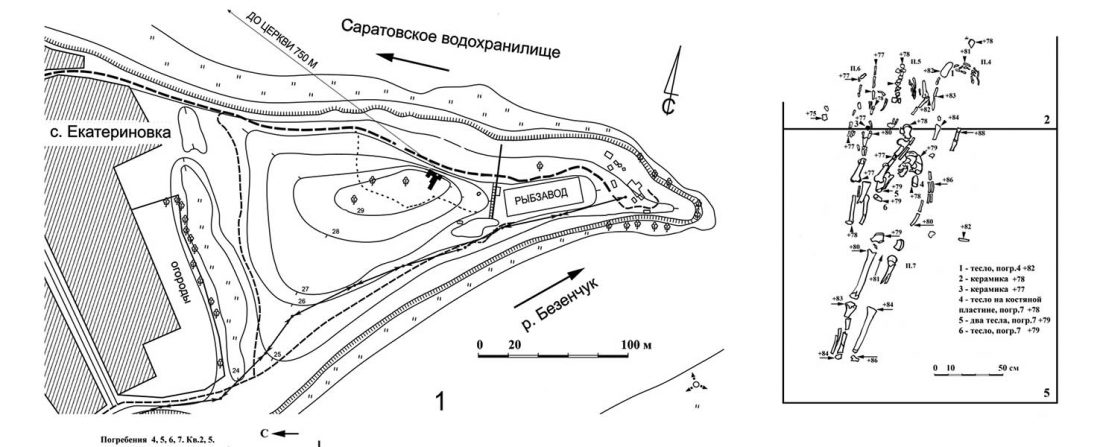
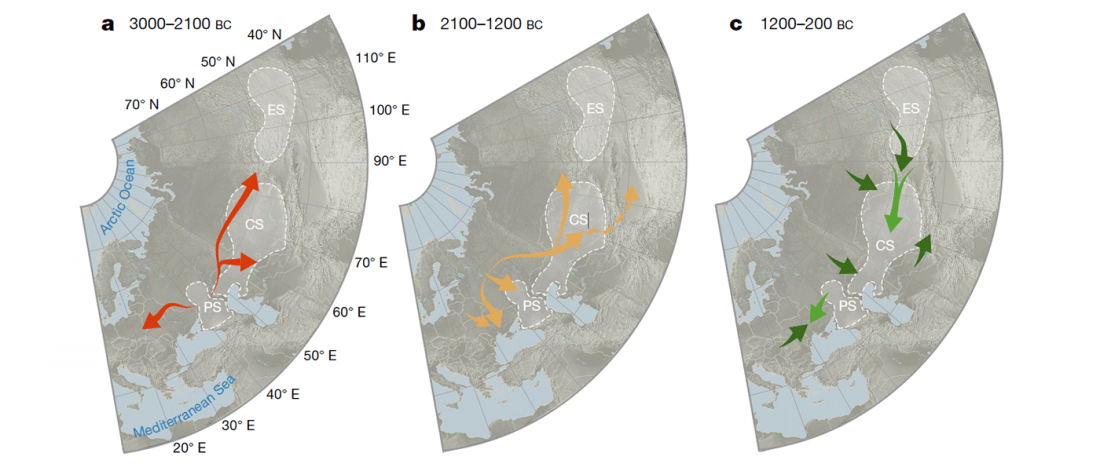
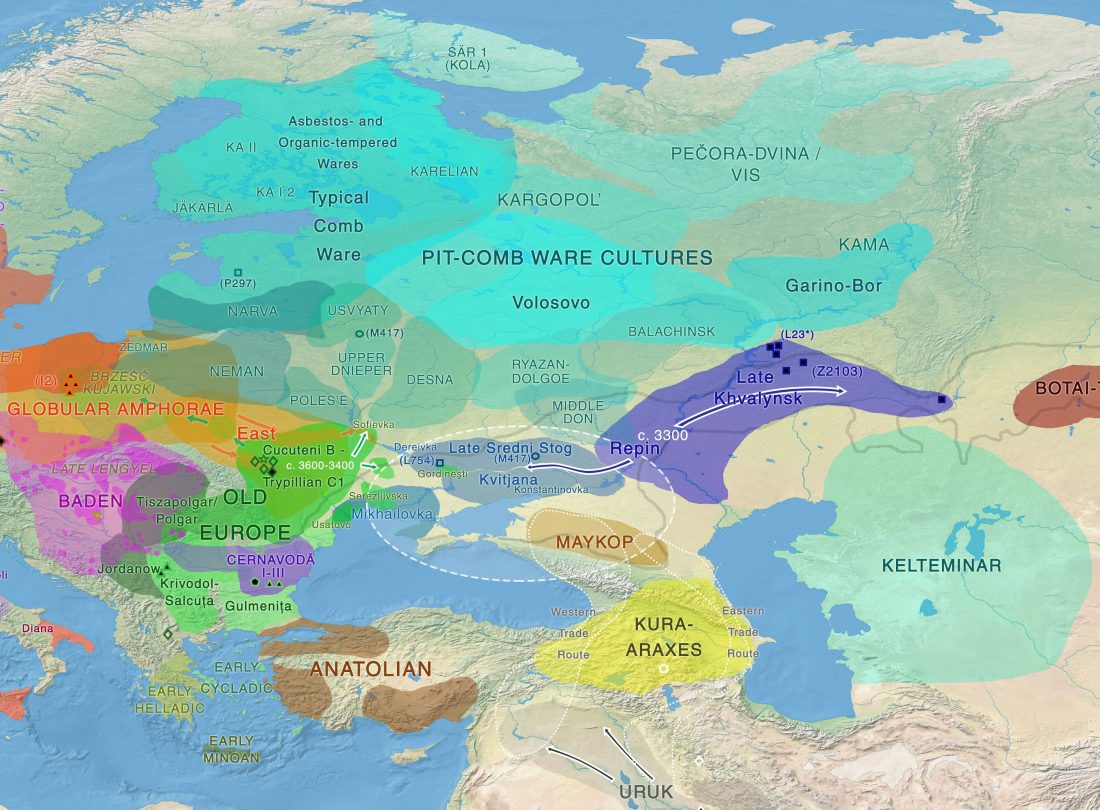
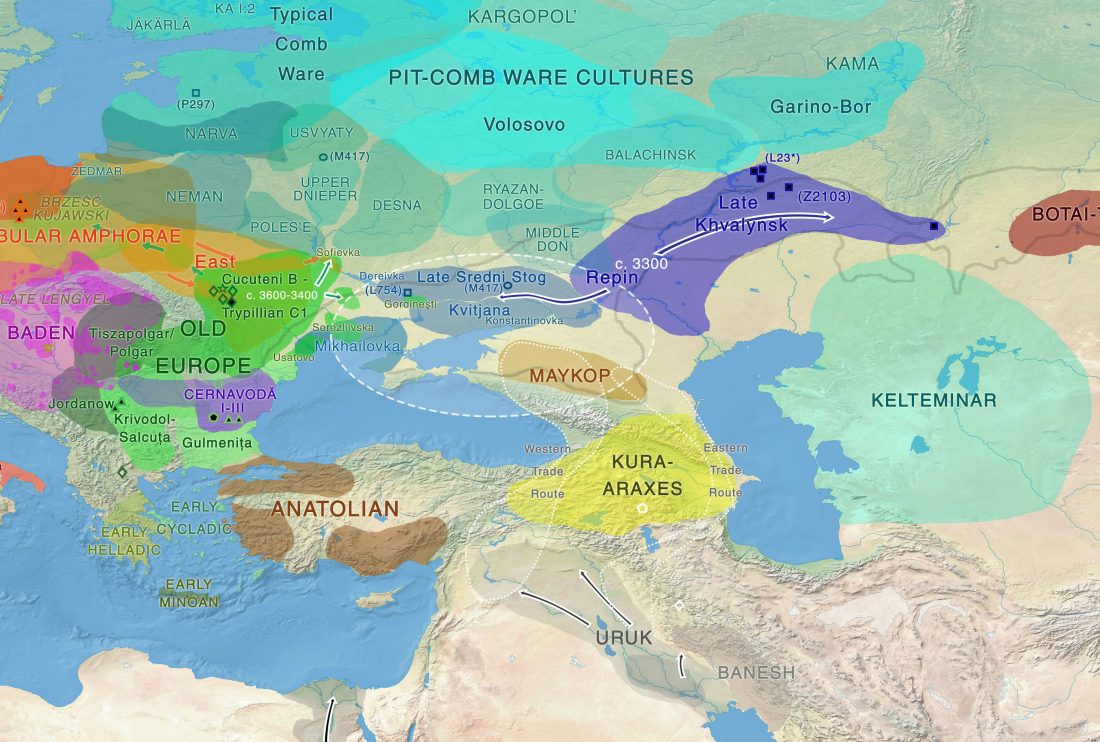
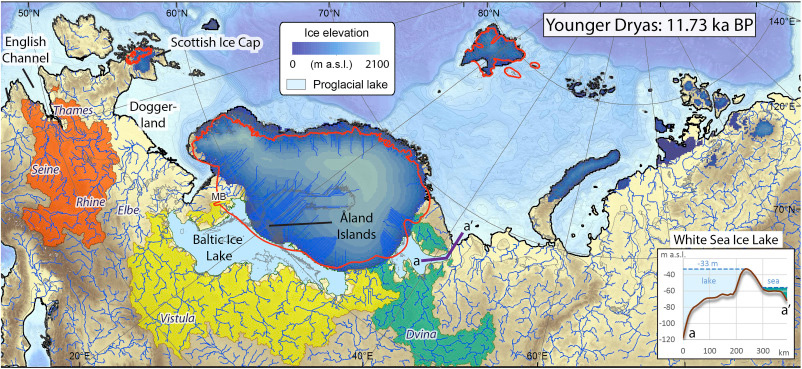
We already had conflicting information about the elite individual from the Yekaterinovsky Cape and the materials of his grave, which seemed quite old:
… Read the rest “Yekaterinovsky Cape, a link between the Samara culture and early Khvalynsk”For the burial of 45 in the laboratory of the University of Pennsylvania, a 14C date was obtained: PSUAMS-2880 (Sample ID 16068)30 kDa gelatin Russia. 12, Ekaterinovka Grave 45 14C age (BP) 6325 ± 25 δ 13C (‰) –23.6 δ15 N (‰) 14.5. The results of dating suggest chronological proximity with typologically close materials from Yasinovatsky and Nikolsky burial grounds (Telegini et al. 2001: 126). The date obtained also precedes the existing dates