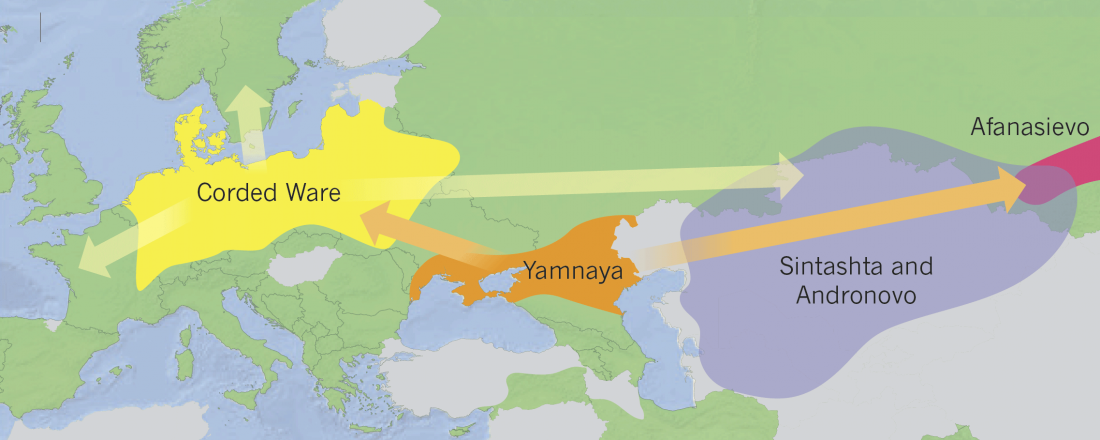
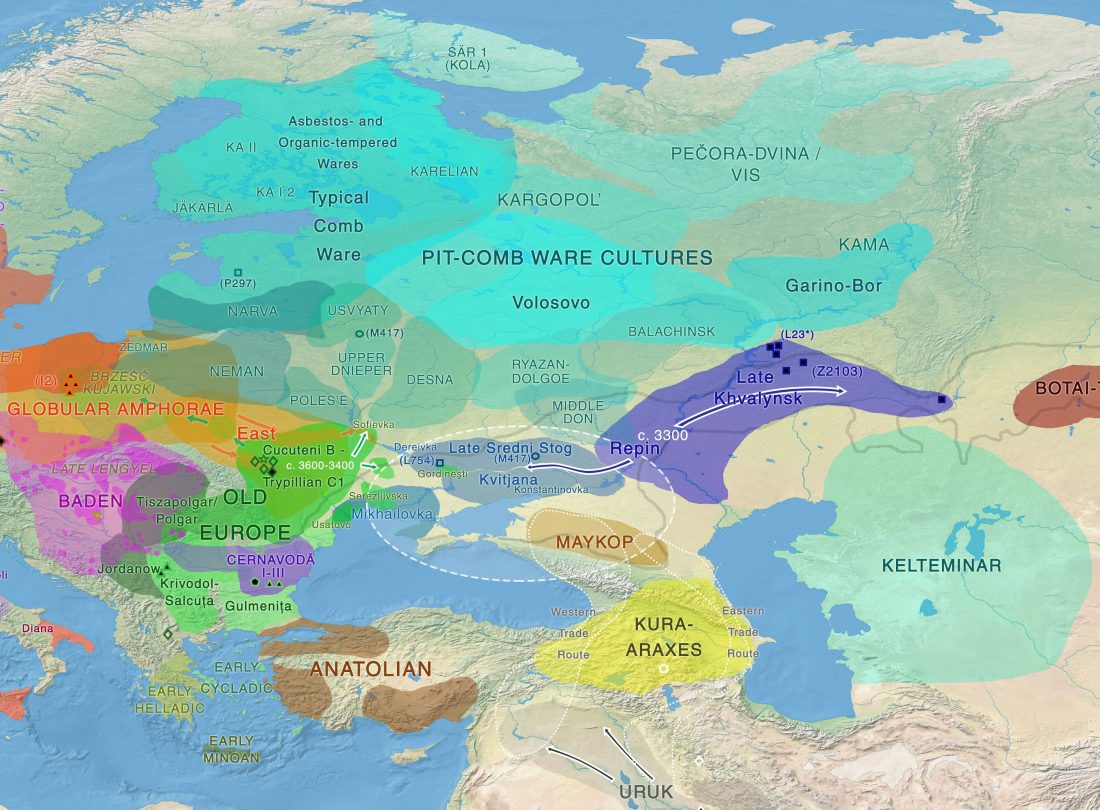
Prehistoric loan relations: Foreign elements in the Proto-Indo-European vocabulary
An interesting ongoing web project, Prehistoric loan relations, on potential loans of Proto-Indo-European words, from Uralic-Yukaghir, Caucasian, and Middle Eastern influence.
Based on a Ph.D. thesis by Bjørn (2017) Foreign elements in the Proto-Indo-European vocabulary (PDF).
From the website (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Prehistoric loan relations: Foreign elements in the Proto-Indo-European vocabulary”This page allows historical linguists to compare and scrutinize proposed prehistoric lexical borrowings from the perspective of Proto-Indo-European. The first entries are all (135 in total) extracted from my master’s thesis “Foreign elements in the Proto-Indo-European vocabulary” (Bjørn 2017). Comments are encouraged at the bottom of each entry. New entries will be added, also on request.
Take this