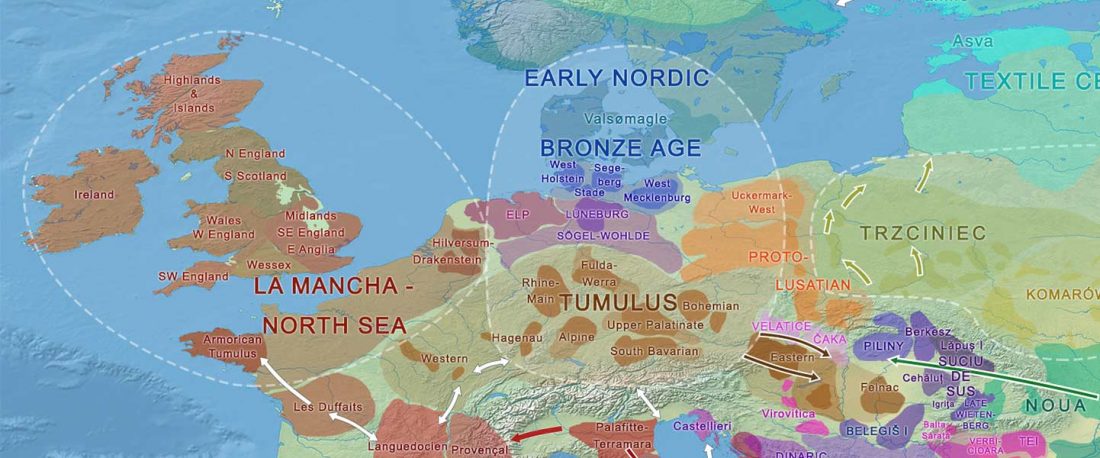
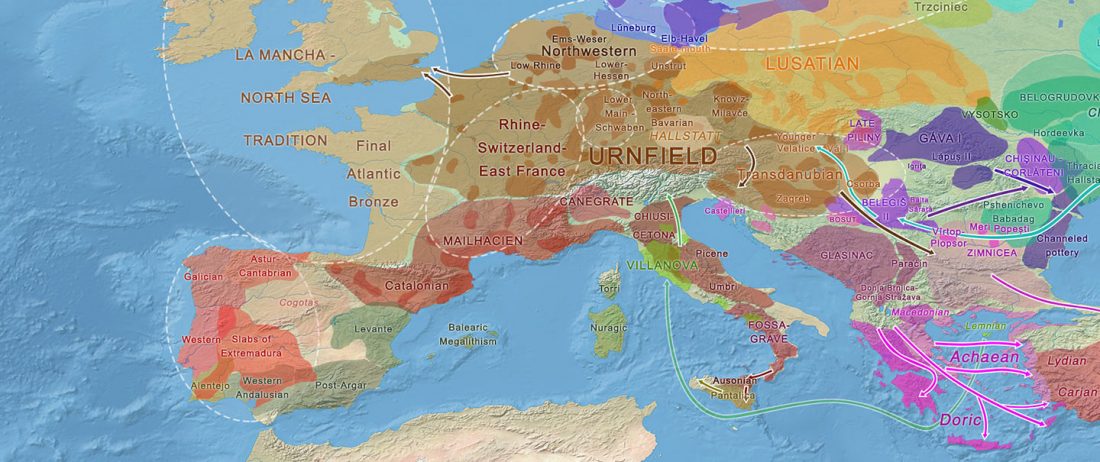
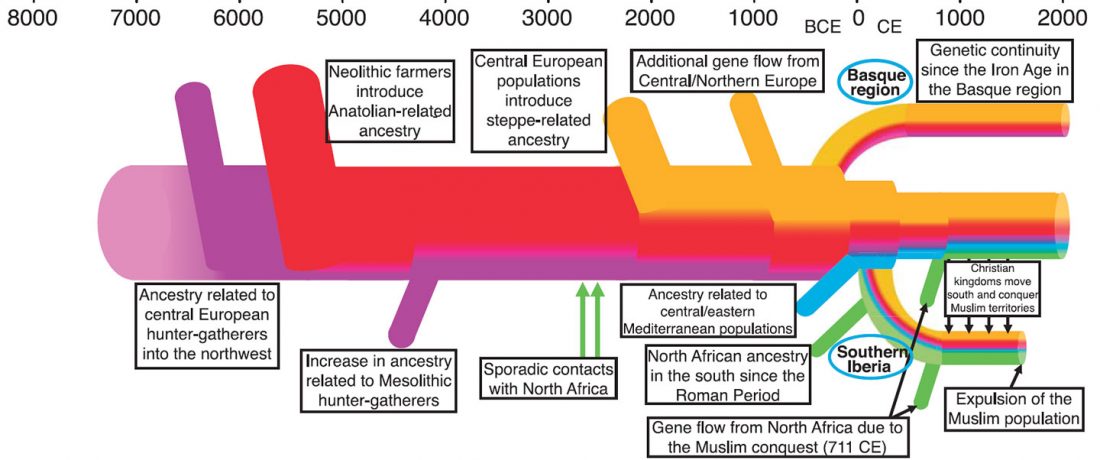
The nature of the prehistoric languages of the British Isles is particularly difficult to address: because of the lack of ancient data from certain territories; because of the traditional interpretation of Old European names simply as “Celtic”; and because Vennemann’s re-labelling of the Old European hydrotoponymy as non-Indo-European has helped distract the focus away from the real non-Indo-European substrate on the islands.
Alteuropäisch and Celtic
An interesting summary of hydronymy in the British Isles was already offered long ago, in British and European River-Names, by Kitson, Transactions of the Philological Society (1996) 94(2):73-118. In it, he discusses, among others:… Read the rest “European hydrotoponymy (VI): the British Isles and non-Indo-Europeans”