Recently published paper Genomic Data from an Ancient European Battlefield Indicates On-Going Strong Selection on a Genomic Region Associated with Lactase Persistence Over the Last 3,000 Years, by Burger et al., submitted to Current Biology, available at CellPress SneakPeek.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
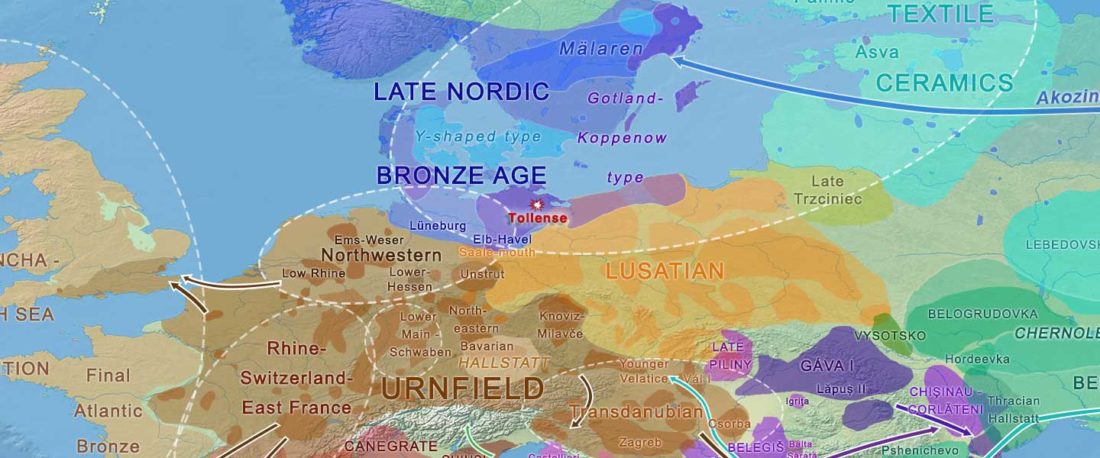
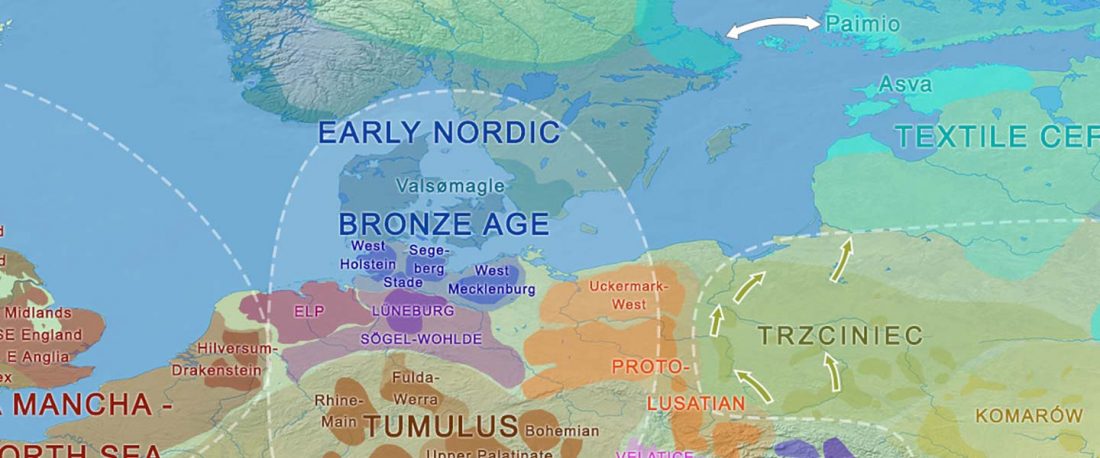
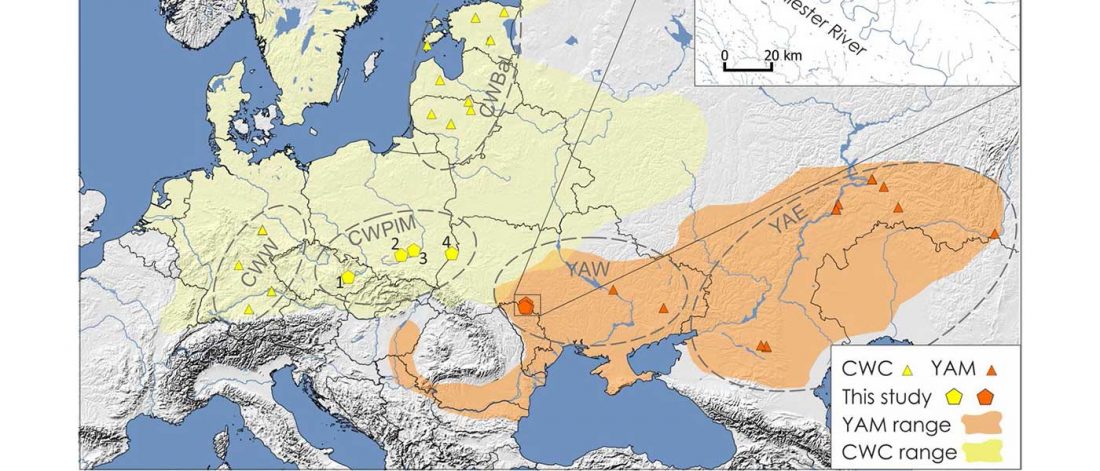
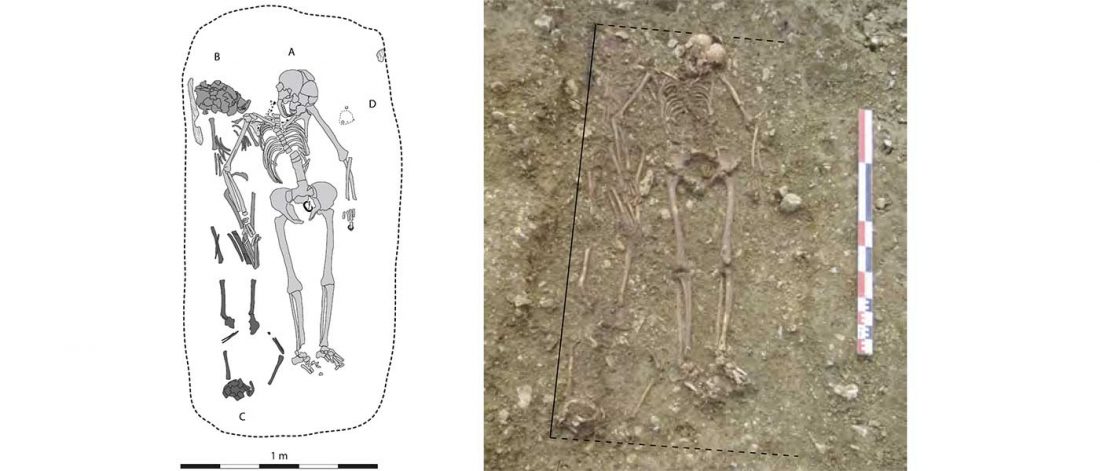
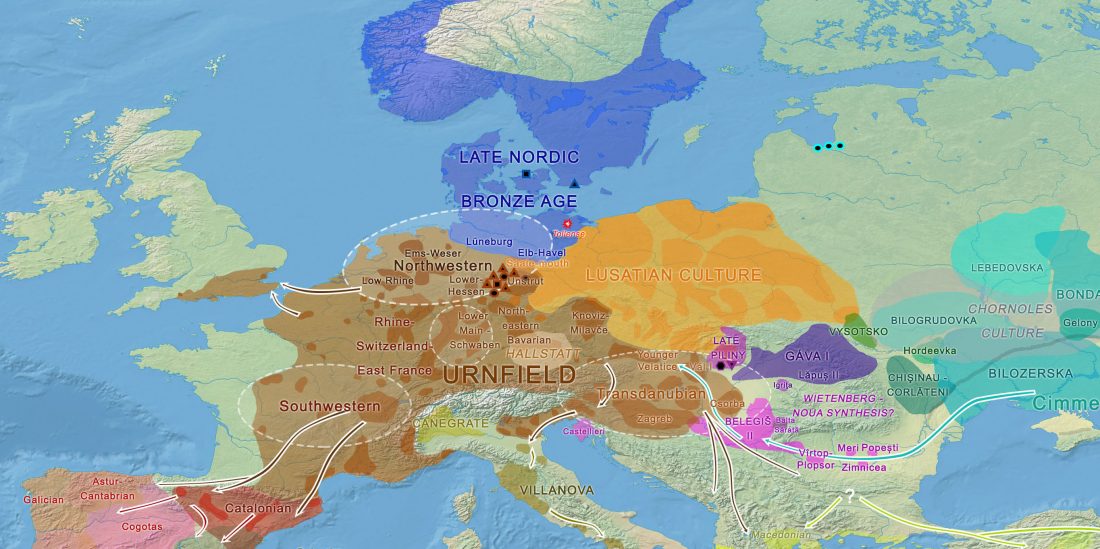
Tollense sample shows no structure
… Read the rest ““Local” Tollense Valley warriors linked to Germanic peoples”Multiple lines of evidence point to little or no genetic structure in the population from which the Tollense individuals were sampled. First, all individuals fall within the range of Central and northern European variation when projected onto a principle component analysis (PCA) trained on modern samples and their spread matches that