The Indo-Iranian – Finno-Ugric connection
On the linguistic aspect, this is what the Copenhagen group had to say (in the linguistic supplement) based on Kuz’mina (2001):
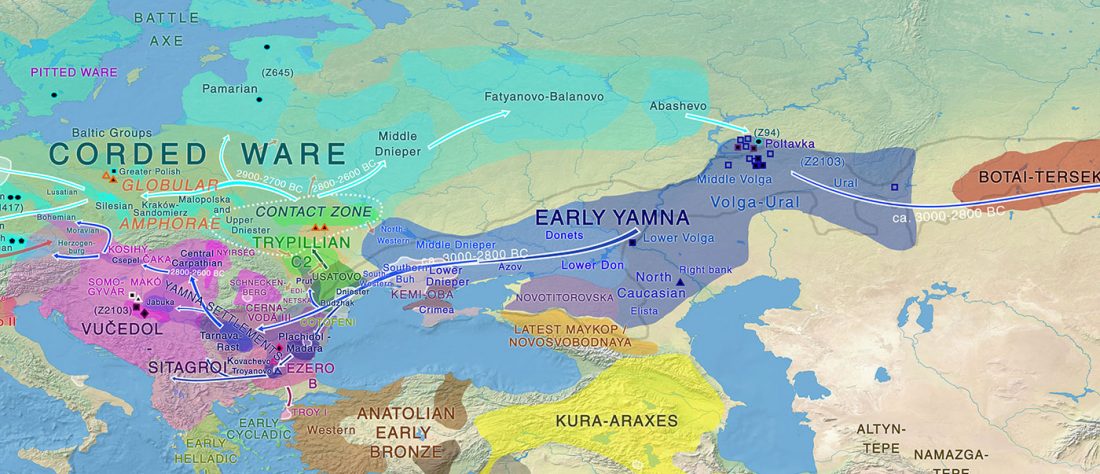
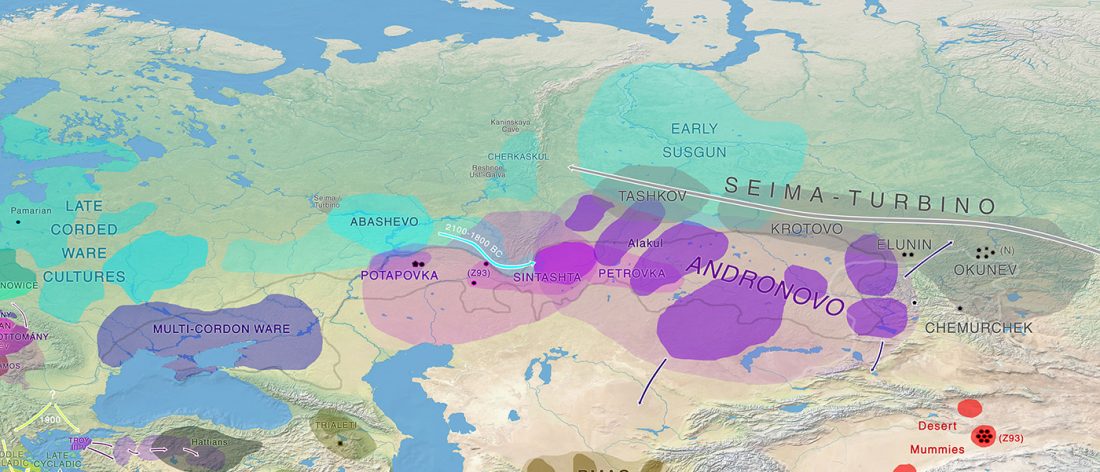
… Read the rest “Consequences of Damgaard et al. 2018 (III): Proto-Finno-Ugric & Proto-Indo-Iranian in the North Caspian region”(…) a northern connection is suggested by contacts between the Indo-Iranian and the Finno-Ugric languages. Speakers of the Finno-Ugric family, whose antecedent is commonly sought in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains, followed an east-to-west trajectory through the forest zone north and directly adjacent to the steppes, producing languages across to the Baltic Sea. In the languages that split off along this trajectory, loanwords from various stages in the development of the