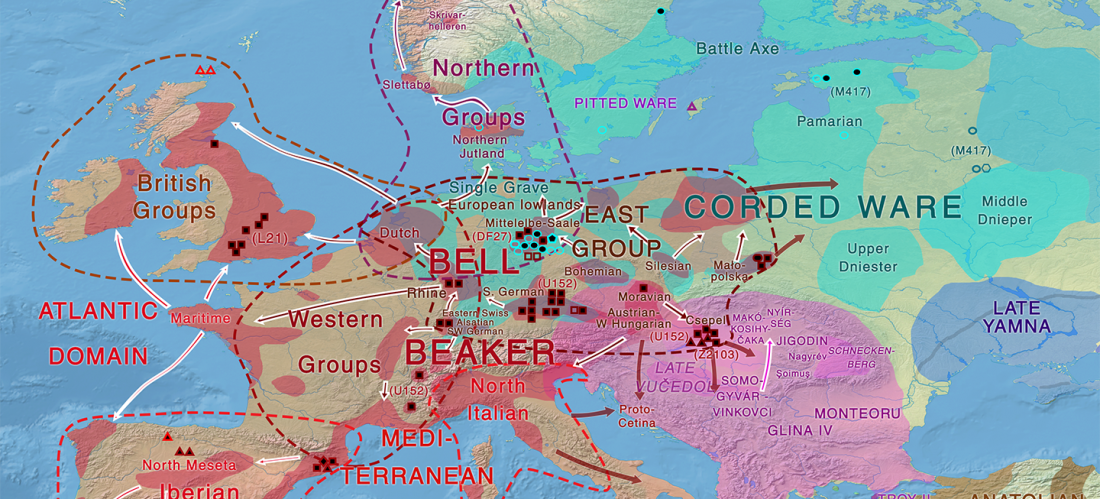
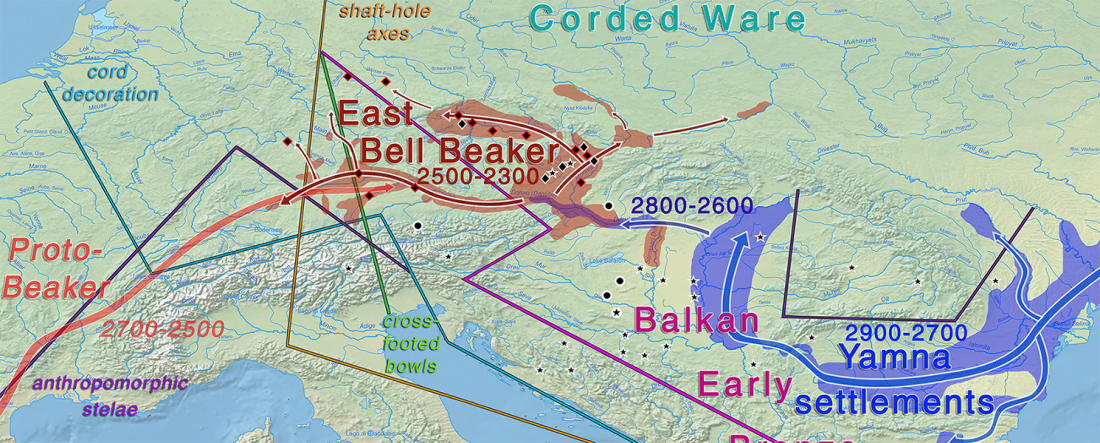
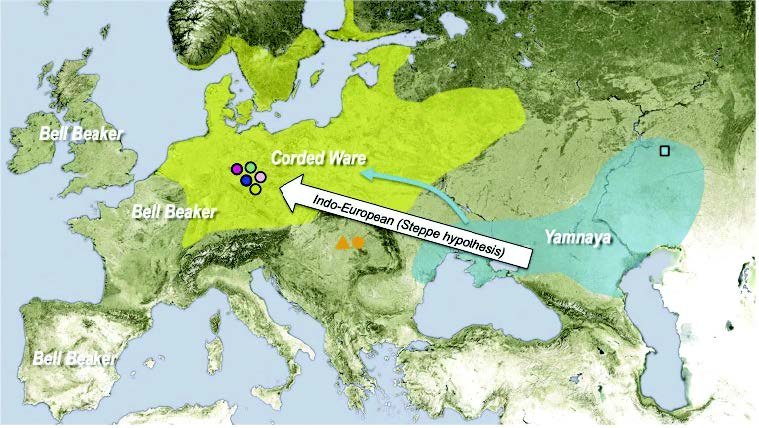
Afanasevo and Yamna
… Read the rest “Yamna/Afanasevo elite males dominated by R1b-L23, Okunevo brings ancient Siberian/Asian population”The Afanasievo culture is the earliest known archaeological culture of southern Siberia, occupying the Minusinsk-Altai region during the Eneolithic era 3600/3300 BC to 2500 BC (Svyatko et al., 2009;