The waves of disinformation are already here, putting the blame again on the European Union, as in the Financial Crisis of 2008. After years of negligent state policies promoted or tolerated by ruling political parties and social majorities of each country in the EU, which have led directly to yet another avoidable crisis. After years of state inactivity in the supranational political arena, hindering European social integration, and stripping EU institutions of any real power. The culprits are, again, not we, but they: evil and foreign hands pulling invisible strings from Brussels. The Age of Populism at its … Read the rest “Winds of change and our shared European past”
Tag: Archaeology
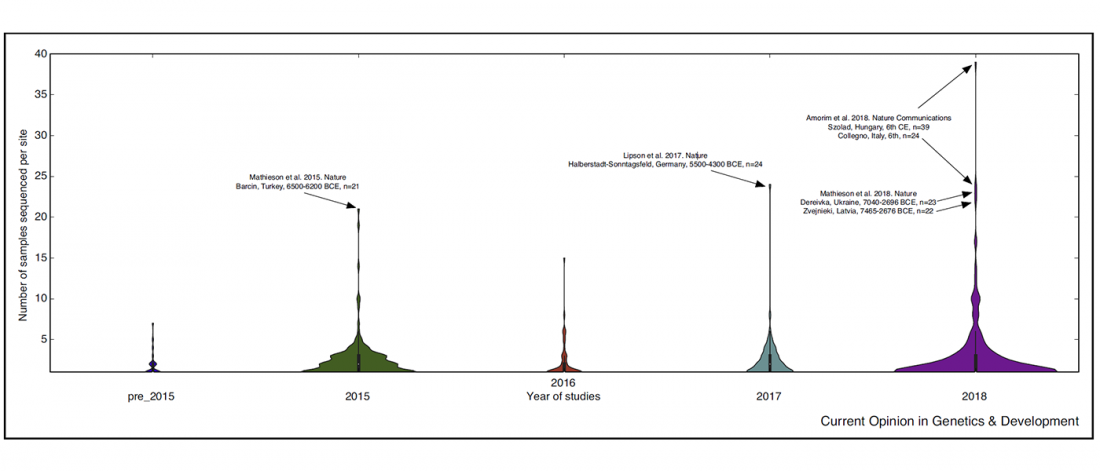
The importance of fine-scale studies for integrating palaeogenomics and archaeology
Short review (behind paywall) The importance of fine-scale studies for integrating paleogenomics and archaeology, by Krishna R. Veeramah, Current Opinion in Genetics & Development (2018) 53:83-89.
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “The importance of fine-scale studies for integrating palaeogenomics and archaeology”There has been an undercurrent of intellectual tension between geneticists studying human population history and archaeologists for almost 40 years. The rapid development of paleogenomics, with geneticists working on the very material discovered by archaeologists, appears to have recently heightened this tension. The relationship between these two fields thus far has largely been of a multidisciplinary nature, with archaeologists providing the raw materials for sequencing, as well as a scaffold
On applications of space-time modelling with 14C age calibration
Open access On Applications of Space–Time Modelling with Open-Source 14C Age Calibration, by T. Rowan McLaughlin J Archaeol Method Theory (2018).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “On applications of space-time modelling with 14C age calibration”In archaeology, the meta-analysis of scientific dating information plays an ever-increasing role. A common thread among many recent studies contributing to this has been the development of bespoke software for summarizing and synthesizing data, identifying significant patterns therein. These are reviewed in this paper, which also contains open-source scripts for calibrating radiocarbon dates and modelling them in space and time, using the R computer language and GRASS GIS. The case studies that undertake new analysis
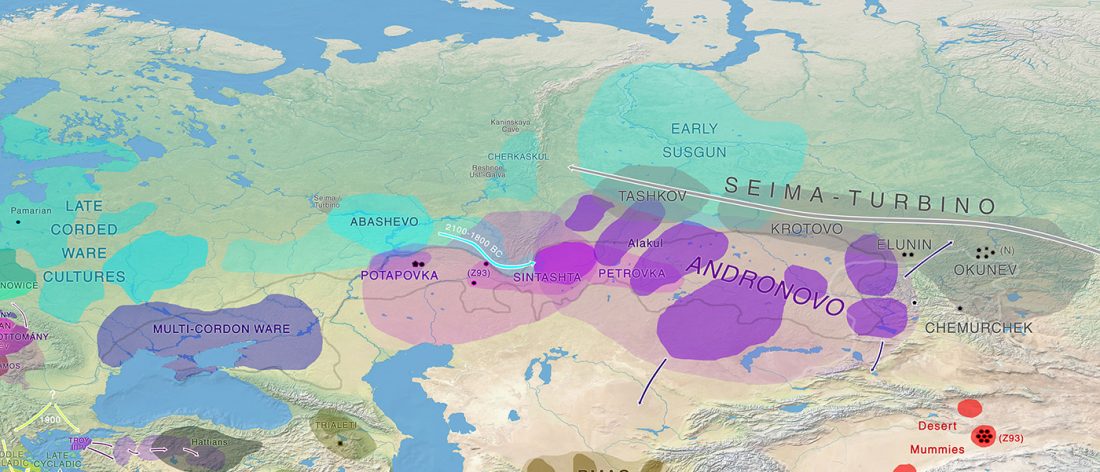
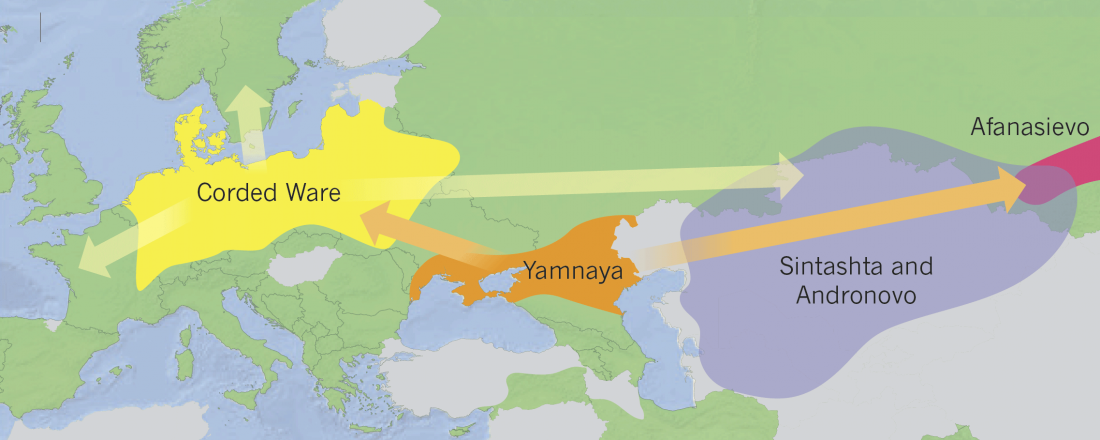
Sintashta-Petrovka and Potapovka cultures, and the cause of the Steppe EMBA – MLBA differences
Interesting recent papers on Sintashta and related Volga-Ural MLBA communities, with relevant excerpts (emphasis mine):
Social Organization of the Sintashta-Petrovka Groups of the Late Bronze Age and a Cause for Origin of Social Elites (Based on Materials of the Settlement of Kamenny Ambar), by Chechushkov et al. Stratum Plus (2018) Nº2.
Abstract (official, in English):
… Read the rest “Sintashta-Petrovka and Potapovka cultures, and the cause of the Steppe EMBA – MLBA differences”The formation of social complexity often unfolded in non-unilineal ways in those regions of the world where the surplus product remained low enough to support institutionalized power and state bureaucracy. The Bronze Age of Northern Eurasia is a vivid example where social complexity arose
The uneasy relationship between Archaeology and Ancient Genomics
News feature Divided by DNA: The uneasy relationship between archaeology and ancient genomics, Two fields in the midst of a technological revolution are struggling to reconcile their views of the past, by Ewen Callaway, Nature (2018) 555:573-576.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “The uneasy relationship between Archaeology and Ancient Genomics”In duelling 2015 Nature papers6,7, the teams arrived at broadly similar conclusions: an influx of herders from the grassland steppes of present-day Russia and Ukraine — linked to Yamnaya cultural artefacts and practices such as pit burial mounds — had replaced much of the gene pool of central and Western Europe around
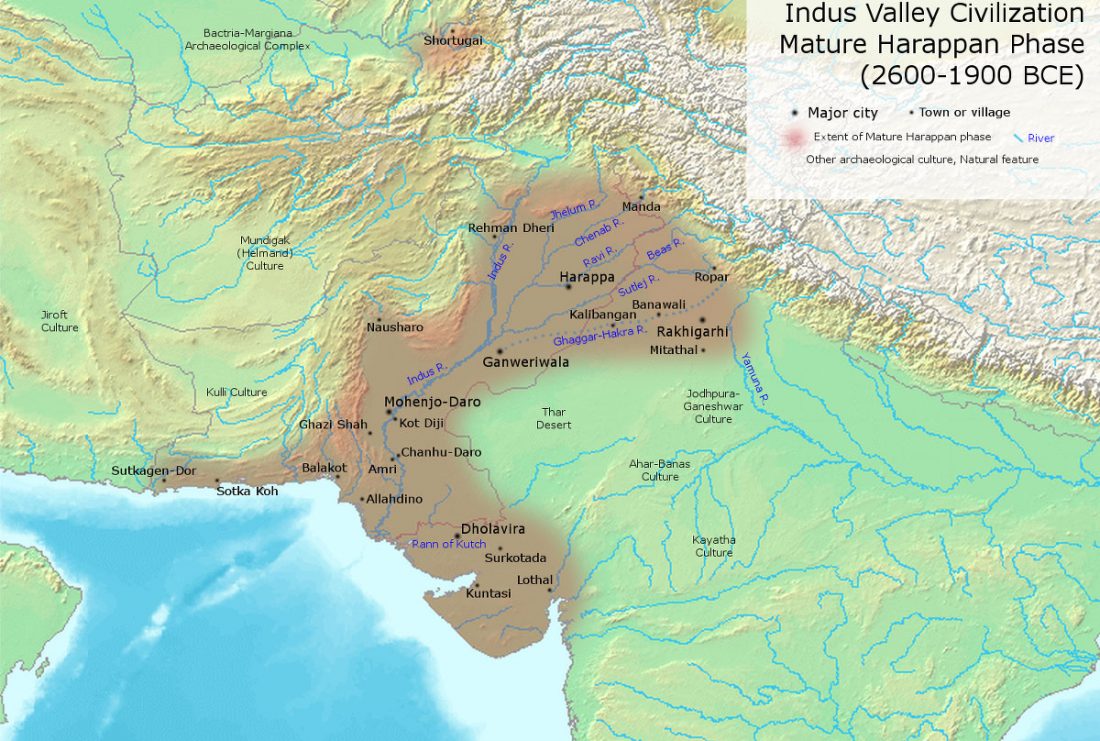
Archaeological and anthropological studies on the Harappan cemetery of Rakhigarhi, India
New open access paper Archaeological and anthropological studies on the Harappan cemetery of Rakhigarhi, India, by Shinde, Kim, Wo, et al. PLOS One (2018) 13(2): e0192299.
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Archaeological and anthropological studies on the Harappan cemetery of Rakhigarhi, India”An insufficient number of archaeological surveys has been carried out to date on Harappan Civilization cemeteries. One case in point is the necropolis at Rakhigarhi site (Haryana, India), one of the largest cities of the Harappan Civilization, where most burials within the cemetery remained uninvestigated. Over the course of the past three seasons (2013 to 2016), we therefore conducted excavations in an attempt to remedy this data shortfall. In brief, we found
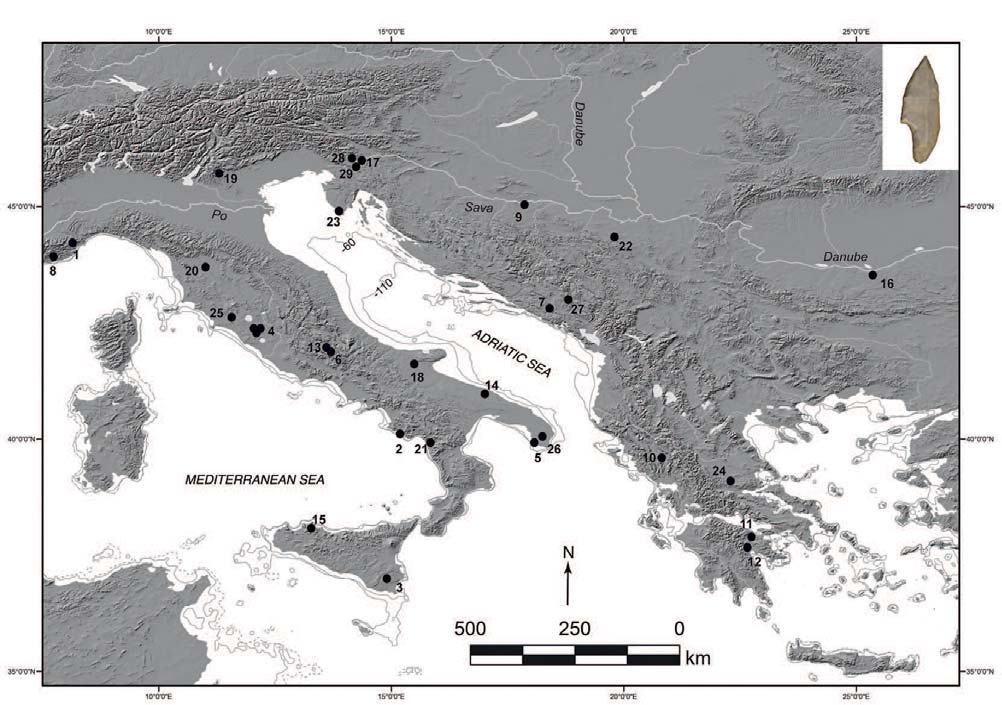
Palaeolithic and Mesolithic connections between Italy and the Balkans, and the potential expansion of the Villabruna cluster and haplogroup R1b in Europe
My speculative bet on the arrival of haplogroup R1b to Europe (and the expansion of R1b-V88 to Africa through southern Italy) was based initially entirely on genomic (especially phylogeographic) finds, but judging by data on the latest papers on south-eastern Europe it seems to have been the right choice.
Archaeological information on these prehistoric periods is scarce – compared to more recent times -, and anthropological models of migration are therefore speculative. Some information on the potential periods for its expansion are contained in the chapter Social Networks and Connectivity among the Palaeolithic and Mesolithic Foragers of the … Read the rest “Palaeolithic and Mesolithic connections between Italy and the Balkans, and the potential expansion of the Villabruna cluster and haplogroup R1b in Europe”
Science and Archaeology (Humanities): collaboration or confrontation?
Another discussion on the role of Science for Archaeology, in The Two Cultures and a World Apart: Archaeology and Science at a New Crossroads, by Tim Flohr Sørensen, Norwegian Archaeological Review, vol. 50, 2 (2017):
… Read the rest “Science and Archaeology (Humanities): collaboration or confrontation?”Within the past decade or so, archaeology has increasingly utilised and contributed to major advances in scientific methods when exploring the past. This progress is frequently celebrated as a quantum leap in the possibilities for understanding the archaeological record, opening up hitherto inaccessible dimensions of the past. This article represents a critique of the current consumption of science in archaeology, arguing that the discipline’s
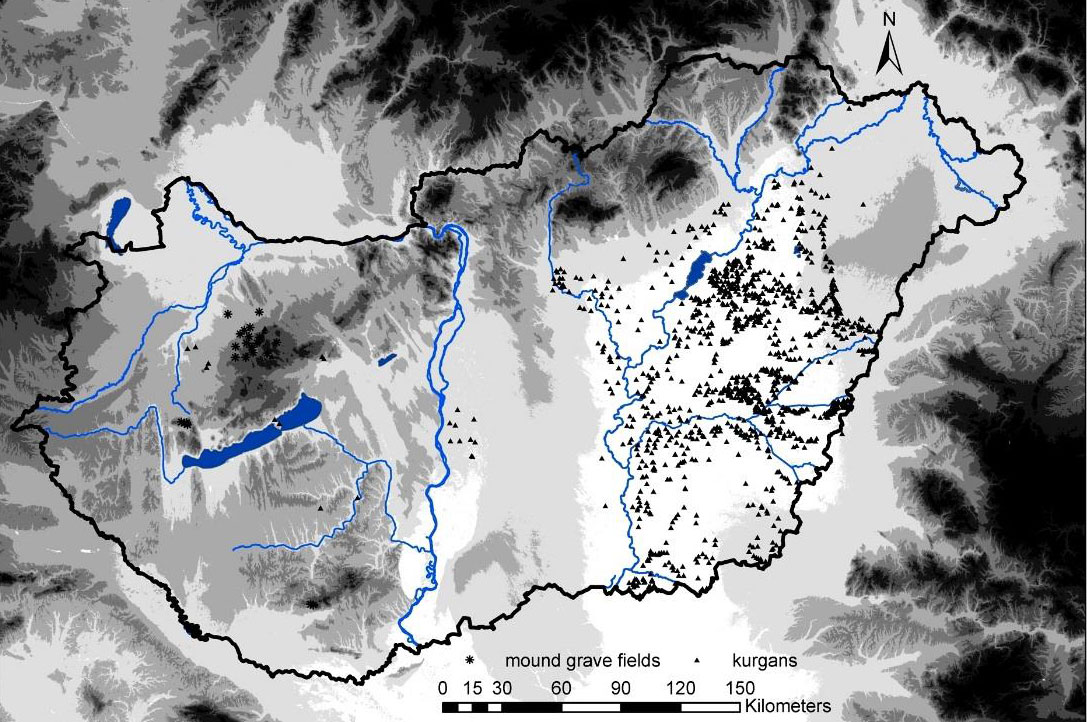
The Great Hungarian Plain in a time of change in the Balkans – Neolithic, Chalcolithic, and Bronze Age
I wrote recently about Anthony’s new model of Corded Ware culture expansion from Yamna settlements of Hungary. I am extremely sceptic about it in terms of current genetic finds, and suspicious of the real reasons behind it – probably misinterpretations of the so-called ‘Yamnaya ancestral component’ in recent genetic papers, rather than archaeological finds.
Nevertheless, it means a definitive rejection by Anthony of:
- The multiple patron-client relationships he proposed to justify a cultural diffusion of Late Indo-European dialects from Yamna into different Corded Ware cultures in the forest-steppe and Forest Zone (see one of his latest summaries of the