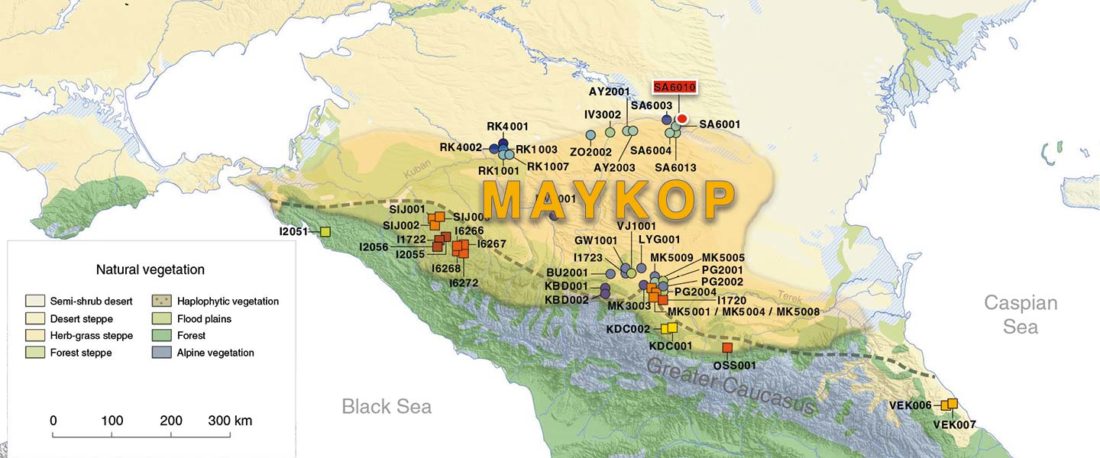
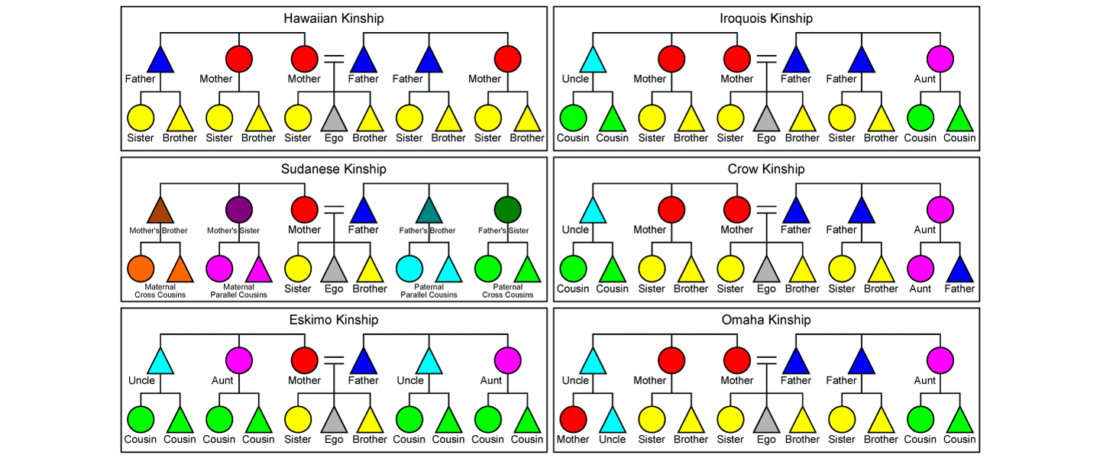
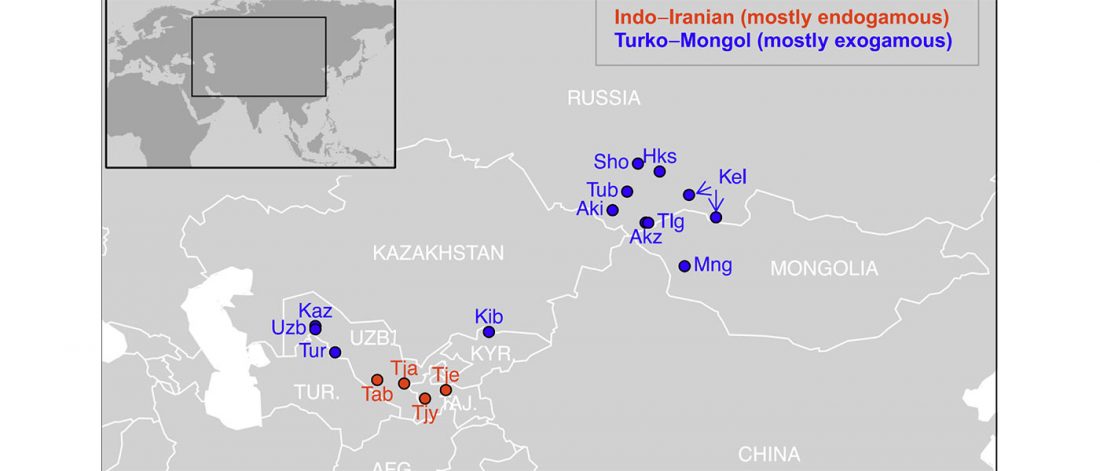
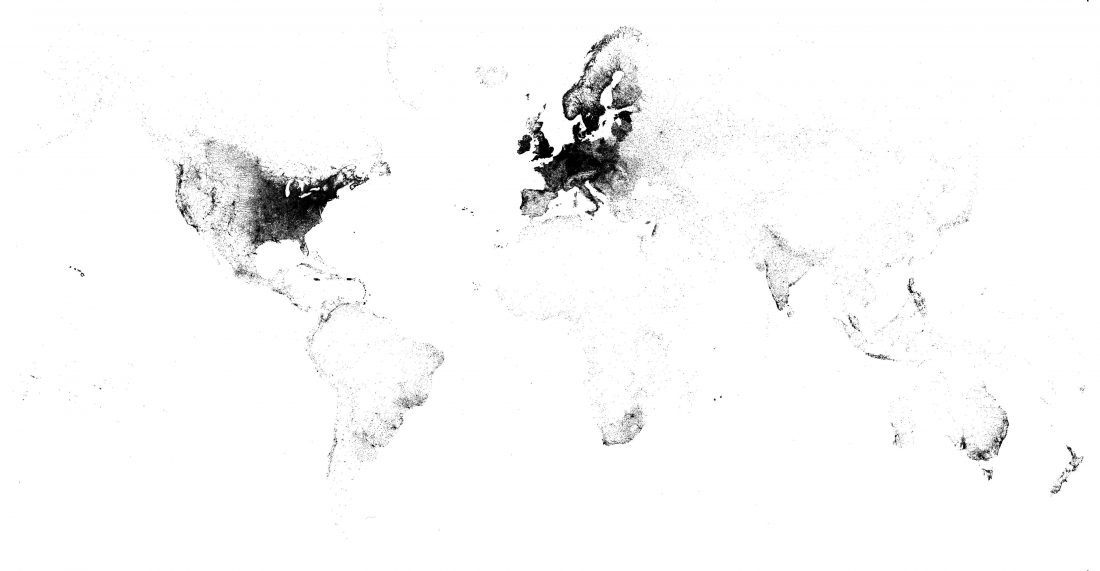
I have updated the Ancient DNA Dataset, including a lot of new information from – among other sources – the latest version of Reich Lab curated Dataset, now renamed Allen Ancient DNA Resource (AADR). This includes new columns:
- Object-ID: I am now using whenever possible the Master-ID; Version-ID for a quick identification of the ‘best’ sample to include in SmartPCA or ADMIXTURE runs; and Index as a key with a unique reference number for each sample. That should make for enough stable references for any external tool to use the data.
- mtDNA: Added mtDNA coverage