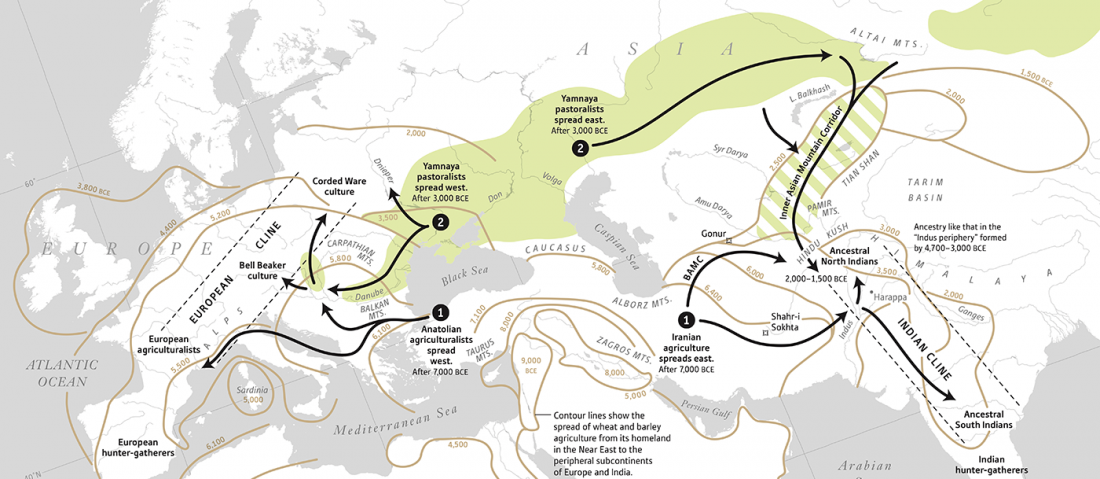
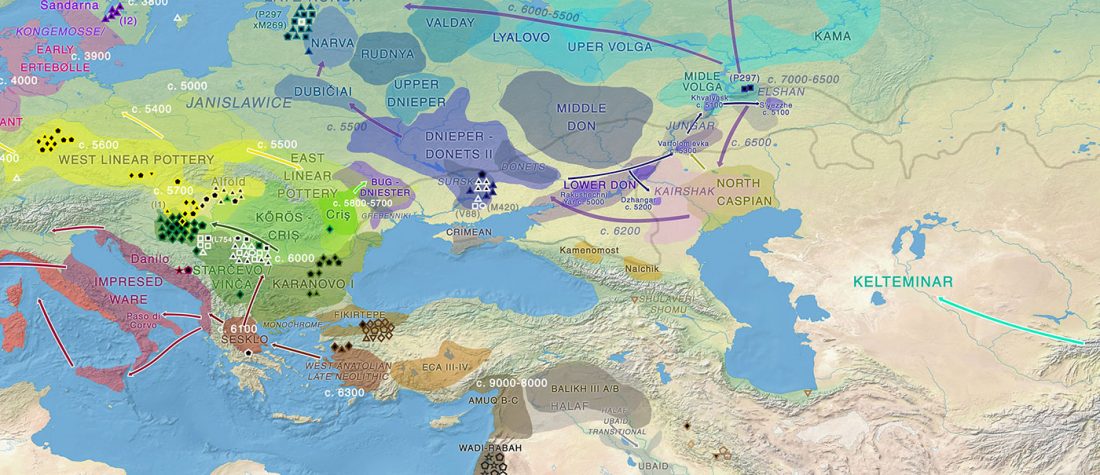
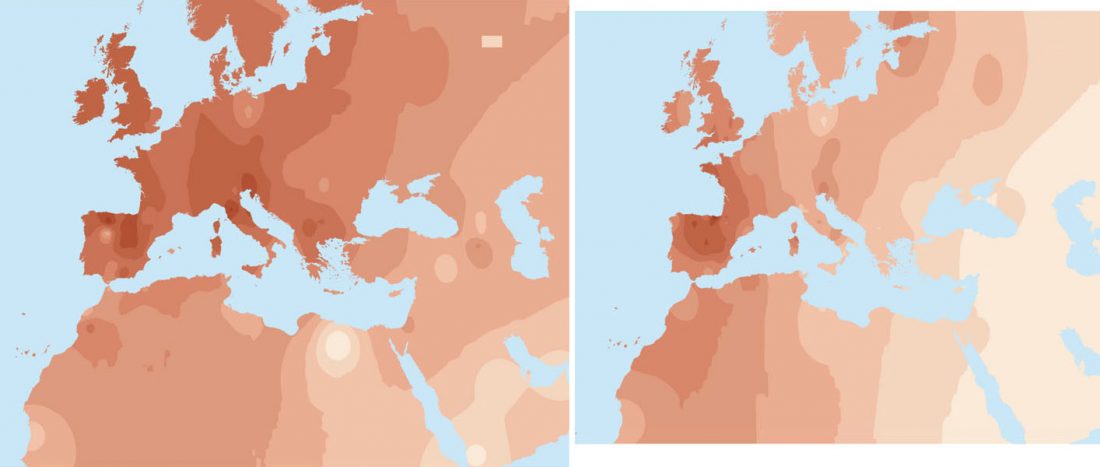
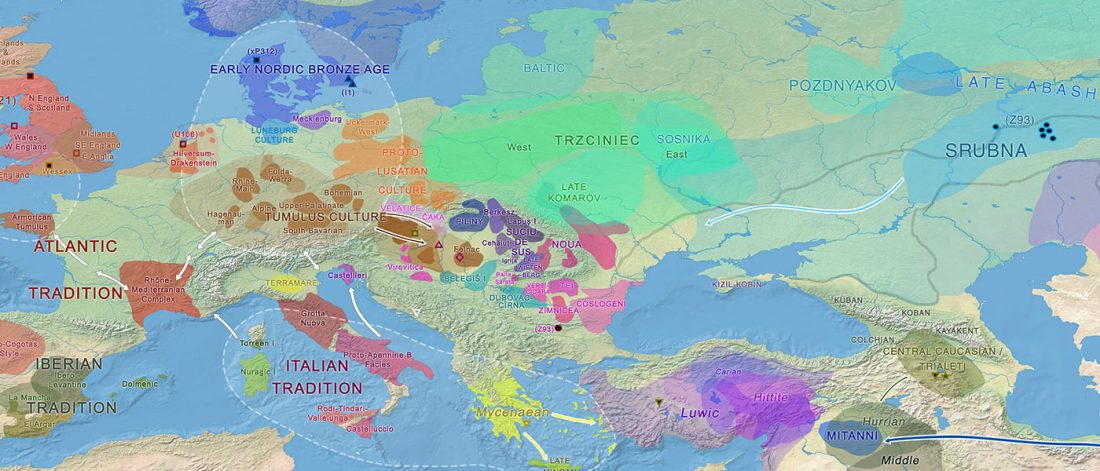
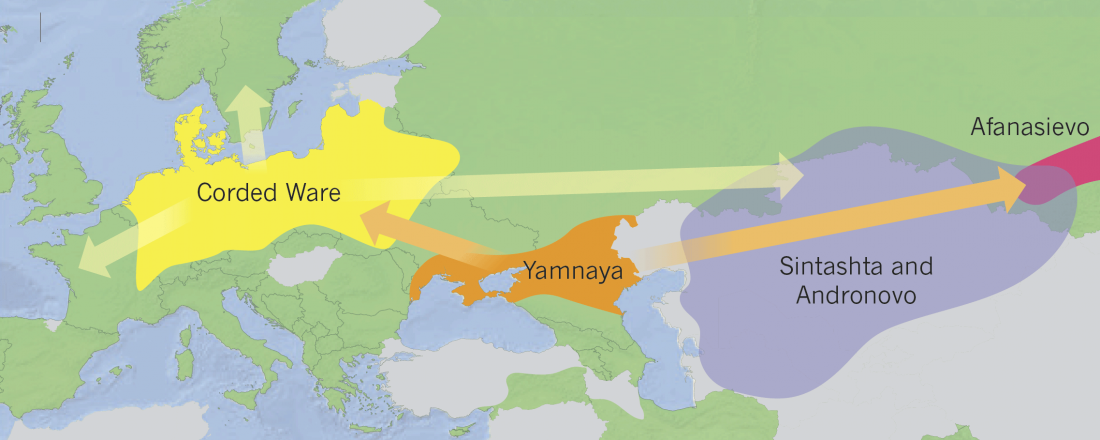
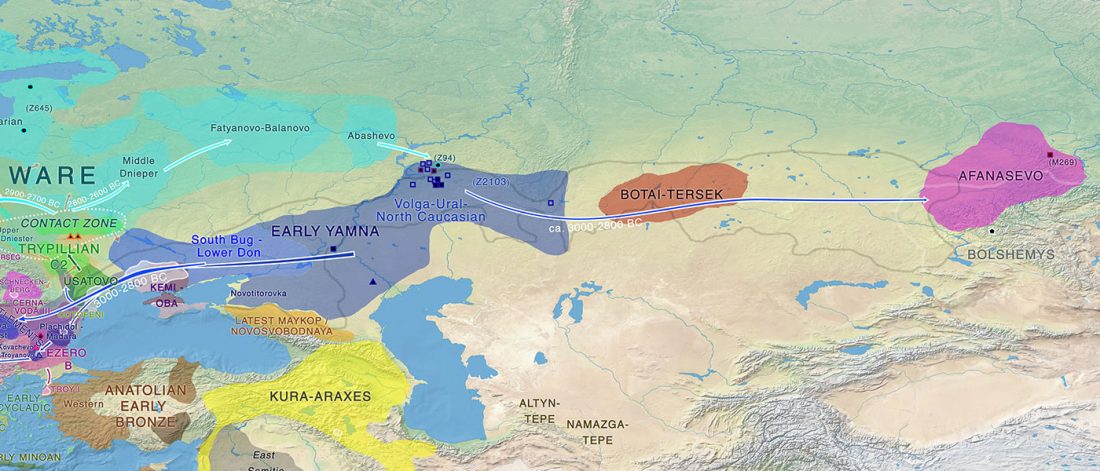
Early Indo-Iranian formed mainly by R1b-Z2103 and R1a-Z93, Corded Ware out of Late PIE-speaking migrations
The awaited, open access paper on Asian migrations is out: The Genomic Formation of South and Central Asia, by Narasimhan et al. bioRxiv (2018).
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Early Indo-Iranian formed mainly by R1b-Z2103 and R1a-Z93, Corded Ware out of Late PIE-speaking migrations”The genetic formation of Central and South Asian populations has been unclear because of an absence of ancient DNA. To address this gap, we generated genome-wide data from 362 ancient individuals, including the first from eastern Iran, Turan (Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan), Bronze Age Kazakhstan, and South Asia. Our data reveal a complex set of genetic sources that ultimately combined to form the ancestry of South Asians today. We document a southward spread of