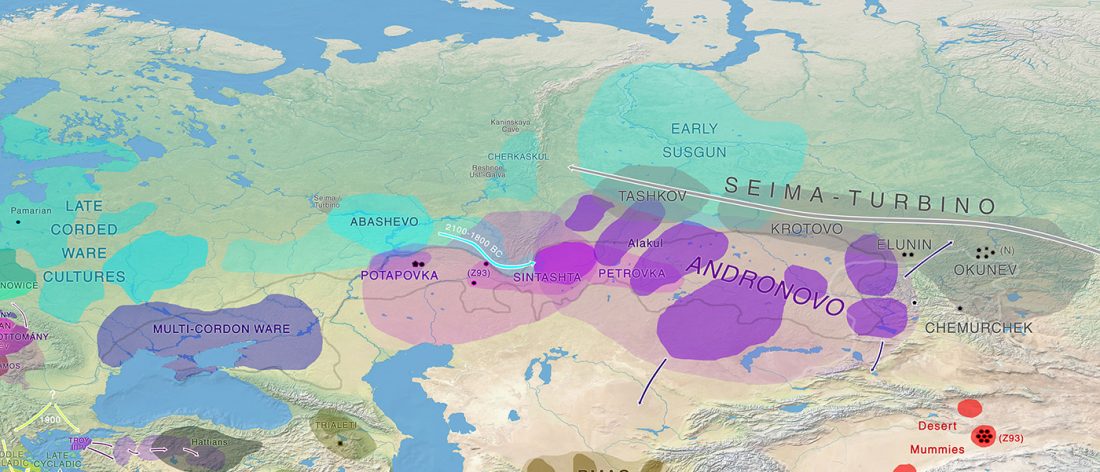
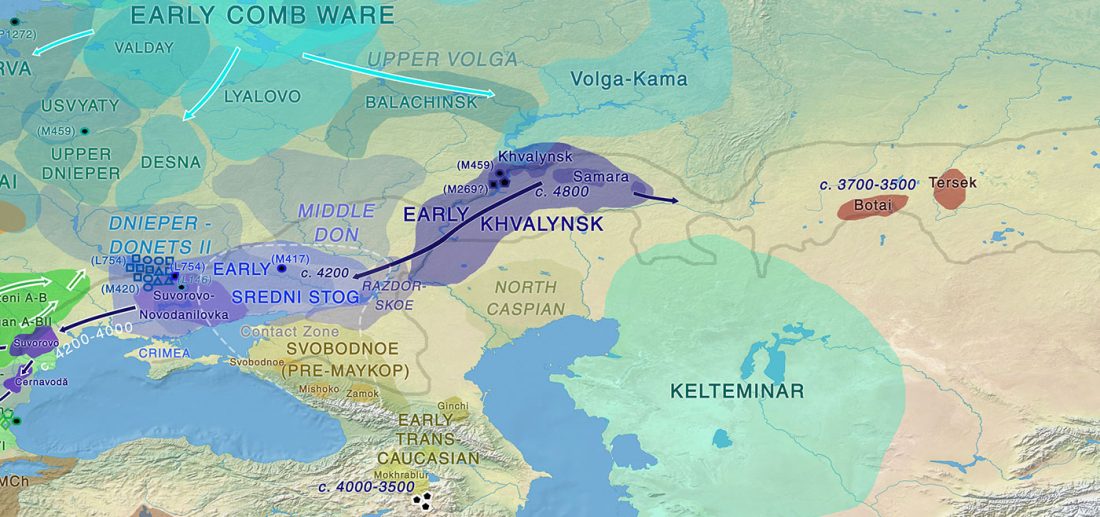
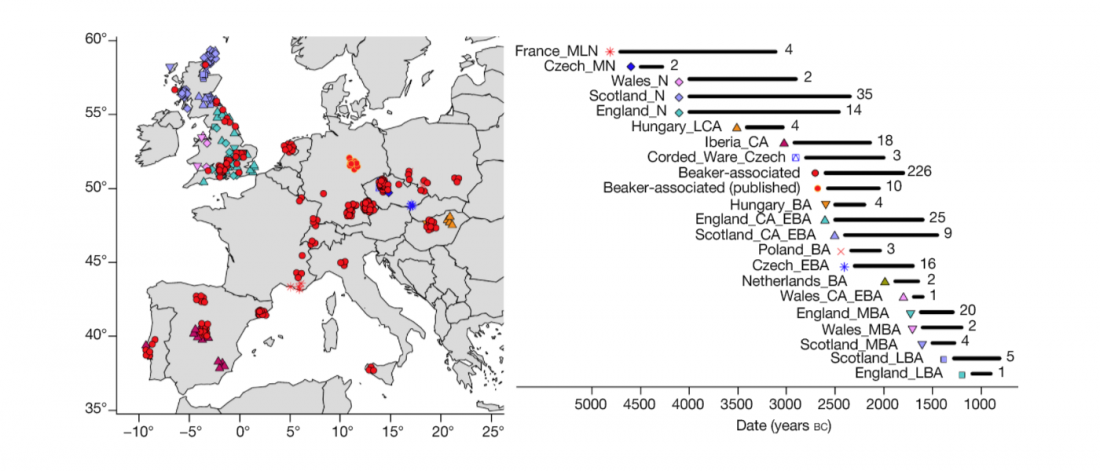
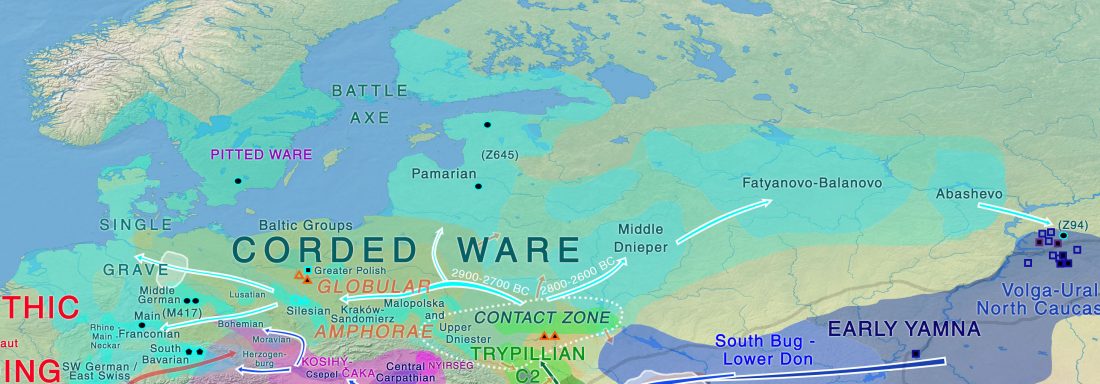
An interesting interview has appeared on The Atlantic, Ancient DNA Is Rewriting Human (and Neanderthal) History, on the occasion of the publication of David Reich’s book Who We Are and How We Got Here: Ancient DNA and the New Science of the Human Past.
An interesting interview has appeared on The Atlantic, Ancient DNA Is Rewriting Human (and Neanderthal) History, on the occasion of the publication of David Reich’s book Who We Are and How We Got Here: Ancient DNA and the New Science of the Human Past.
Some interesting excerpts (I have emphasized some of Reich’s words):
On the efficiency of the Reich Lab
… Read the rest “David Reich on the influence of ancient DNA on Archaeology and Linguistics”Zhang: How much does it cost to process an ancient DNA sample right now?
Reich: In our hands, a successful sample costs less than $200. That’s only two or three times more than processing them