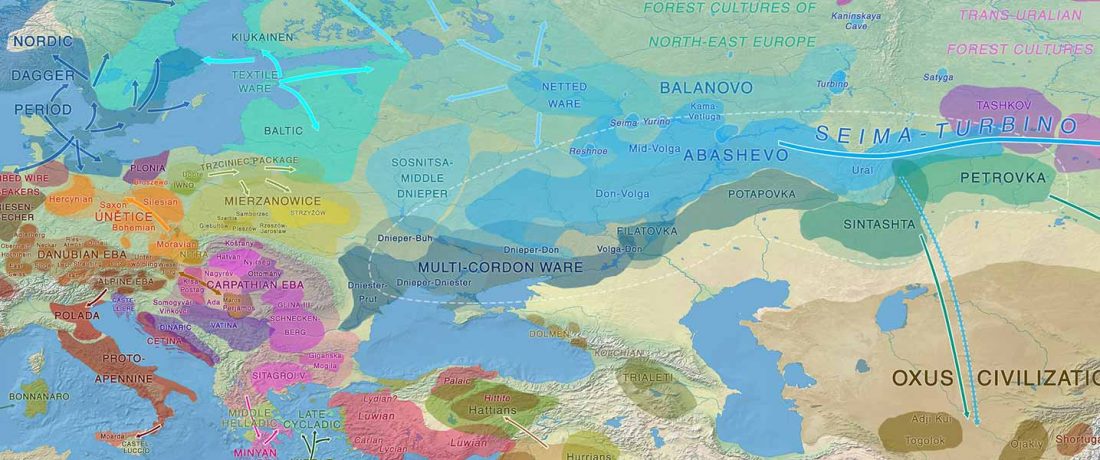
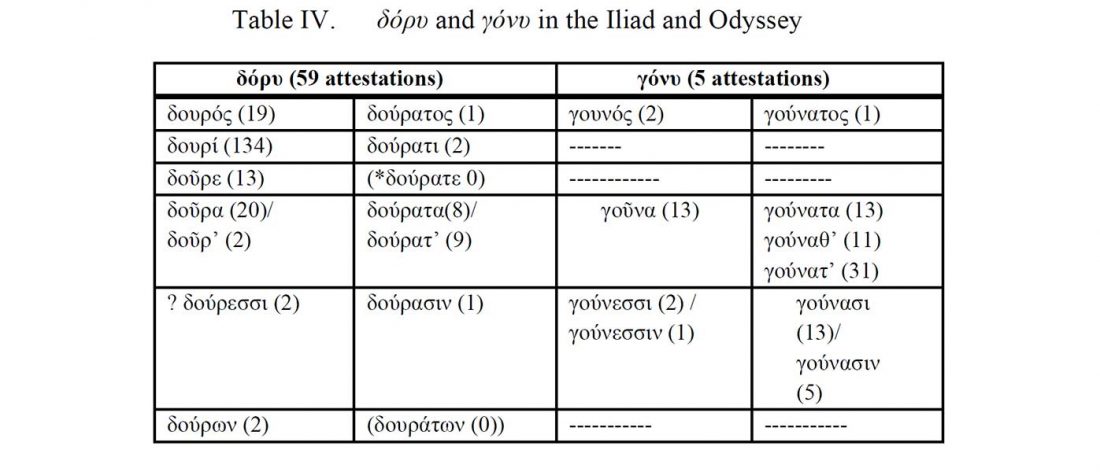
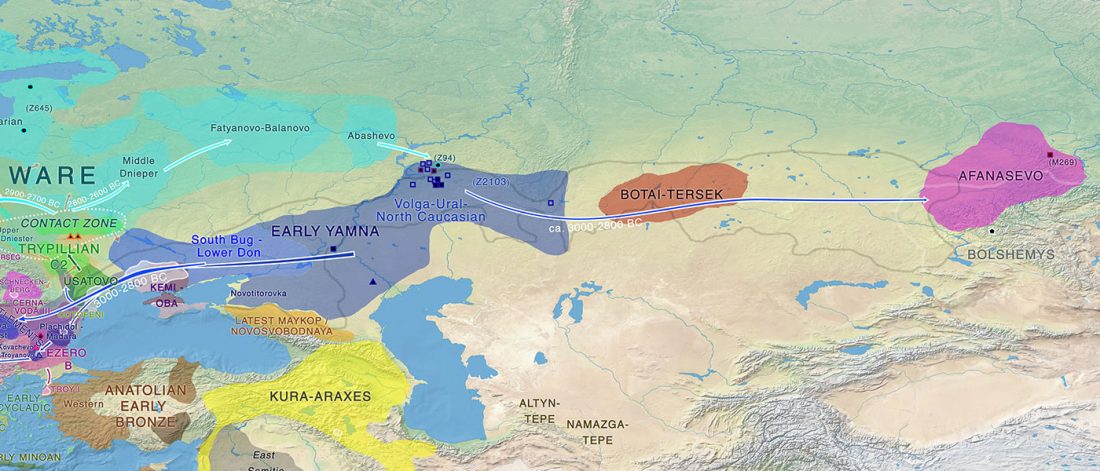
The final paper on Indo-Iranian peoples, by Narasimhan and Patterson (see preprint), is soon to be published, according to the first author’s Twitter account.
One of the interesting details of the development of Bronze Age Iberian ethnolinguistic landscape was the making of Proto-Iberian and Proto-Basque communities, which we already knew were going to show R1b-P312 lineages, a haplogroup clearly associated during the Bell Beaker period with expanding North-West Indo-Europeans:
… Read the rest “Aquitanians and Iberians of haplogroup R1b are exactly like Indo-Iranians and Balto-Slavs of haplogroup R1a”From the Bronze Age (~2200–900 BCE), we increase the available dataset from 7 to 60 individuals and show how ancestry from the Pontic-Caspian steppe (Steppe ancestry) appeared throughout Iberia