Recent paper (behind paywall) An Alternative to ‘Celtic from the East’ and ‘Celtic from the West’, by Patrick Sims-Williams Camb. Archaeol. J (2020) First View.
NOTE. For those who don’t have access to it, you can check other recent similar papers by the same author, like Sims-Williams (2009, 2012, 2017).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Celtic origins
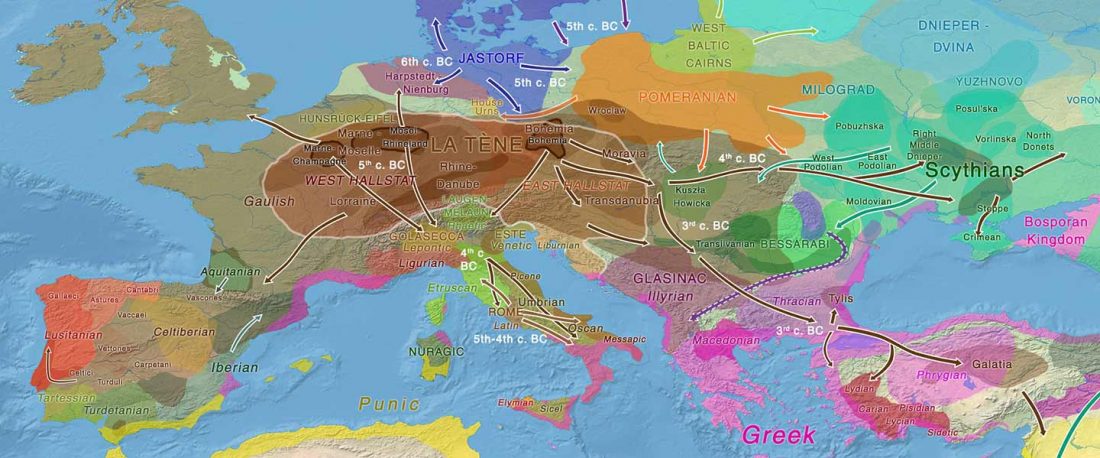
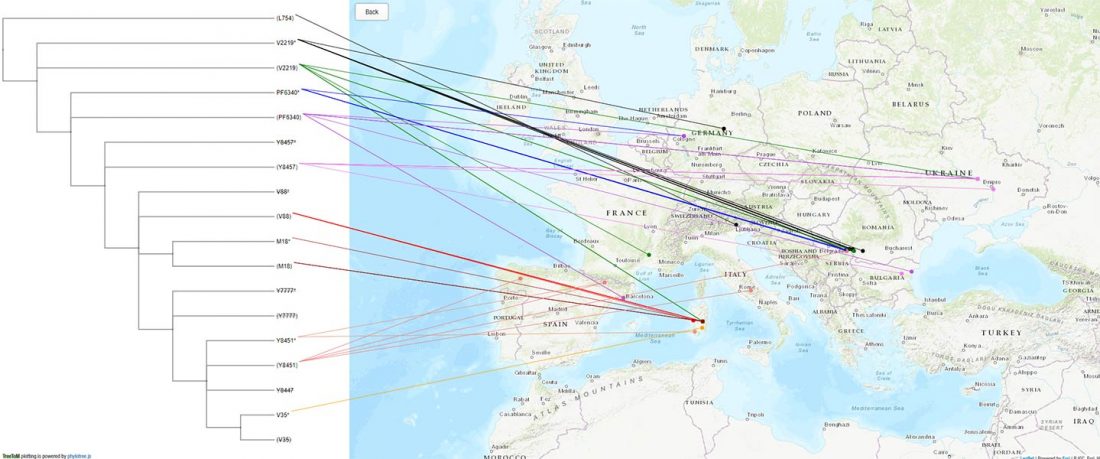
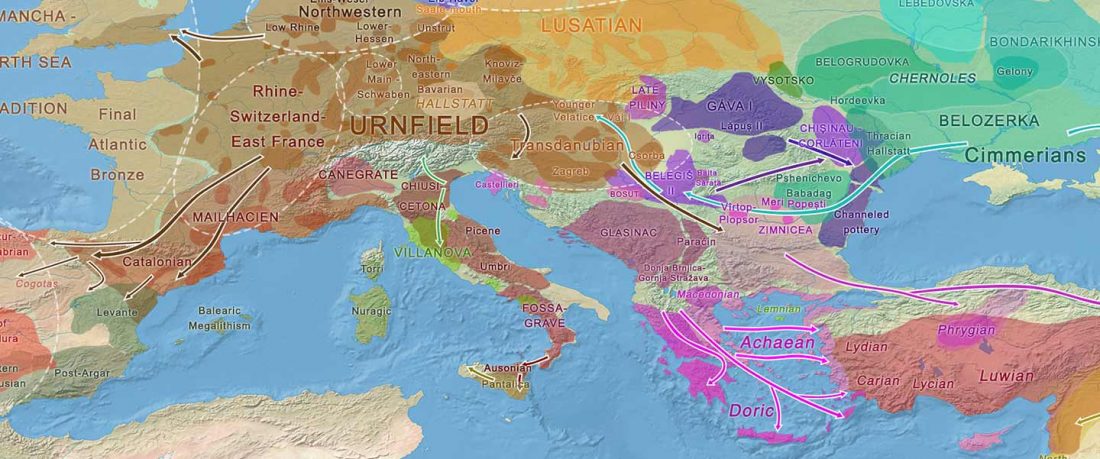
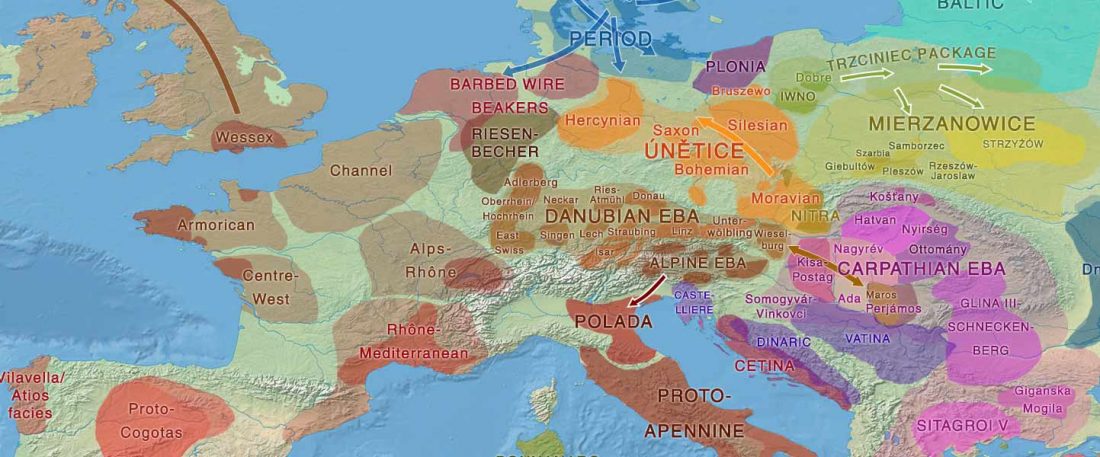
… Read the rest “European hydrotoponymy (VII): Celtic From the West or the East?”(…) there have been three main stages of scholarship: (1) the Celts are identified with the Hallstatt and La Tène ‘cultures’ of the first millennium BC; (2) then the discovery of contemporary Celtic language inscriptions (Lepontic and Celtiberian) in the ‘wrong’ areas