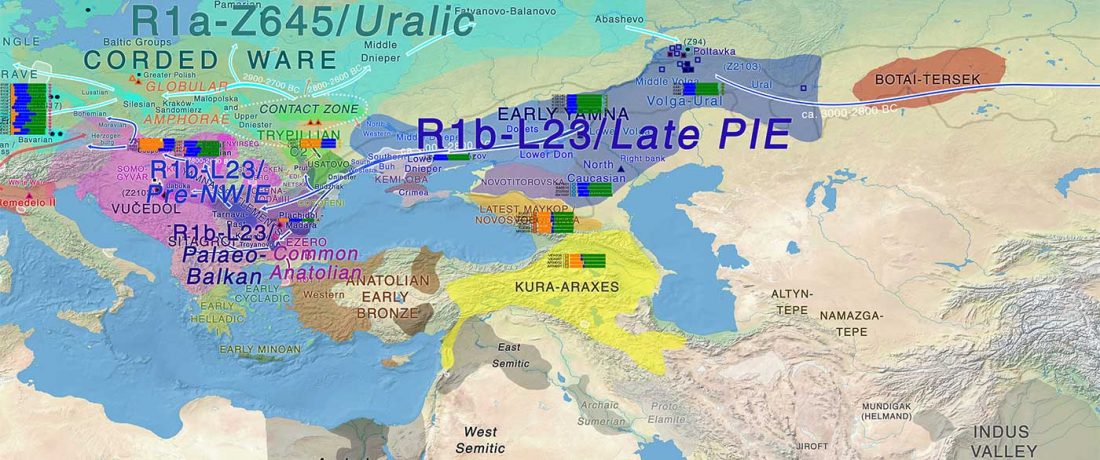
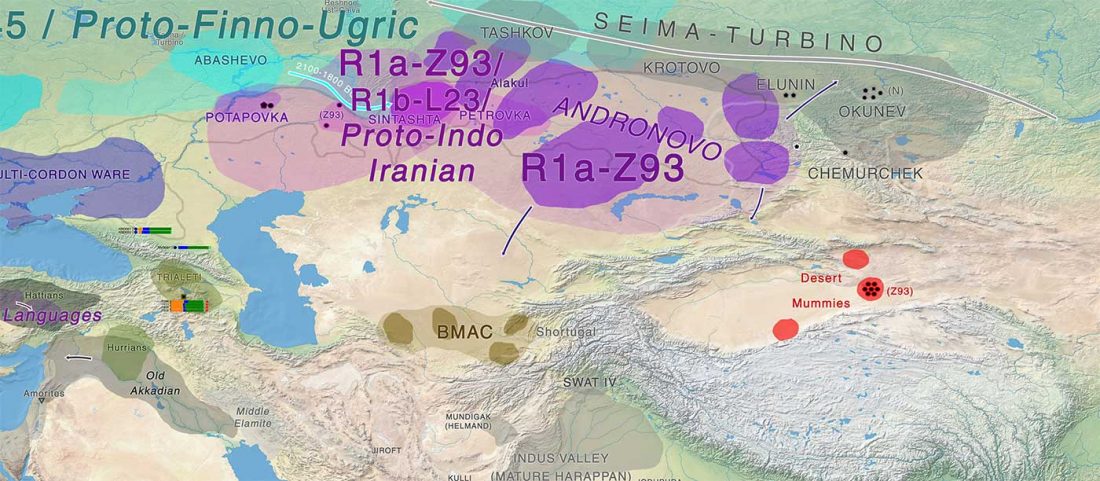
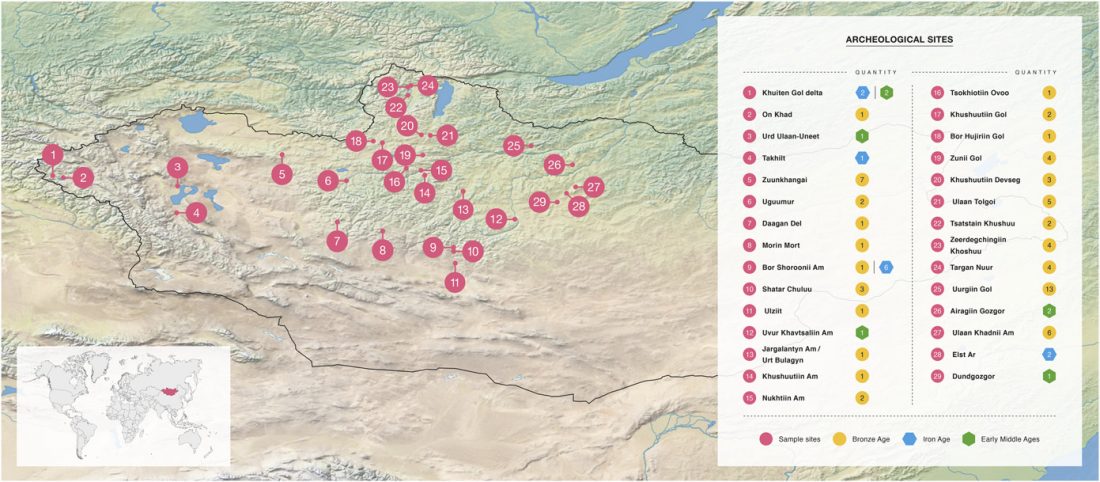
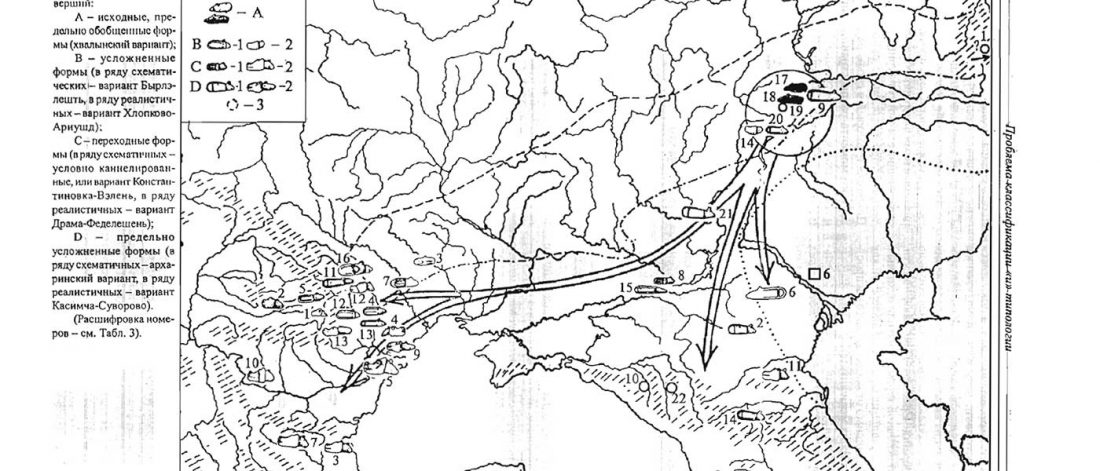
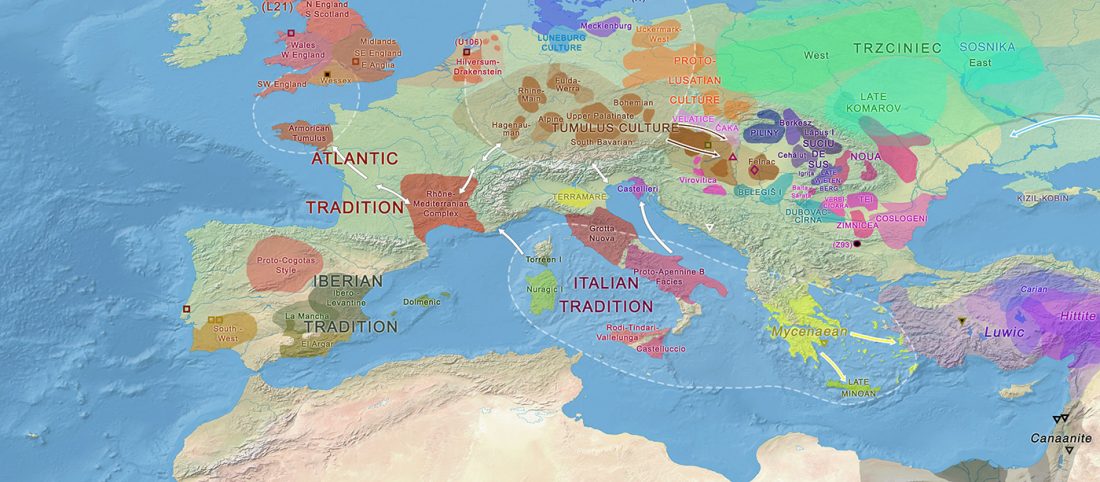
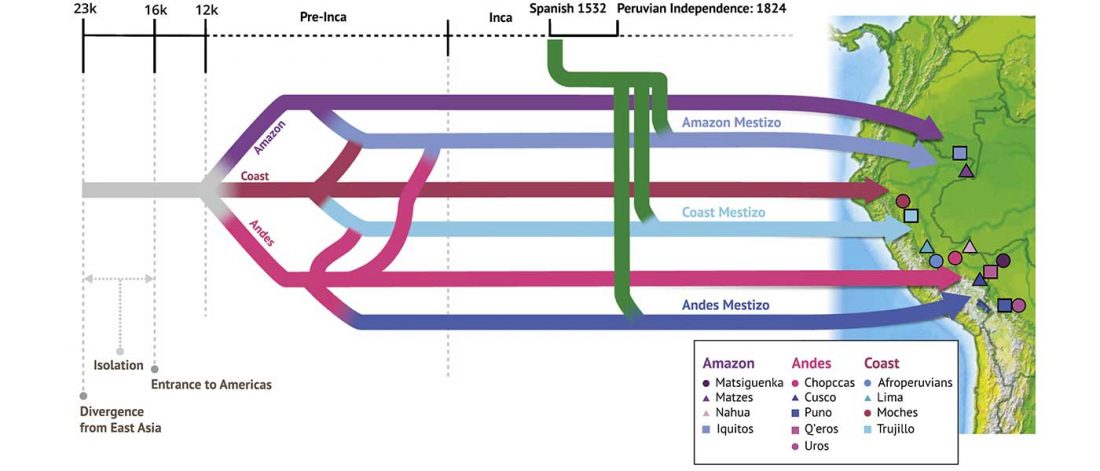
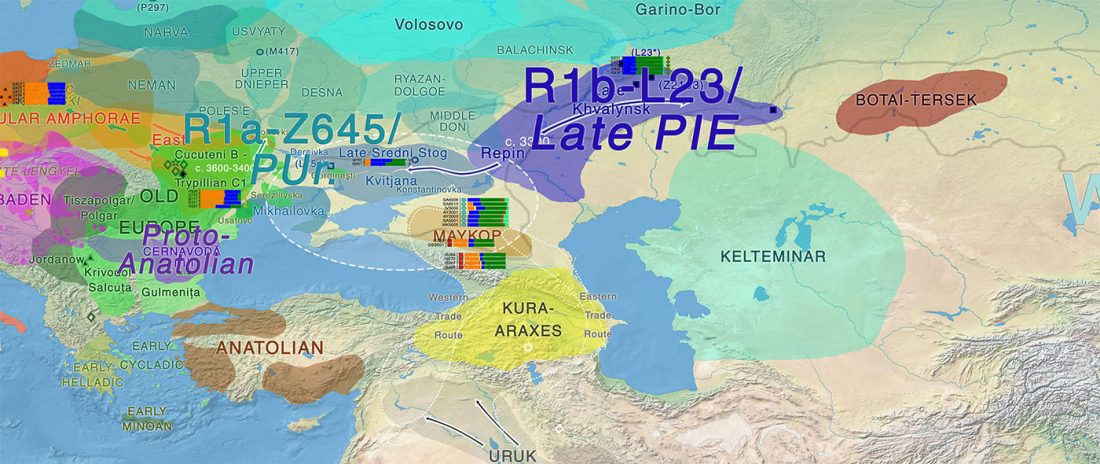
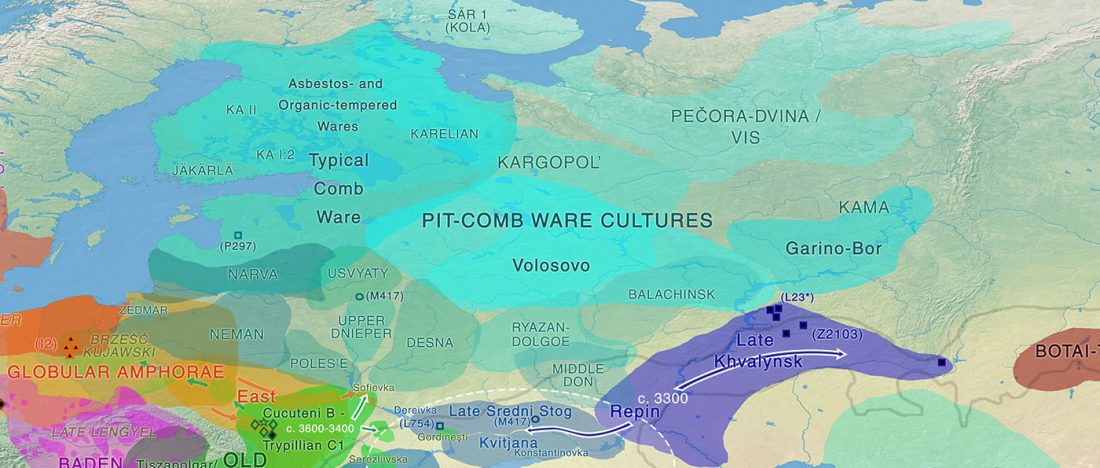
Human sacrifice as means of social control and power display in Upper Mesopotamia (early 3rd mill. BC)
Radical ‘royals’? Burial practices at Başur Höyük and the emergence of early states in Mesopotamia, by Hasset and Sağlamtimur, Antiquity (2018) 92:640-654.
Interesting excerpts:
… Read the rest “Human sacrifice as means of social control and power display in Upper Mesopotamia (early 3rd mill. BC)”The discovery of sacrificial burials attending a ‘royal’ burial in a cist tomb at Early Bronze Age Arslantepe in Anatolia (Frangipane 2006; Erdal 2012) has dramatically broadened the known range of social responses to the political upheaval of the early third millennium BC. Following the longstanding interpretation of human sacrifice at the Royal Cemetery of Ur just a few hundred years later (Woolley 1934), this raises new questions about the role of human sacrifice in