This post is part of a draft on South Siberian language homelands and Sprachbünde.
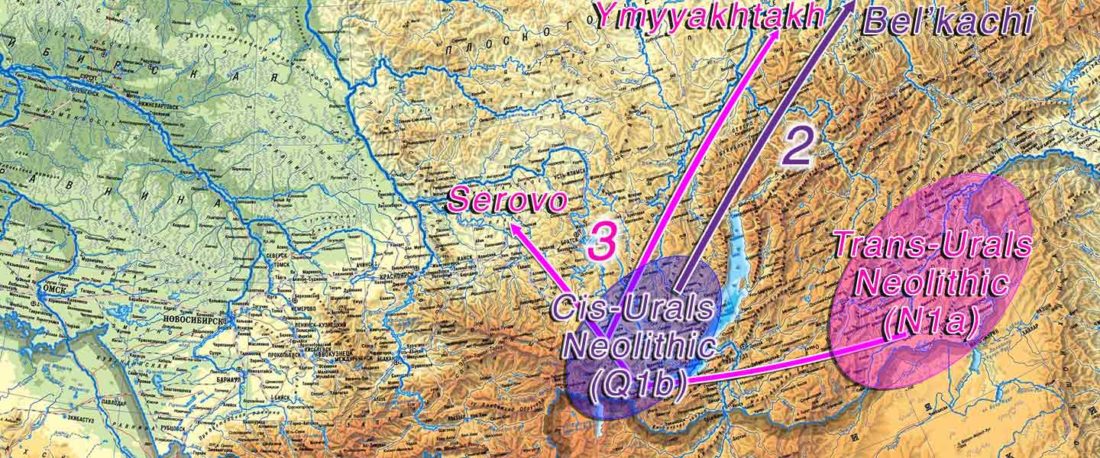
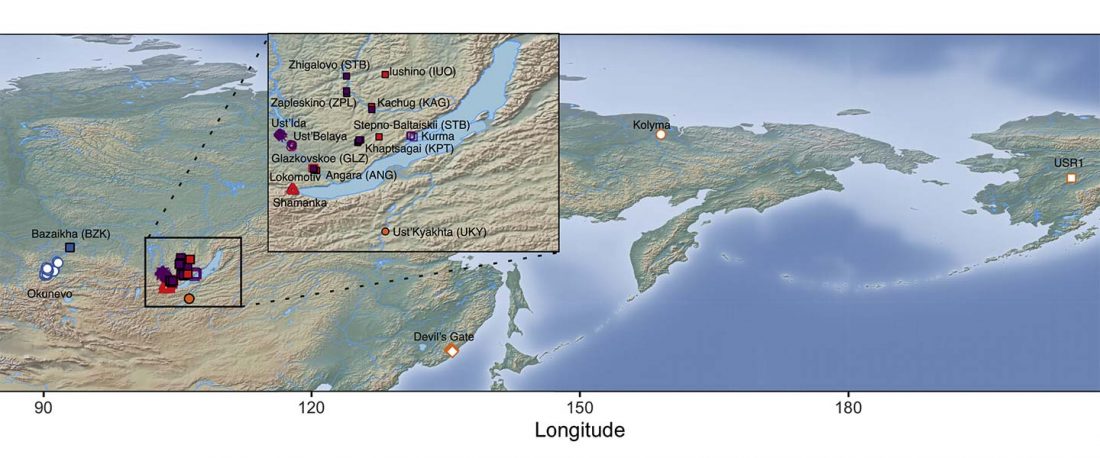
At least three major genetic changes have been described to date involving the Lena and Kolyma regions in East Siberia, and all are probably associated with some of the archaeological and linguistic developments that led to the known Early Modern distribution of languages in the Russian Far East and in Northern America.
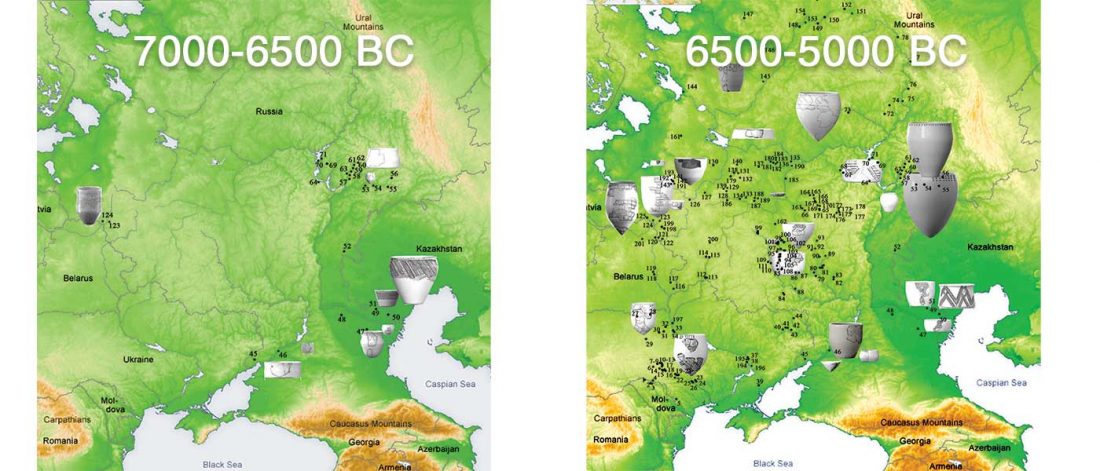
The following is a tentative description of such intertwined linguistic-archaeological-genetic developments, based on the few available data from each field. For this guesswork, first genetic-archeological results, and then plausible … Read the rest “Dene-Yeniseian, Eskimo-Aleut, and Chukotko-Kamchatkan”