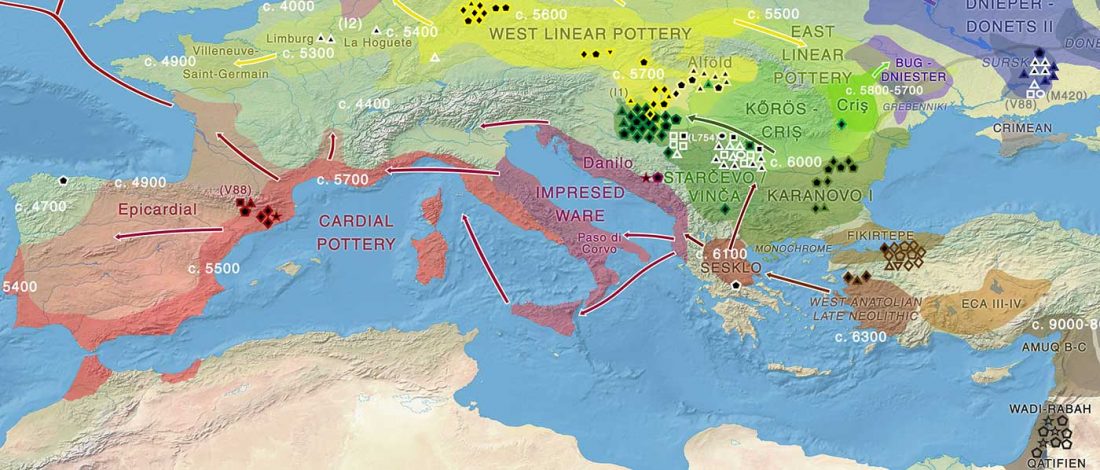
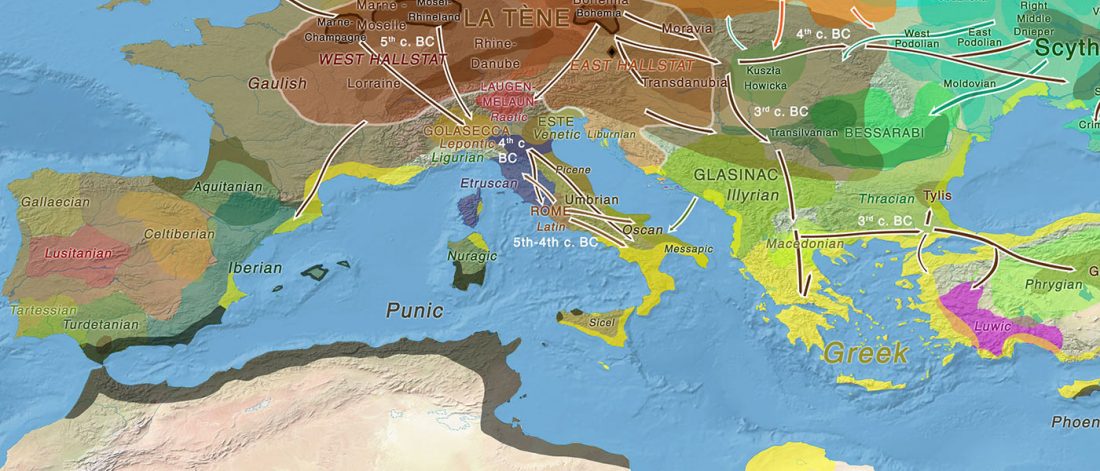
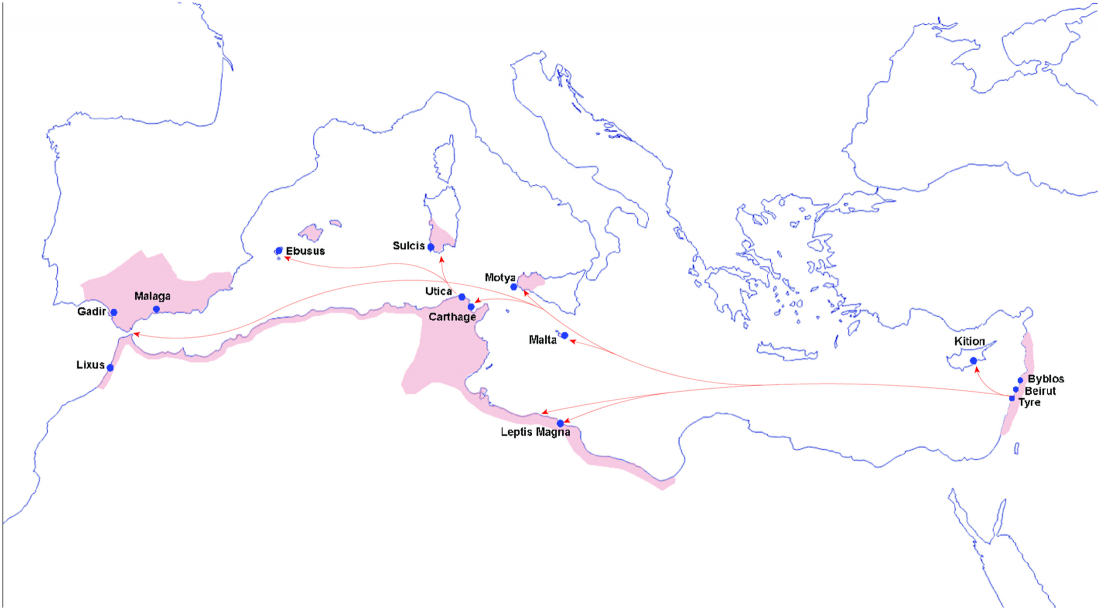
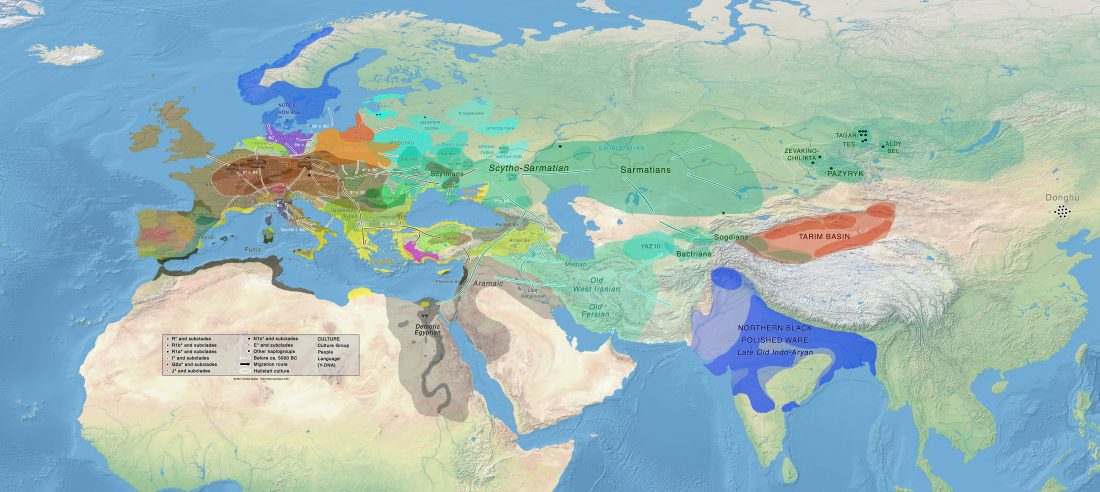
Open access Prehistoric migrations through the Mediterranean basin shaped Corsican Y-chromosome diversity, by Di Cristofaro et al. PLOS One (2018).
Interesting excerpts:
This study included 321 samples from men throughout Corsica; samples from Provence and Tuscany were added to the cohort. All samples were typed for 92 Y-SNPs, and Y-STRs were also analyzed.
… Read the rest “Y-chromosome mixture in the modern Corsican population shows different migration layers”Haplogroup R represented approximately half of the lineages in both Corsican and Tuscan samples (respectively 51.8% and 45.3%) whereas it reached 90% in Provence. Sub-clade R1b1a1a2a1a2b-U152 predominated in North Corsica whereas R1b1a1a2a1a1-U106 was present in South Corsica. Both SNPs display clinal distributions of frequency variation in