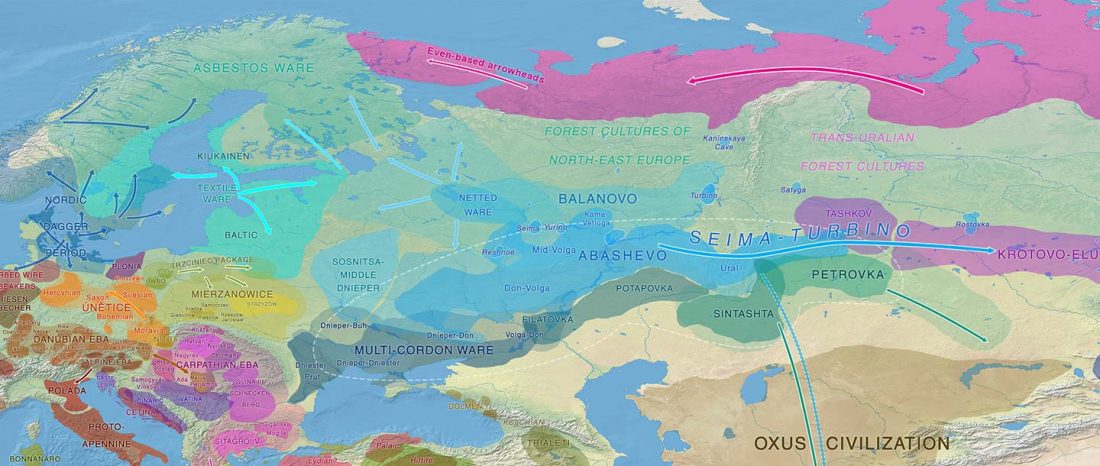
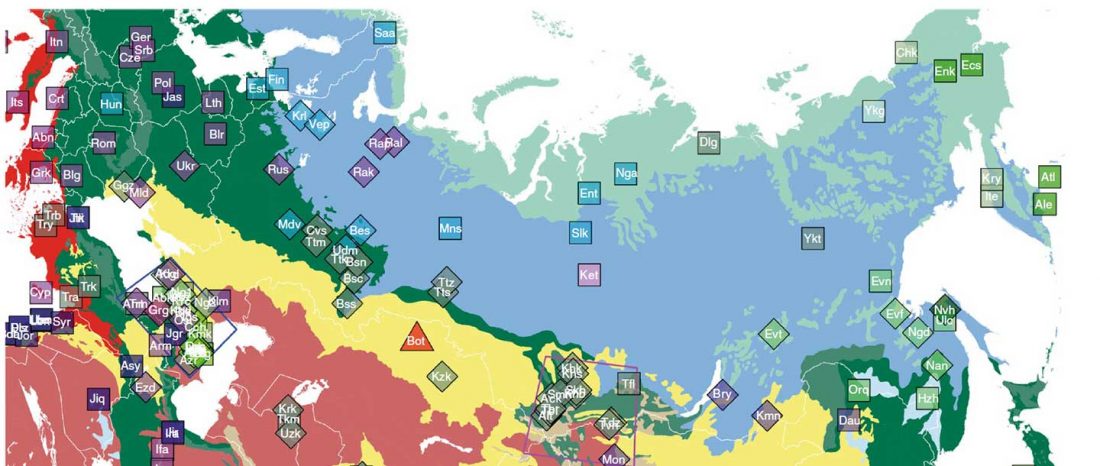
The recent study of Estonian Late Bronze Age/Iron Age samples has shown, as expected, large genetic continuity of Corded Ware populations in the East Baltic area, where West Uralic is known to have been spoken since at least the Early Bronze Age.
The most interesting news was that, unexpectedly for many, the impact of “Siberian ancestry” (whatever that actually means) was small, slow, and gradual, with slight increases found up to the Middle Ages, compatible with multiple contact events in north-eastern Europe. Haplogroup N became prevalent among Finnic populations only through late bottlenecks, as research of modern … Read the rest “Genetic continuity among Uralic-speaking cultures in north-eastern Europe”