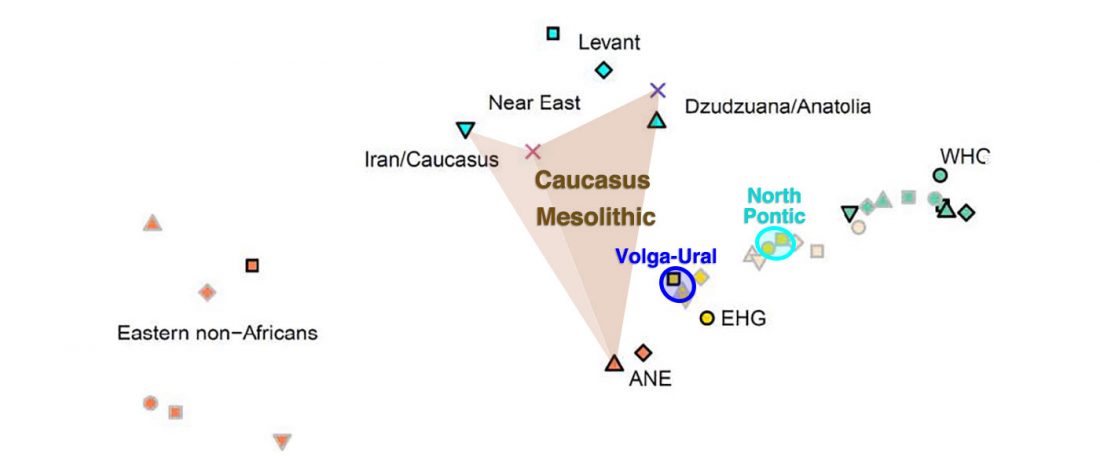
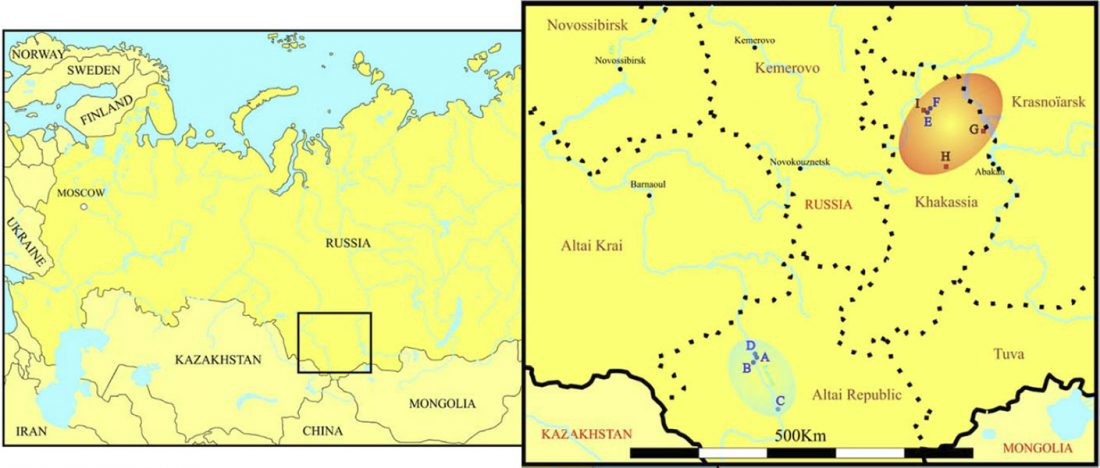
Interesting recent developments:
Celts and hg. R1b
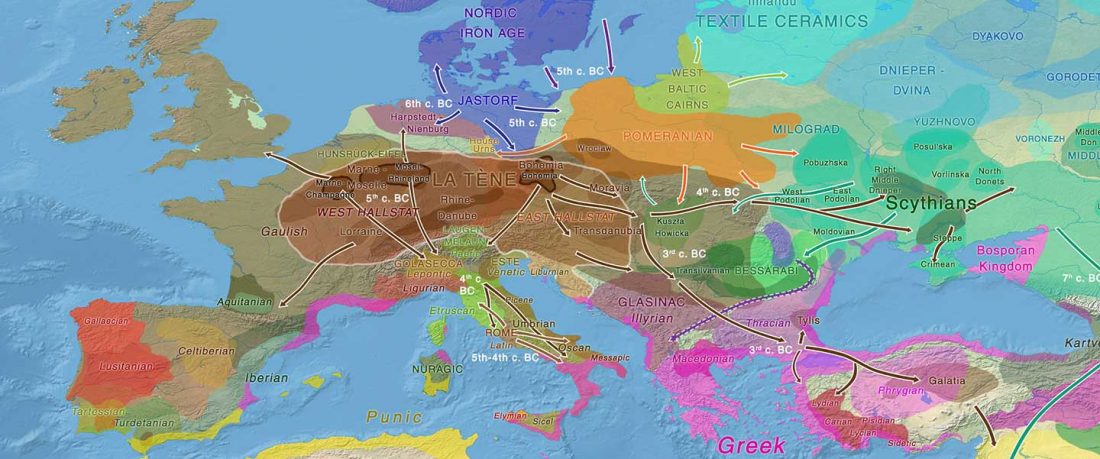
Gauls
Recent paper (behind paywall) Multi-scale archaeogenetic study of two French Iron Age communities: From internal social- to broad-scale population dynamics, by Fischer et al. J Archaeol Sci (2019).
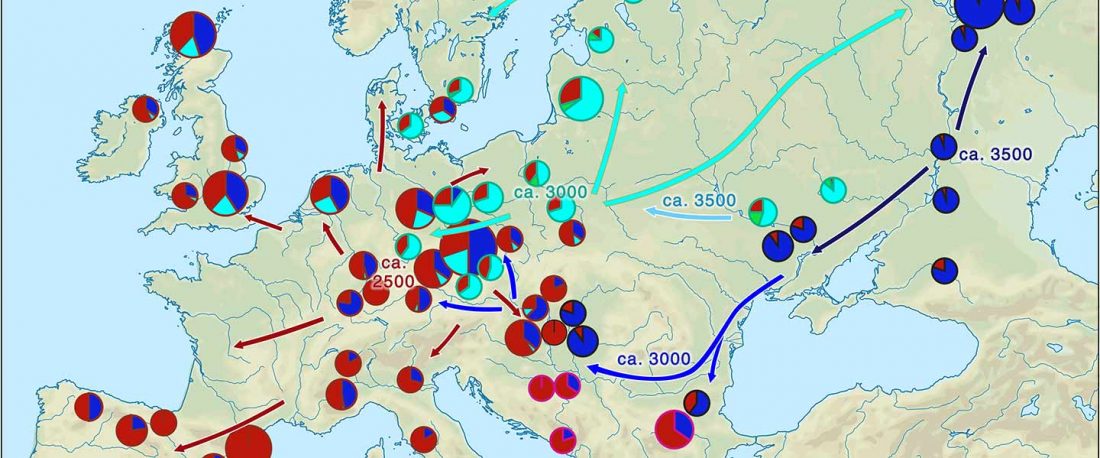
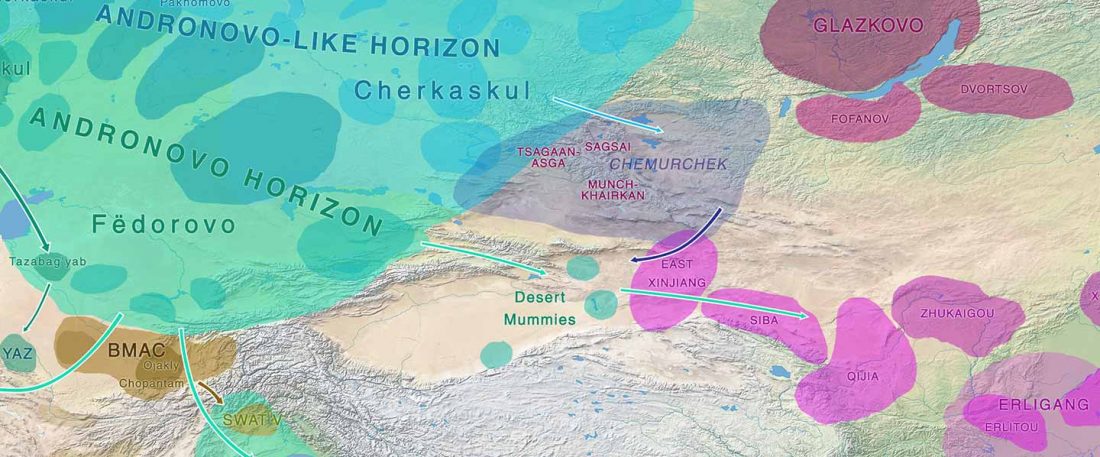
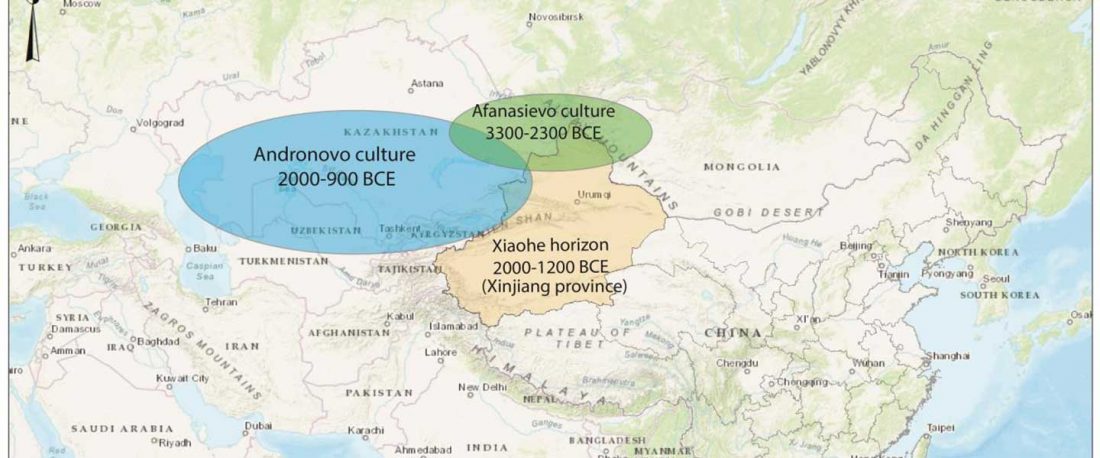
In it, Fischer and colleagues update their previous data for the Y-DNA of Gauls from the Urville-Nacqueville necropolis, Normandy (ca. 300-100 BC), with 8 samples of hg. R, at least 5 of them R1b. They also report new data from the Gallic cemetery at Gurgy ‘Les Noisats’, Southern Paris Basin (ca. 120-80 BC), with 19 samples of hg. R, at least 13 of … Read the rest “More Celts of hg. R1b, more Afanasievo ancestry, more maps”