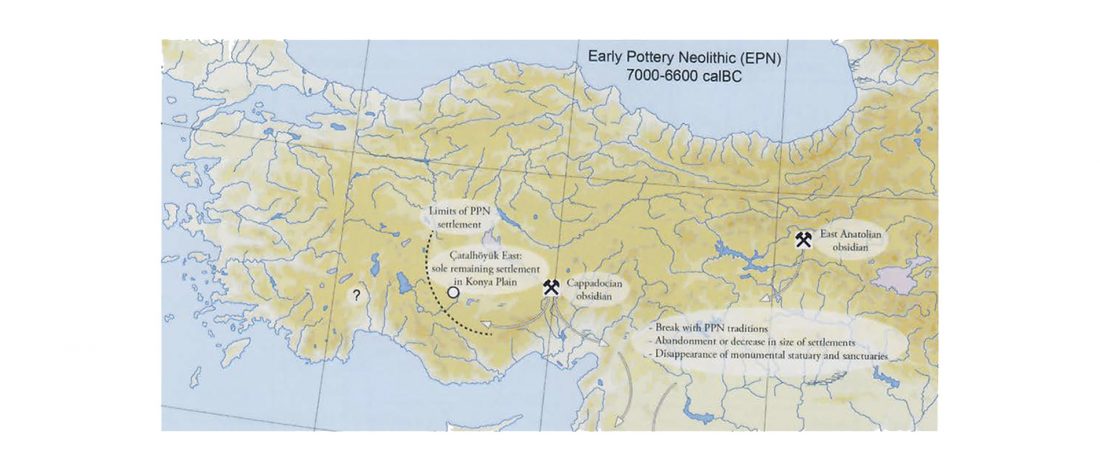
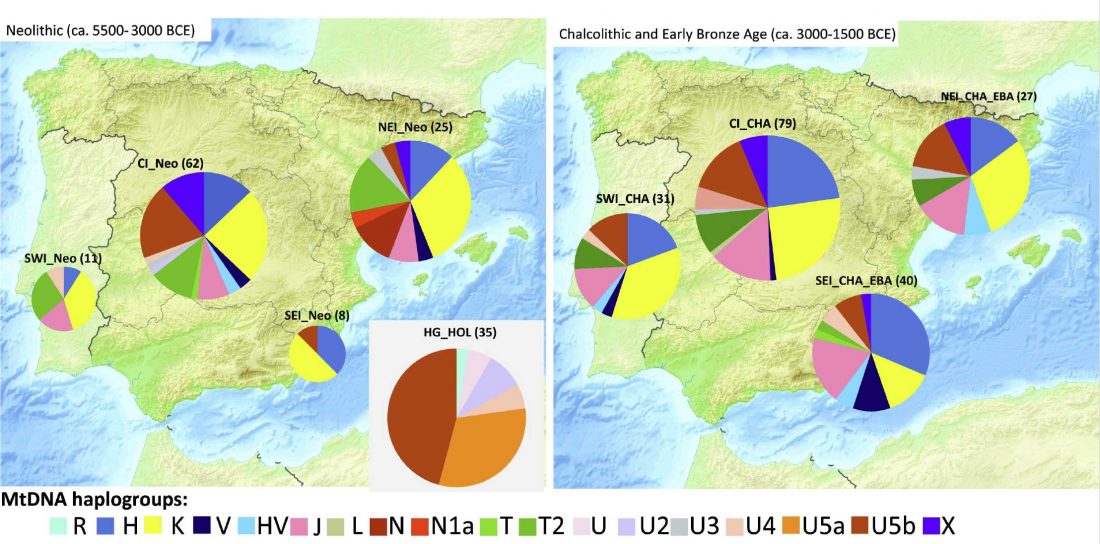
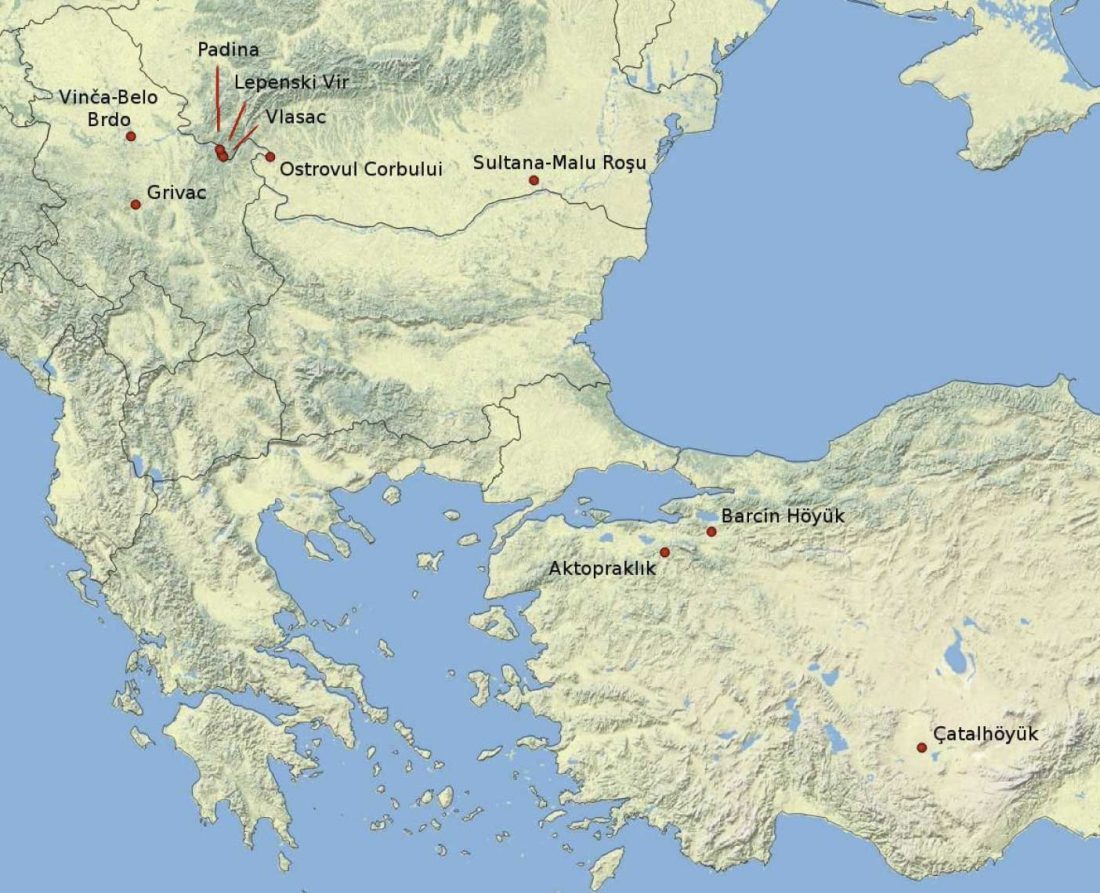
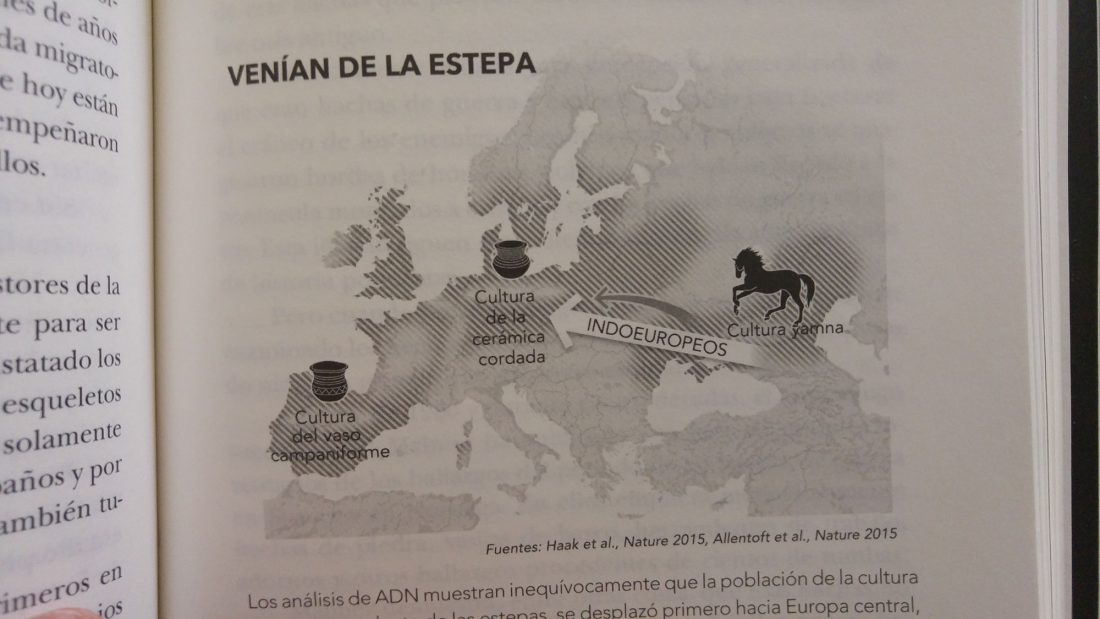
New paper (behind paywall) Agricultural origins on the Anatolian plateau, by Baird et al. PNAS (2018), published ahead of print (March 19).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Agricultural origins on the Anatolian plateau”This paper explores the explanations for, and consequences of, the early appearance of food production outside the Fertile Crescent of Southwest Asia, where it originated in the 10th/9th millennia cal BC. We present evidence that cultivation appeared in Central Anatolia through adoption by indigenous foragers in the mid ninth millennium cal BC, but also demonstrate that uptake was not uniform, and that some communities chose to actively disregard cultivation. Adoption of cultivation