This post is part of a draft on South Siberian language homelands and Sprachbünde.
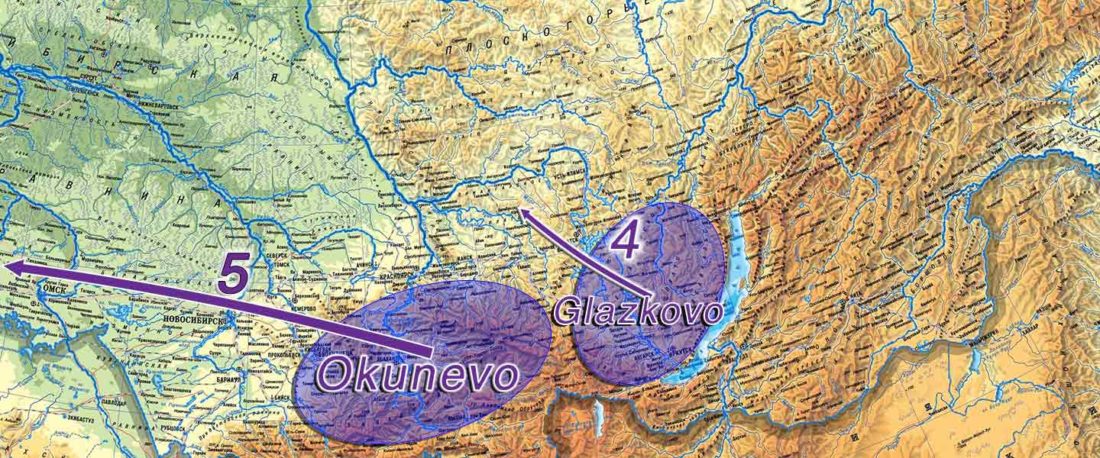
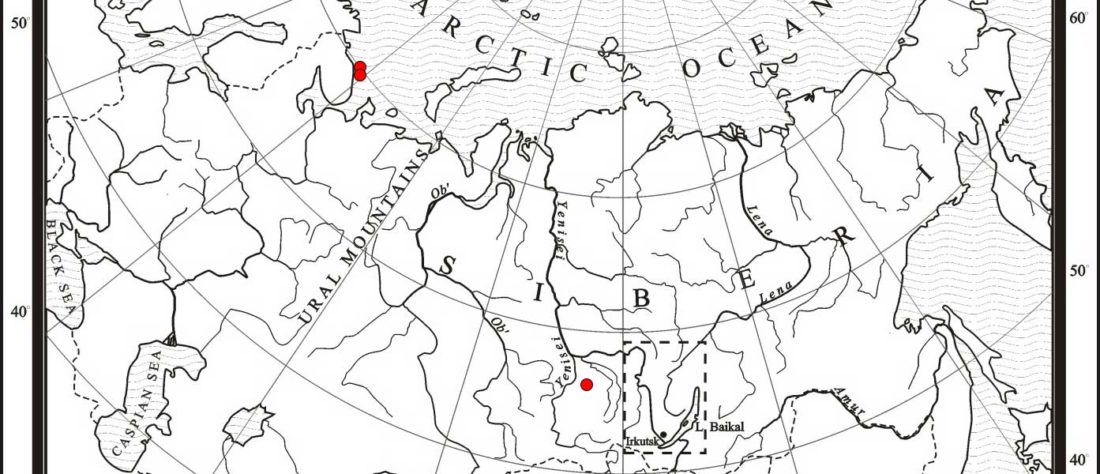
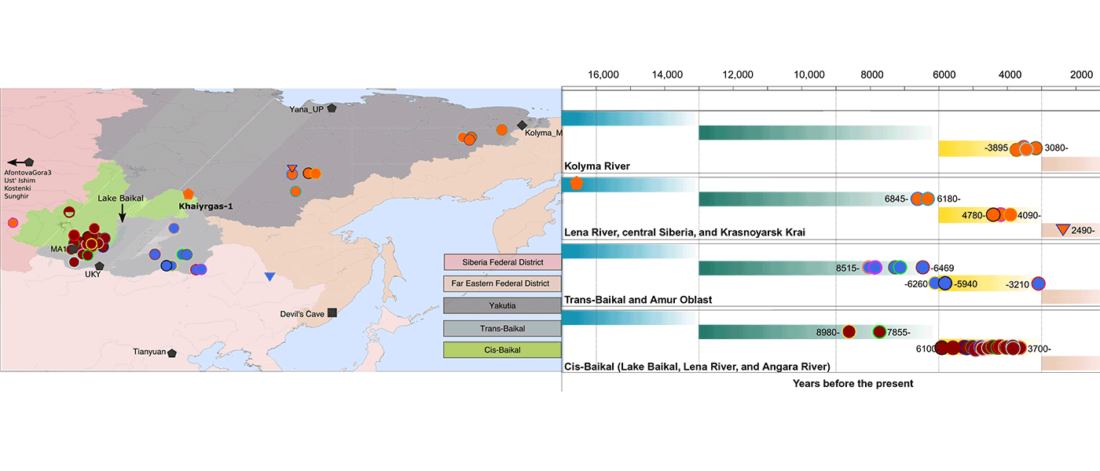
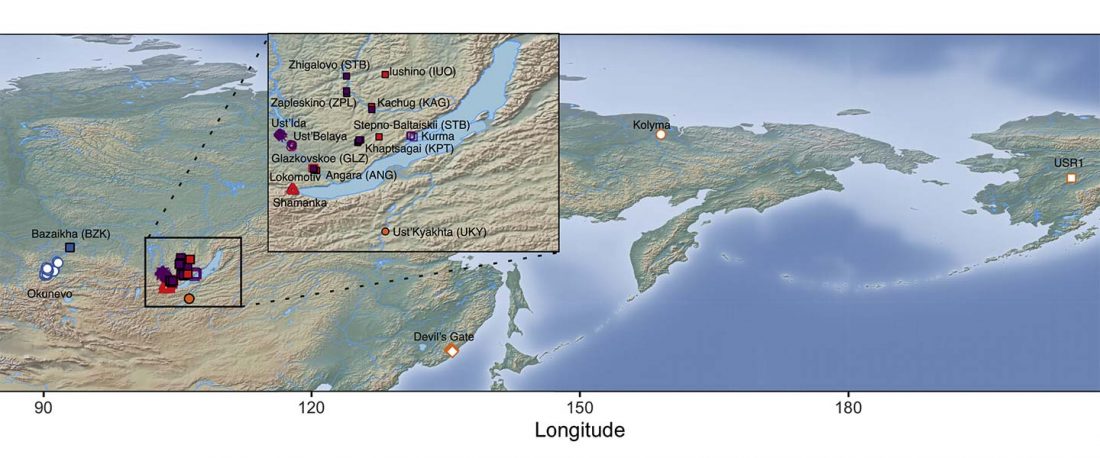
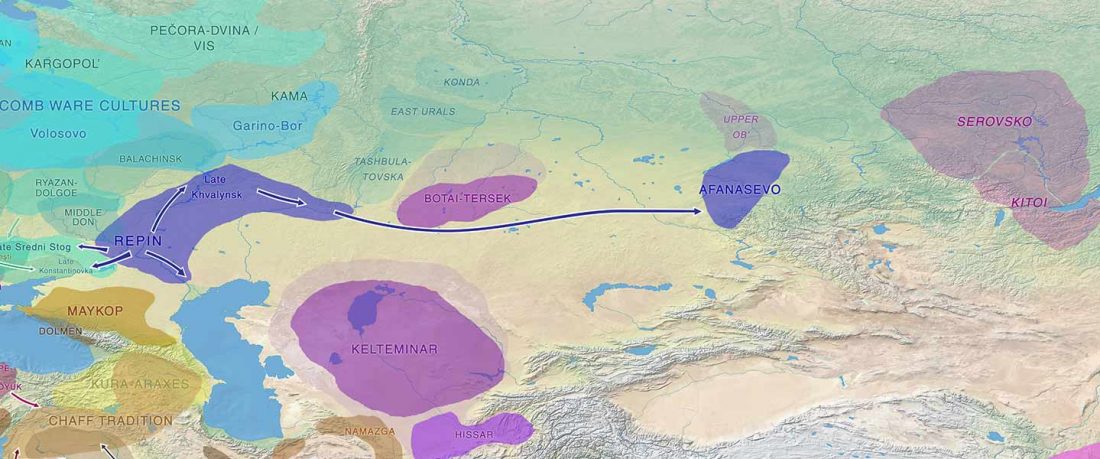
The following text contains a description of Yeniseian languages, their dialectal groupings and likely evolution among surrounding ethnolinguistic groups before they were first documented. Special emphasis is placed on ancient Yeniseic formants for water bodies, widely distributed through Western, Southern, and Central Siberia. Finally, the archaeological-archaeogenetic discussion is focused on Early Bronze Age Glazkovo-related and Okunevo-like cultures, due to their patrilineal connection to sampled Yeniseian and ancient Na-Dene populations.
… Read the rest “Proto-Yeniseian Homeland”