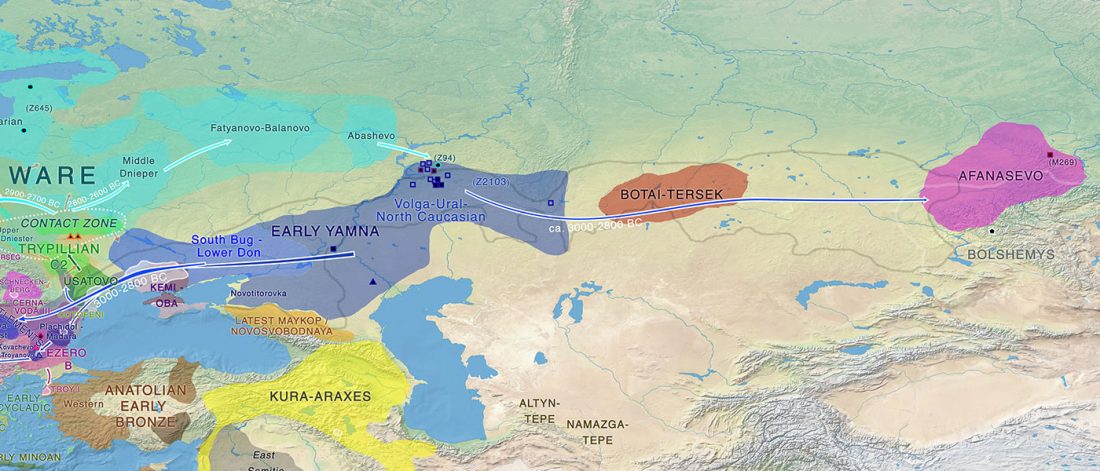
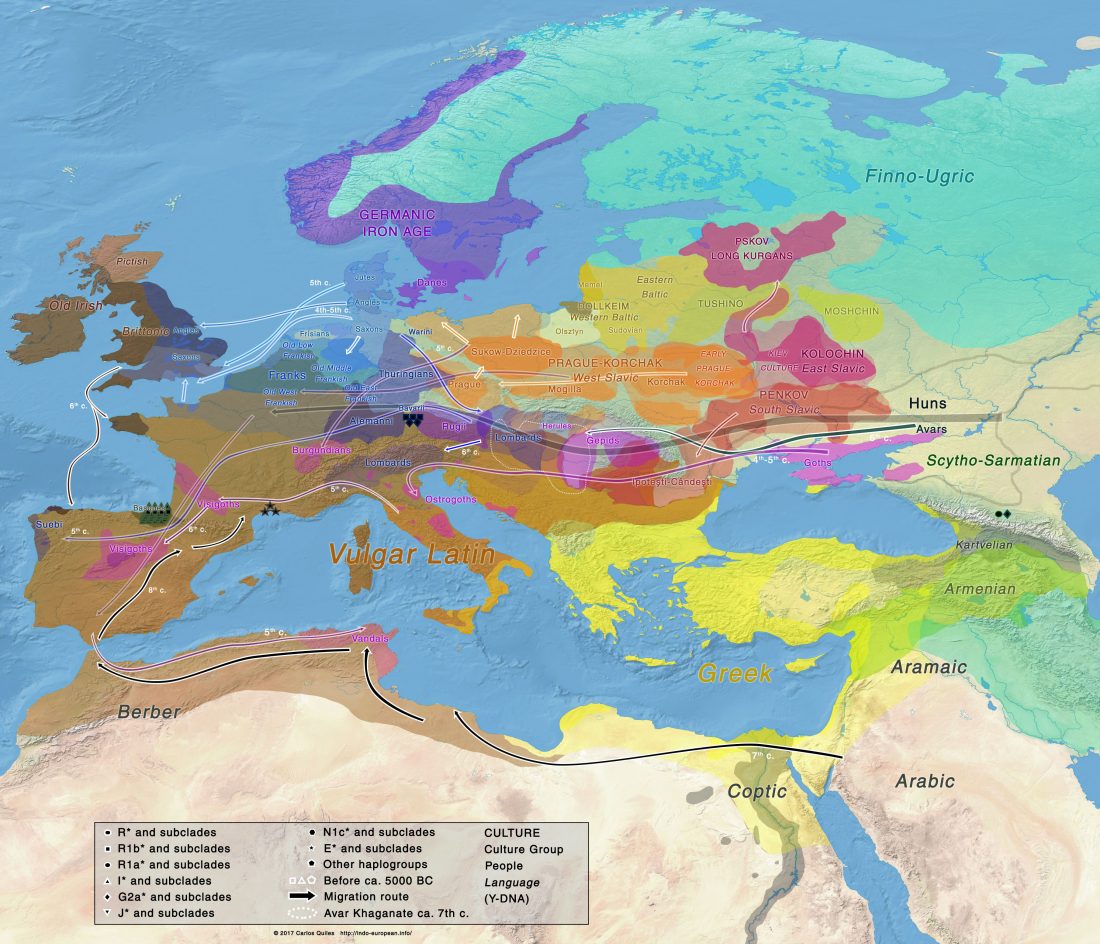
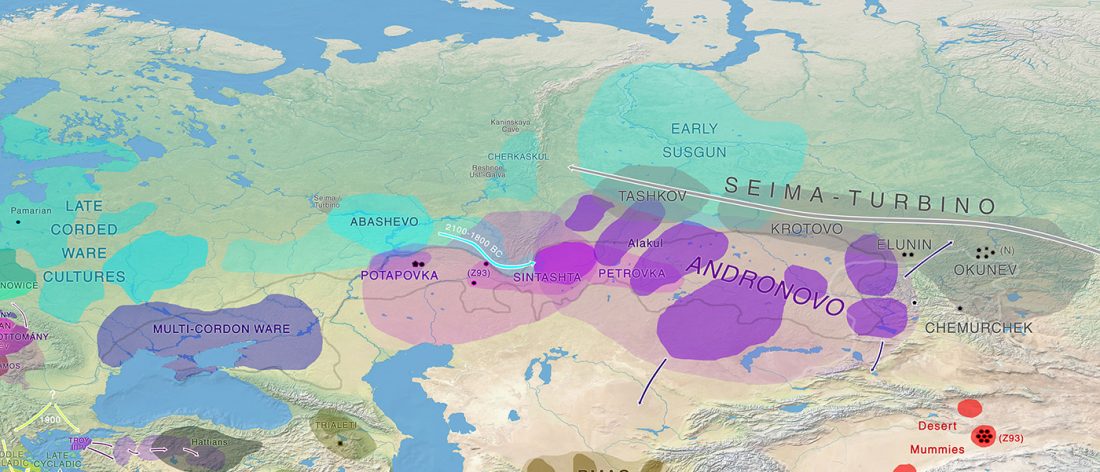
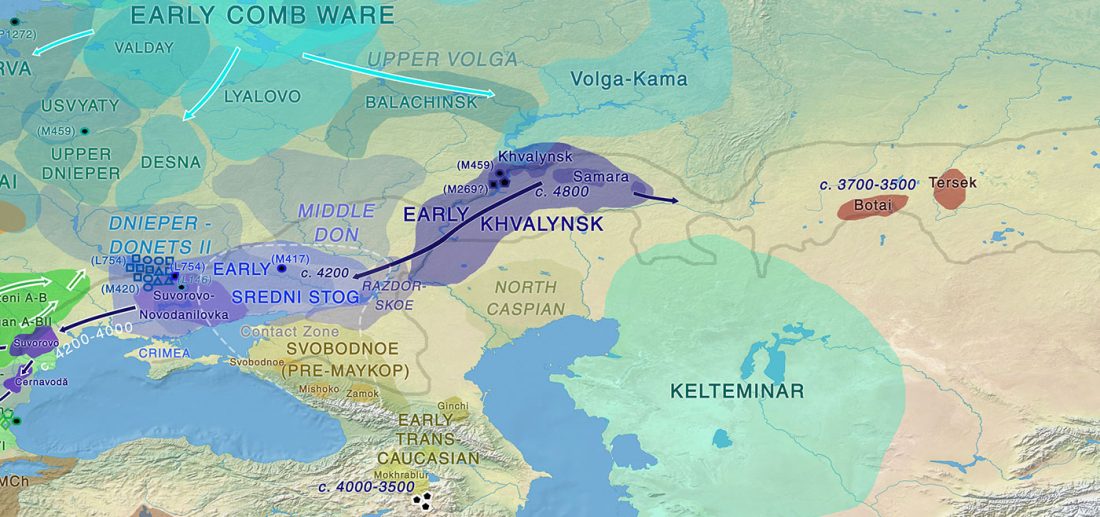
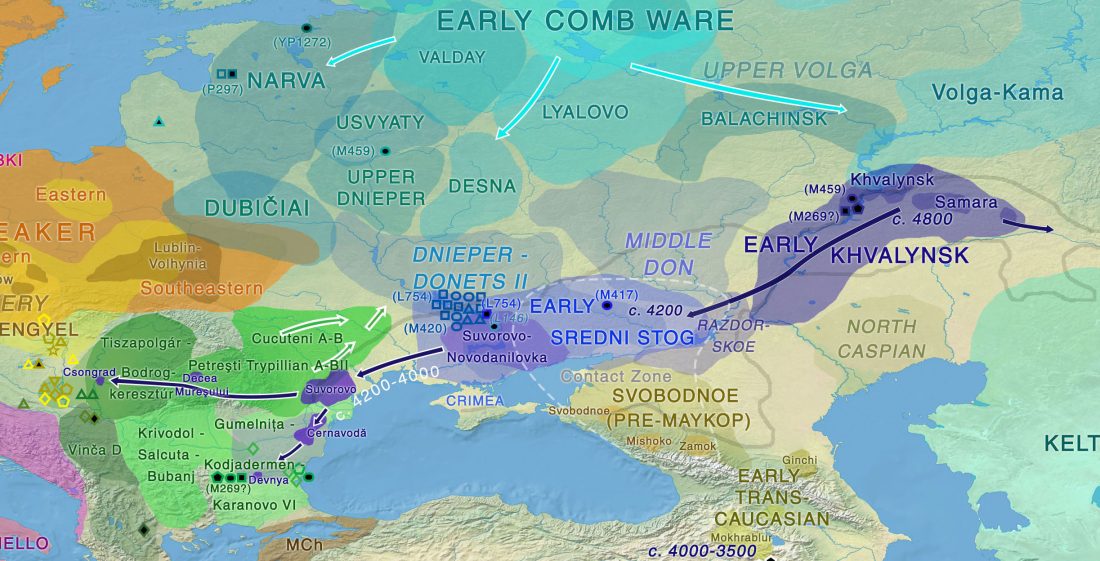
Y-DNA haplogroup R1b-Z2103 in Proto-Indo-Iranians?
We already know that the Sintashta -Andronovo migrants will probably be dominated by Y-DNA R1a-Z93 lineages. However, I doubt it will be the only Y-DNA haplogroup found.
I said in my predictions for this year that there could not be much new genetic data to ascertain how Pre-Indo-Iranian survived the invasion, gradual replacement and founder effects that happened in terms of male haplogroups after the arrival of late Corded Ware migrants, and that we should probably have to rely on anthropological explanations for language continuity despite genetic replacement, as in the Basque case.
Nevertheless, since … Read the rest “Y-DNA haplogroup R1b-Z2103 in Proto-Indo-Iranians?”