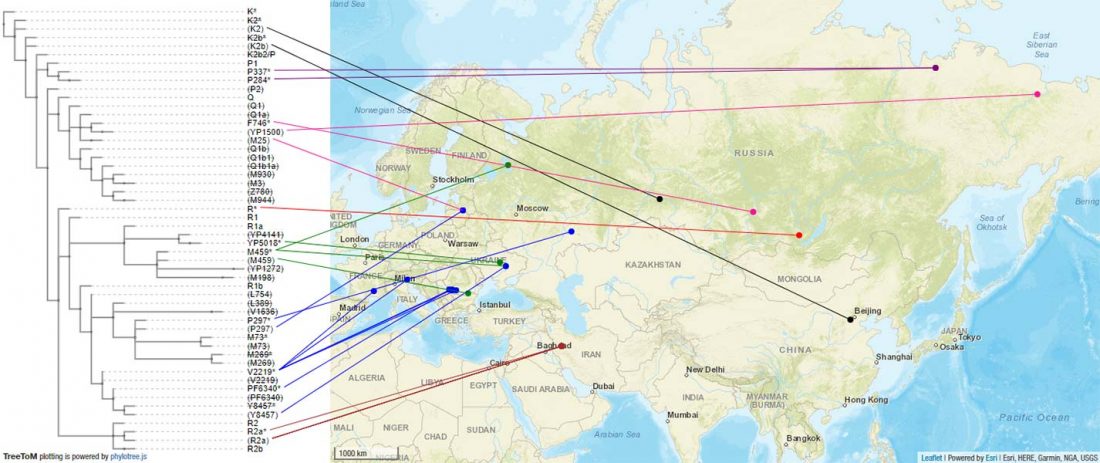
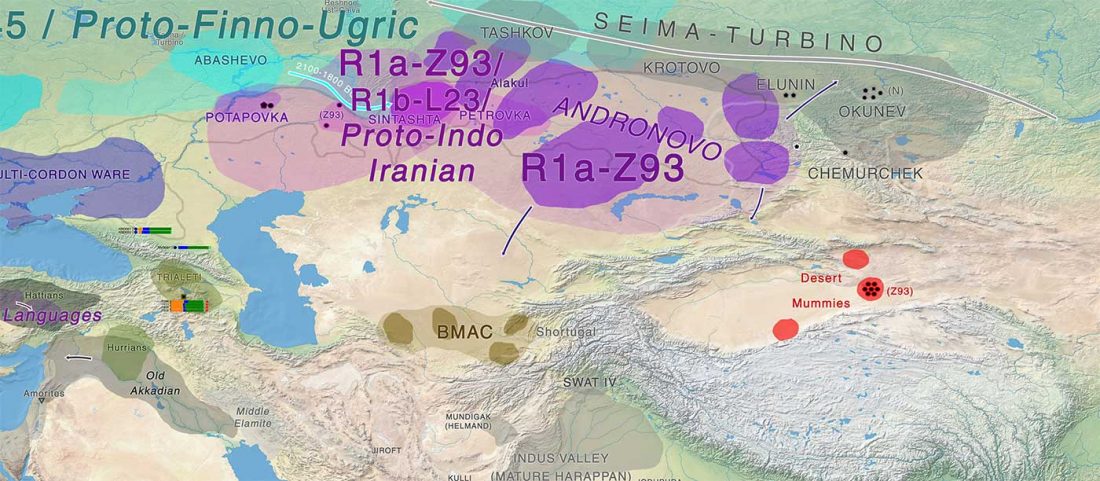
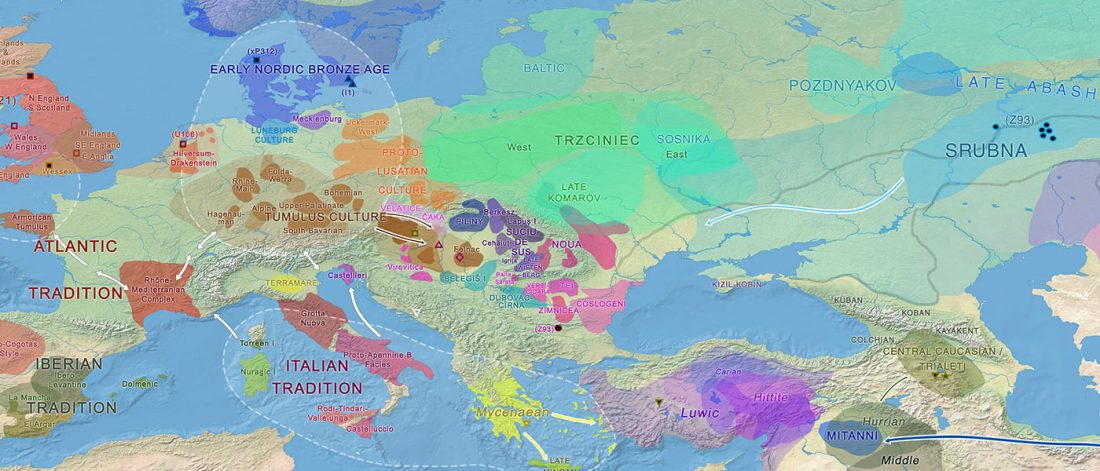
The previous post showed the potential use of TreeToM to visualize ancient DNA samples in maps together with their Y-DNA phylogenetic trees. I have written Newick trees for Y-chromosome haplogroups R1b-L388 (encompassing R-V1636 and R-P297, which in turn split into R-M73 and R-M269), R1a, and N.
I have reviewed some of the BAM files from my previous bulk analyses with YLeaf v.2, to add information that I had not previously included in the All Ancient DNA Dataset, and which might be relevant to the proper depiction of phylogenetic trees; in particular, positive and negative SNPs potentially distinguishing archaic… Read the rest “Ancient phylogeography: spread of haplogroups R1b, R1a and N”