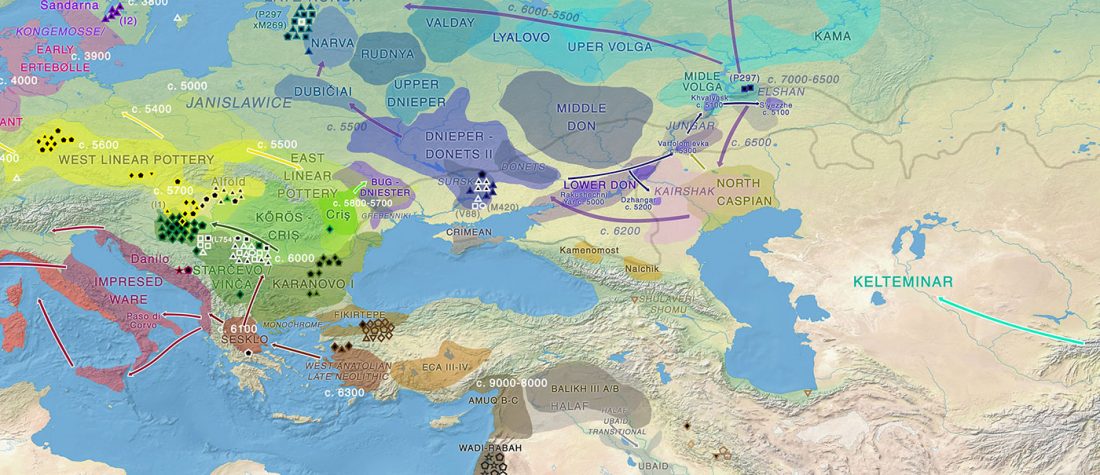
New papers Genomic History of Neolithic to Bronze Age Anatolia, Northern Levant, and Southern Caucasus, by Skourtanioti et al., and (open access) The Genomic History of the Bronze Age Southern Levant, by Agranat-Tamir et al., both in Cell (2020) 181(5).
Interesting excerpts from Skourtanioti et al. (2020) (emphasis mine):
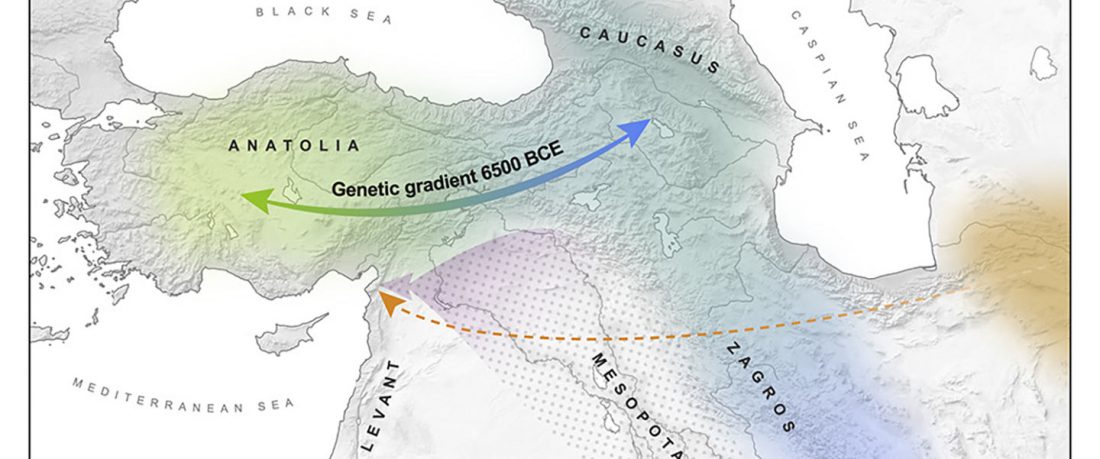
Genetic Continuity in Anatolia
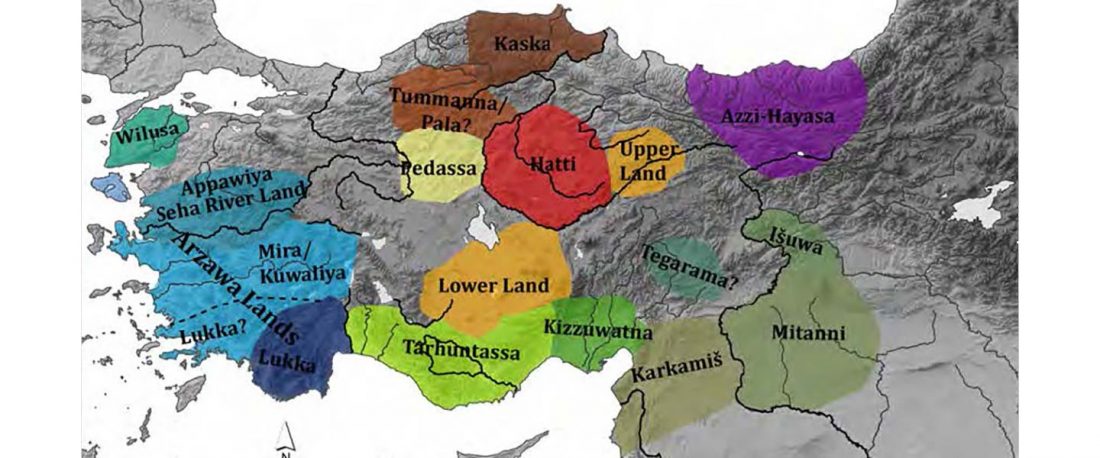
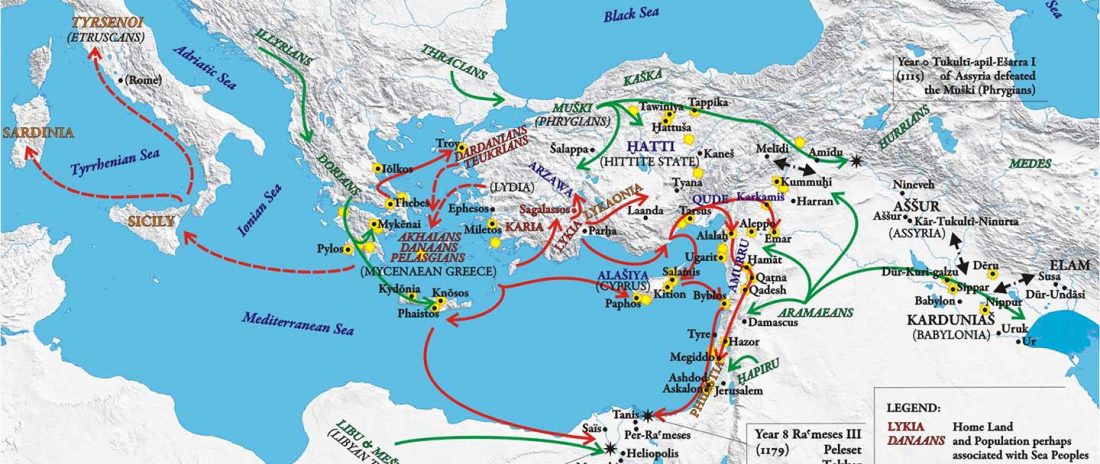
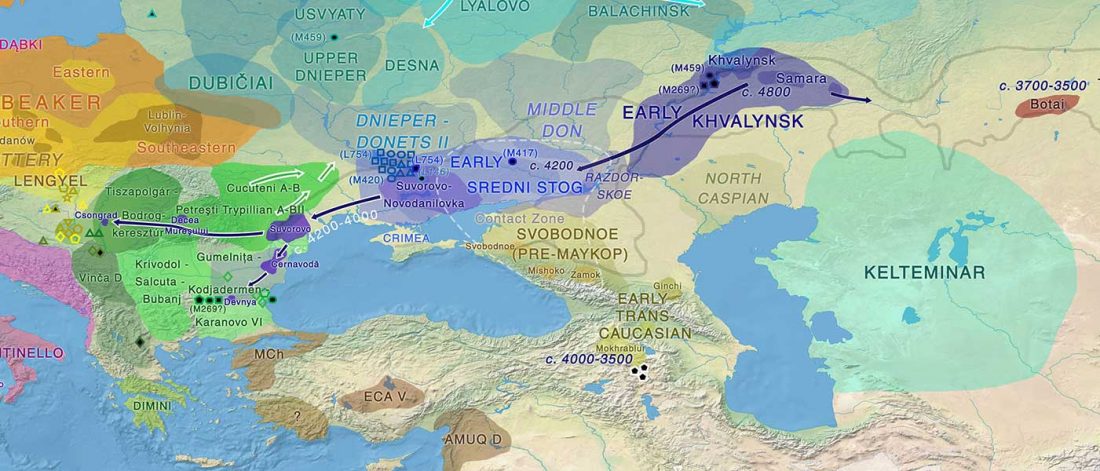
… Read the rest “Demographically complex Near East hints at Anatolian and Indo-Aryan arrival”We focused on the three Late Chalcolithic groups with sufficiently large sample size and who are the earliest in time among the LC-LBA groups: ÇamlıbelTarlası_LC (n = 9), İkiztepe_LC (n = 11), and Arslantepe_LC (n = 17). Taking individual estimates from all these individuals together