Recent paper A dynastic elite in monumental Neolithic society, by Cassidy et al. Nature (2020) 582:384–388.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Neolithic Admixture
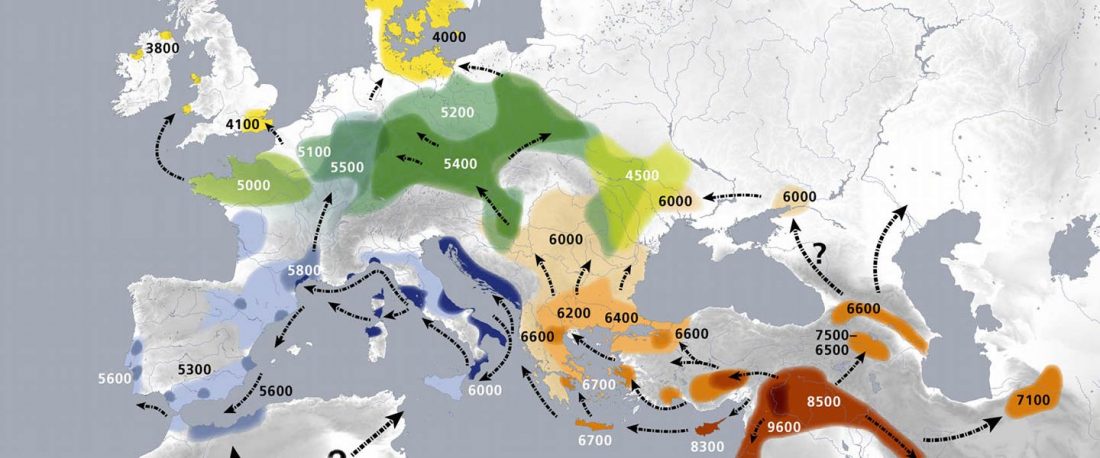
… Read the rest “Demic vs. cultural diffusion and patrilineal Megalithic societies”We sampled remains from all of the major Irish Neolithic funerary traditions: court tombs, portal tombs, passage tombs, Linkardstown-type burials and natural sites. Within this dataset, the earliest Neolithic human remains from the island—interred at Poulnabrone portal tomb14—are of majority ‘Early_Farmer’ ancestry (as defined by ADMIXTURE modelling), and show no evidence of inbreeding, which implies that, from the very onset, agriculture was accompanied by large-scale maritime colonization. Our ADMIXTURE and ChromoPainter analyses do not distinguish between