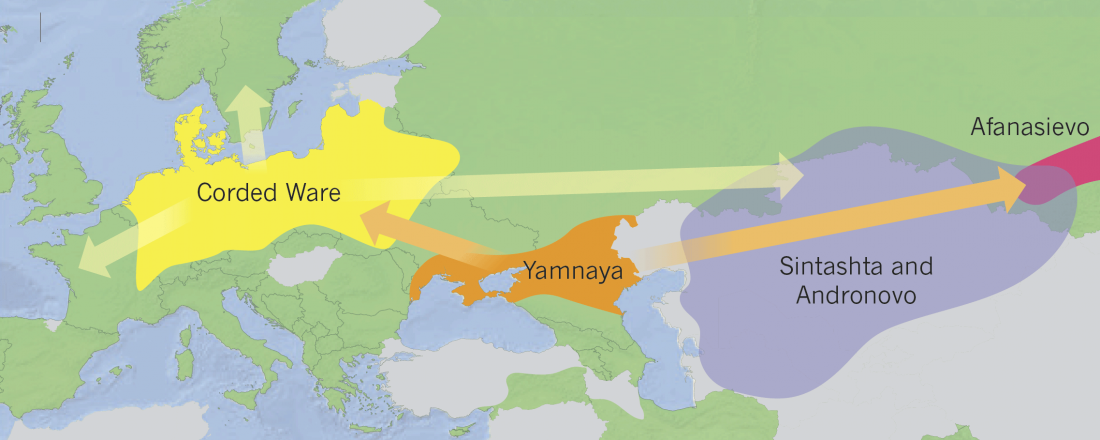
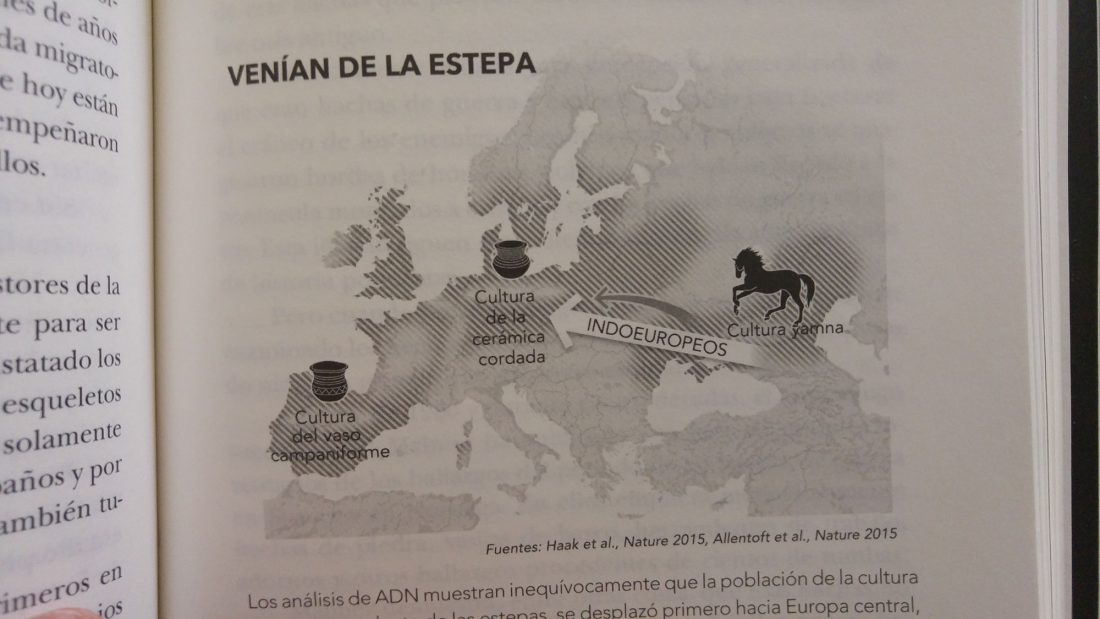
The concept of ‘Kurgan peoples’ is a general idea whereby ‘kurgan builders’ are identified with Indo-European speakers. It is a consequence of the oversimplification of Gimbutas’ theory, and is still widespread among linguists, archaeologists, geneticists, and amateurs alike.
NOTE. On the already simplistic assumptions of Gimbutas regarding the so-called ‘kurgan’ burials, see e.g. Häusler’s early criticism.
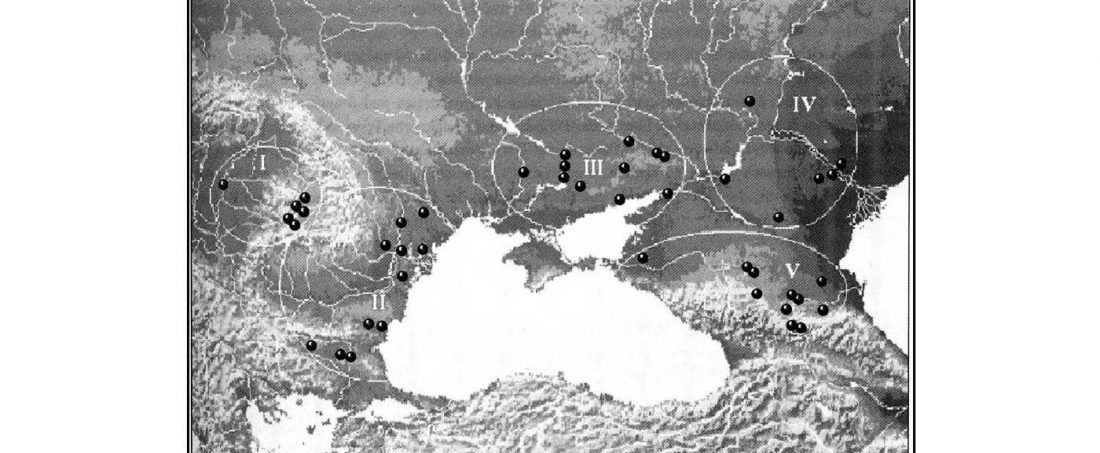
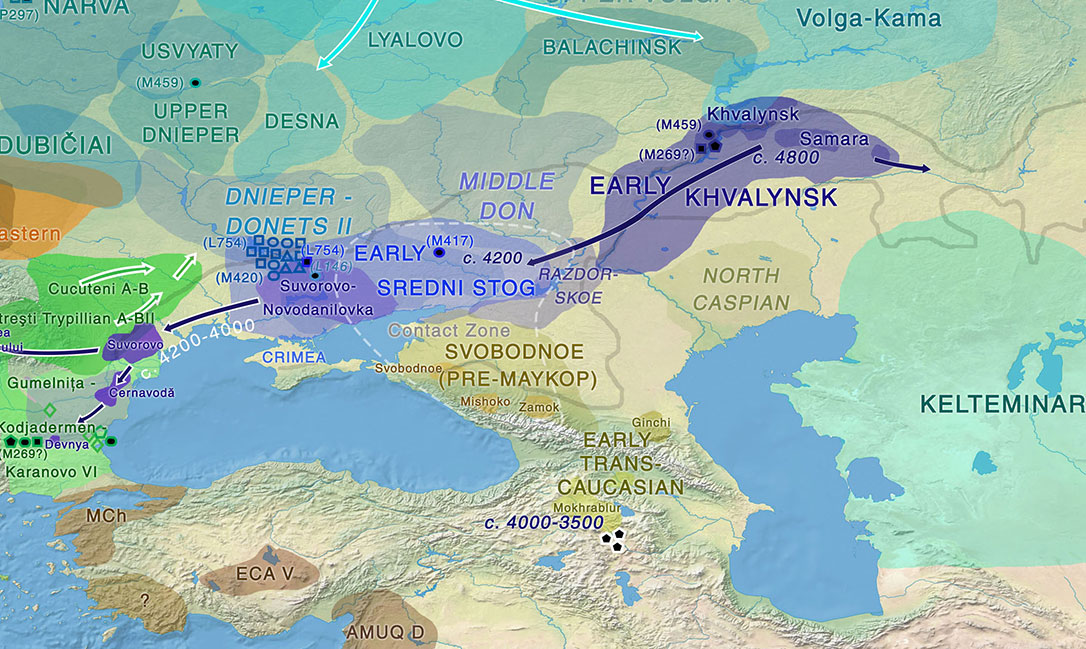
However, as more ancient DNA studies appear, many ancient cultures once held as ‘kurganized’ are becoming more and more clearly disconnected from Proto-Indo-Europeans: So for example Varna, Cucuteni-Trypillia, Maykop, or Northern Iranian kurgan builders.
The first marked burials
In his chapter Aspects of … Read the rest “Kurgan origins and expansion with Khvalynsk-Novodanilovka chieftains”