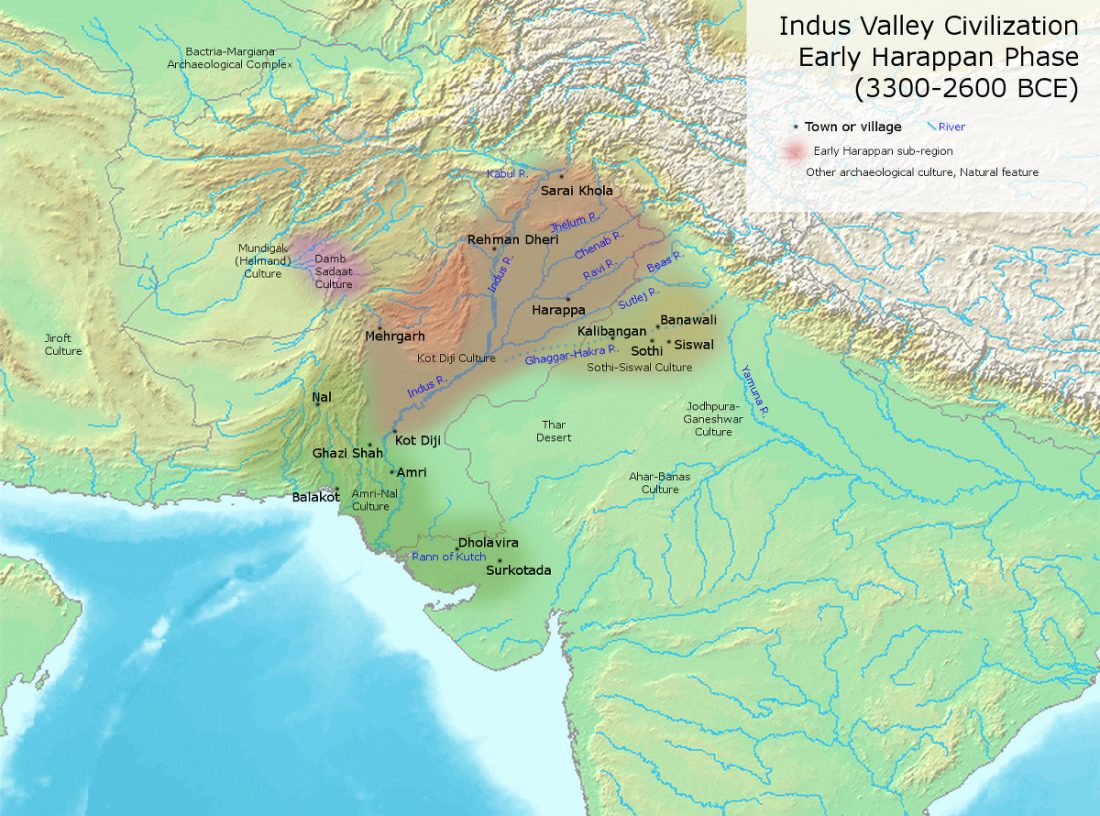
New article on The Caravan, Indus Valley People Did Not Have Genetic Contribution From The Steppes: Head Of Ancient DNA Lab Testing Rakhigarhi Samples, by Hartosh Singh Val.
Niraj Rai, head of the DNA Laboratory where the samples from the Harappan site of Rakhigarhi in Haryana are being analysed, has this to say:
It will show that there is no steppe contribution to the Indus Valley DNA.
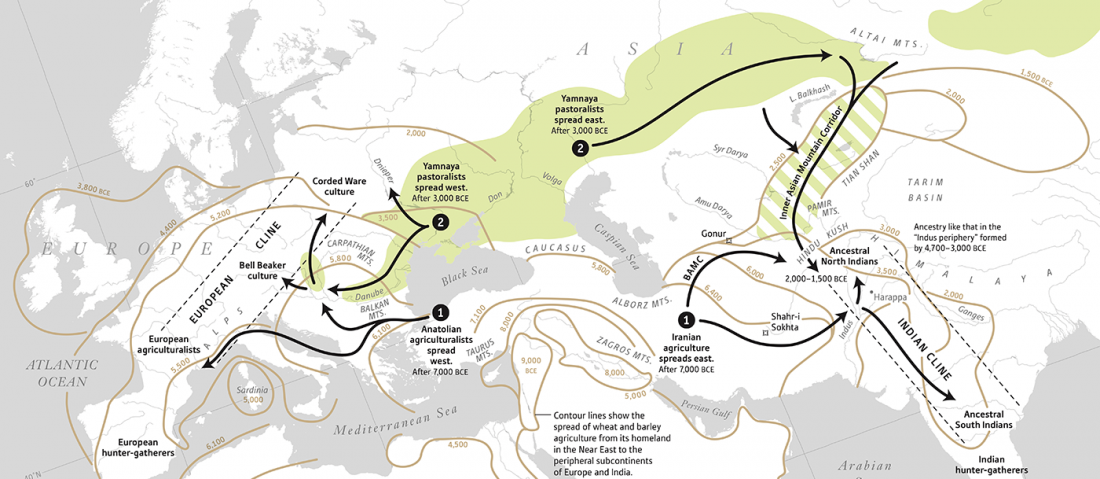
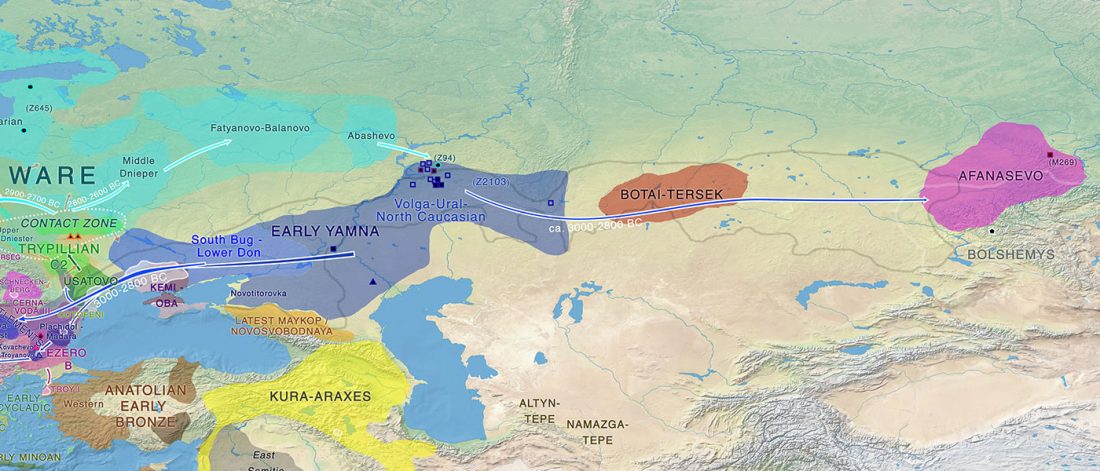
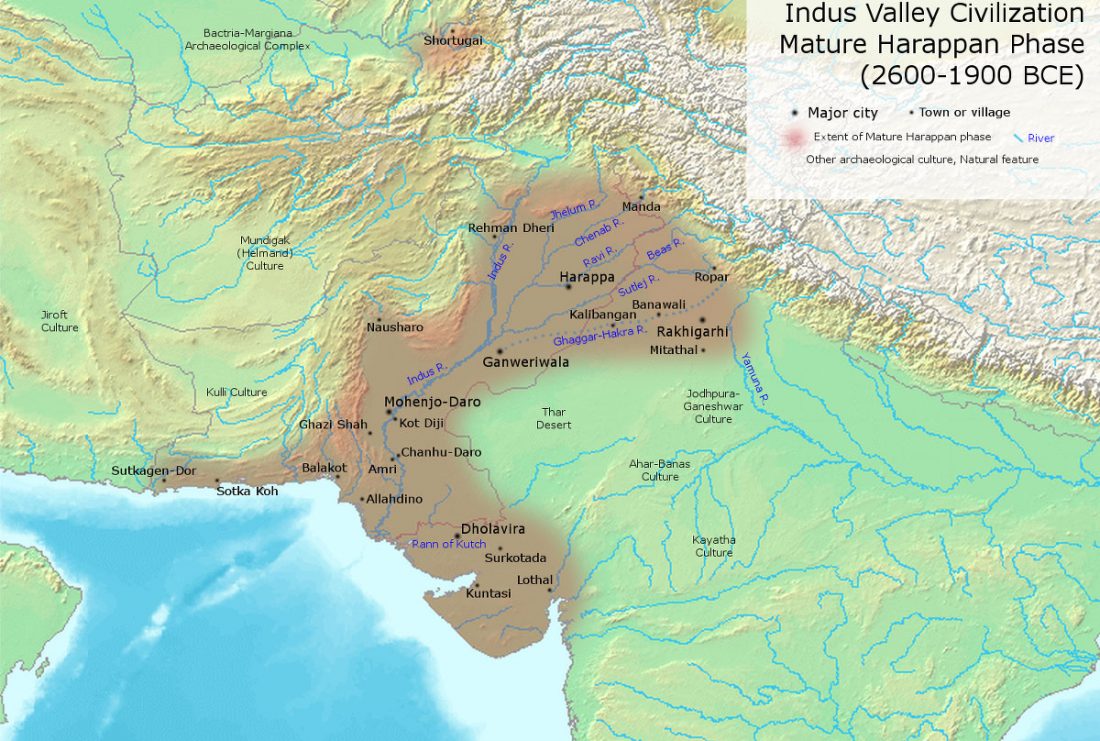
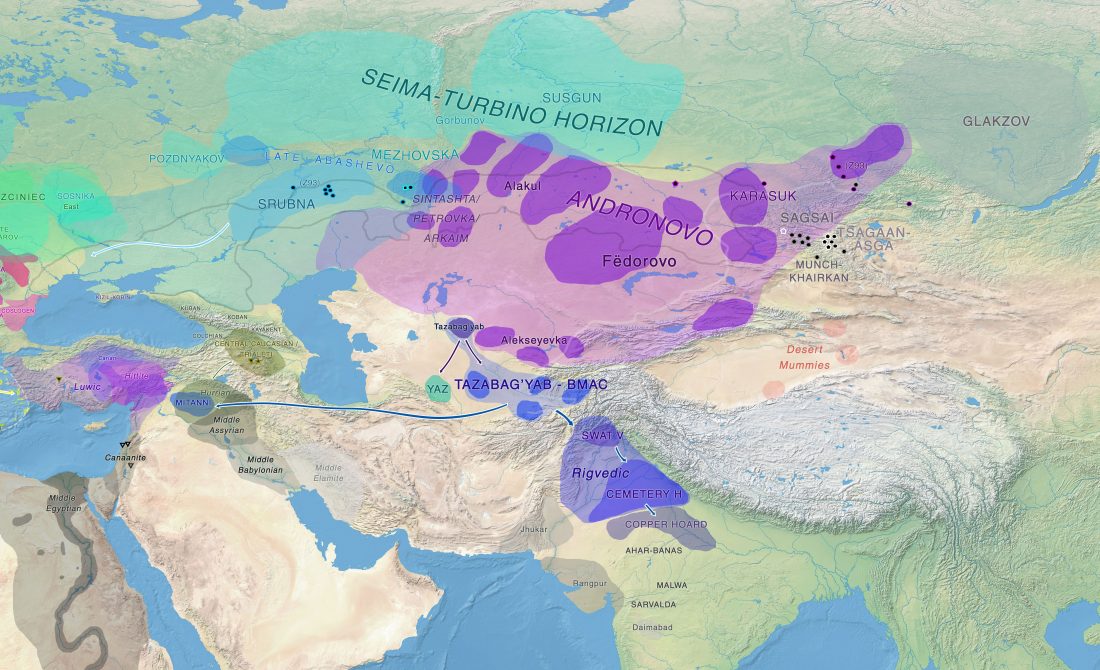
… Read the rest “Rakhigarhi samples from the Indus Valley Civilisation will support the conclusions of Narasimhan et al. (2018)”The Indus Valley people were indigenous, but in the sense that their DNA had contributions from near eastern Iranian farmers mixed with the Indian hunter-gatherer DNA, that is still reflected in the