Open access paper Ancient genomes reveal social and genetic structure of Late Neolithic Switzerland by Furtwängler et al. Nat. Commun. (2020).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
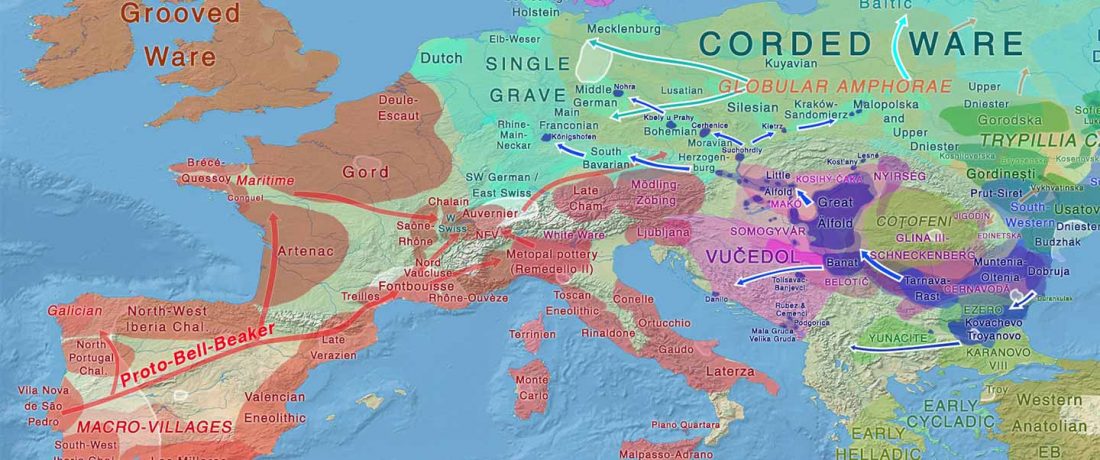
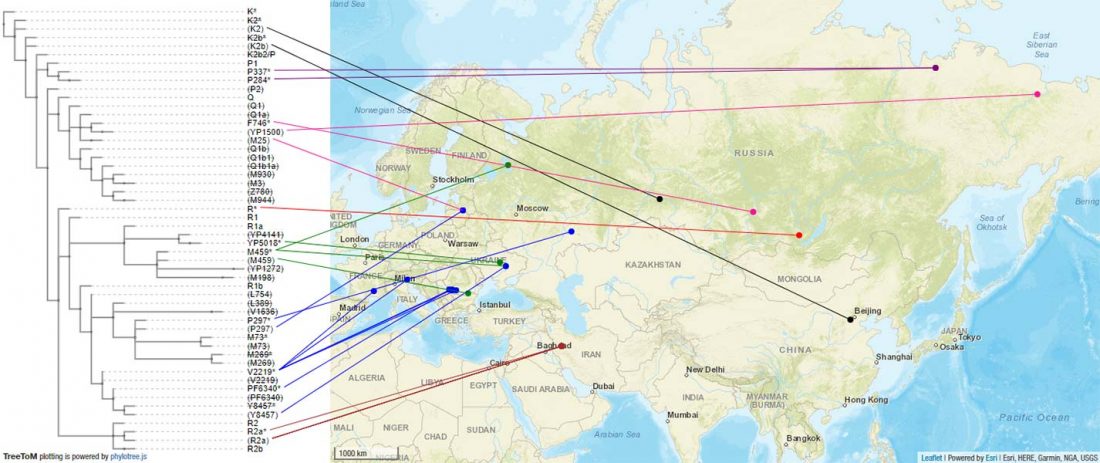
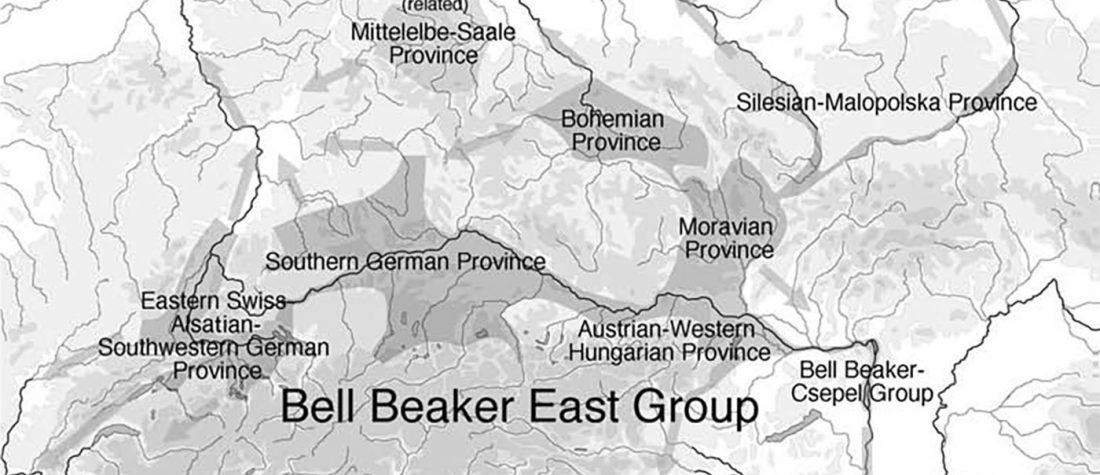
The ancient individuals from this study originate from 13 Neolithic and Early Bronze Age sites in Switzerland, Southern Germany, and the Alsace region in France. All samples taken from the individuals were radiocarbon dated.
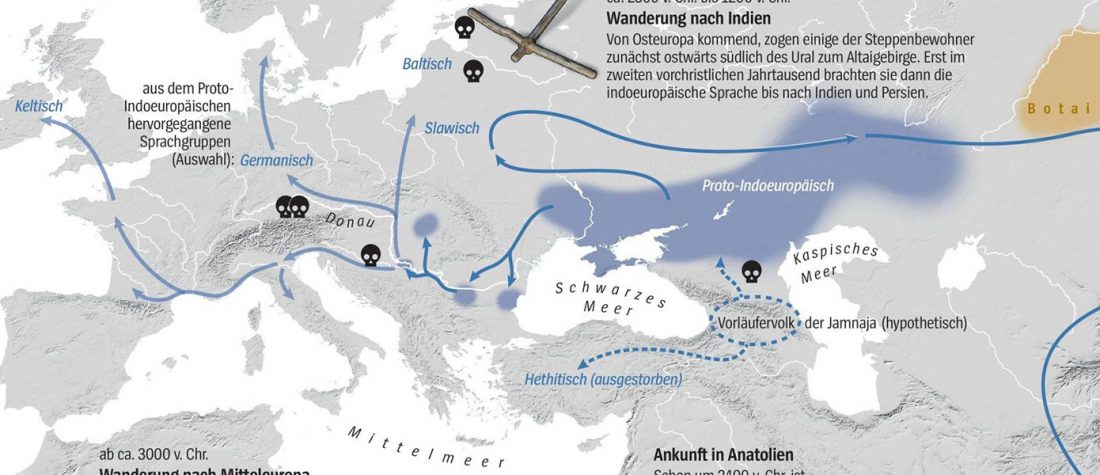
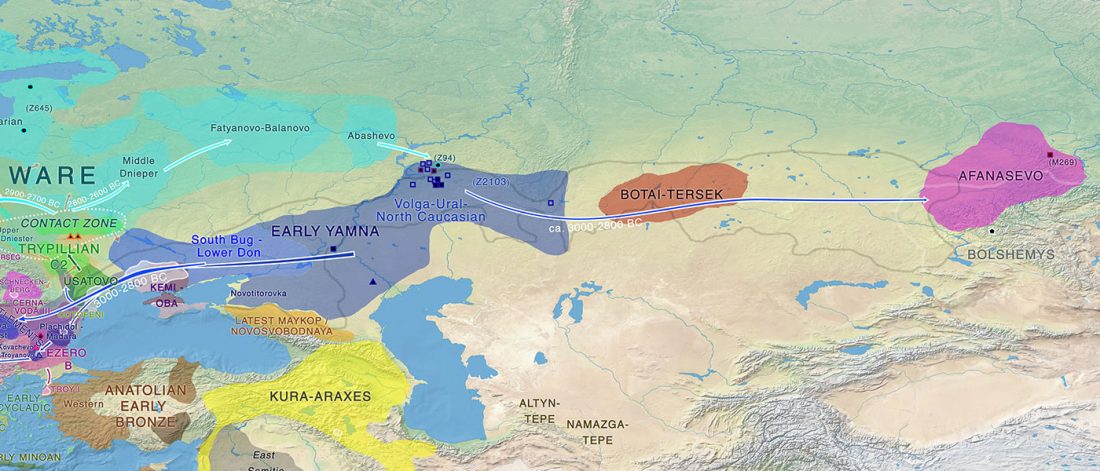
The arrival of Steppe ancestry
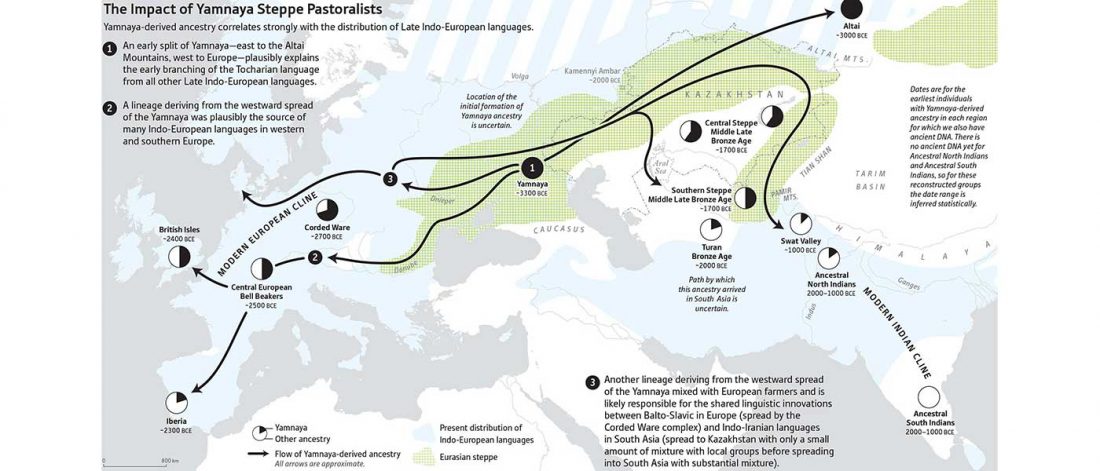
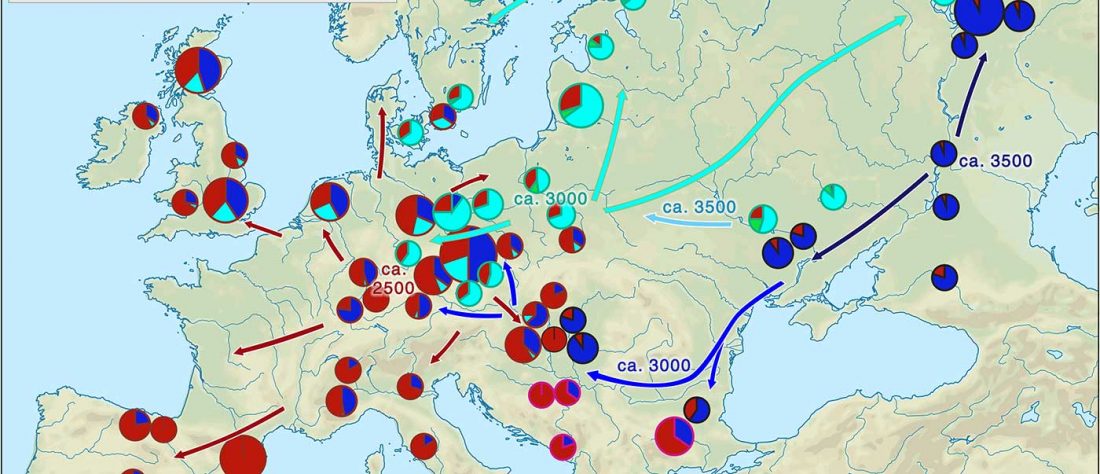
… Read the rest “Early arrival of Steppe ancestry in Switzerland”Two distinct clusters can be identified and were also confirmed by ADMIXTURE analysis, one consisting of individuals dating to 4770–2500 calBCE, and one comprising individuals dating to 2900–1750 calBCE. The oldest individuals from the sites of