Open access paper Mobility and Social Change: Understanding the European Neolithic Period after the Archaeogenetic Revolution, by Martin Furholt, J. Archaeol. Res. (2021).
Content under CC-BY license. Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine, stylistic changes for clarity):
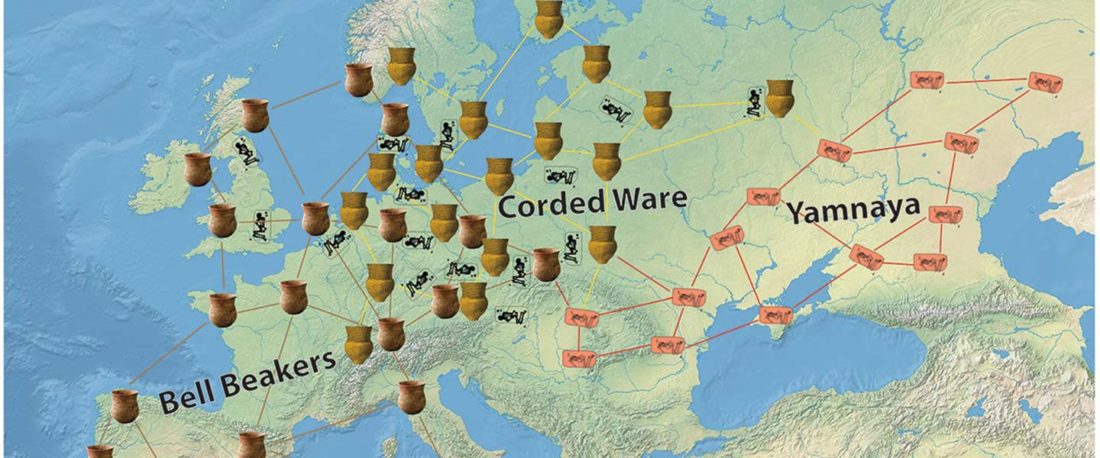
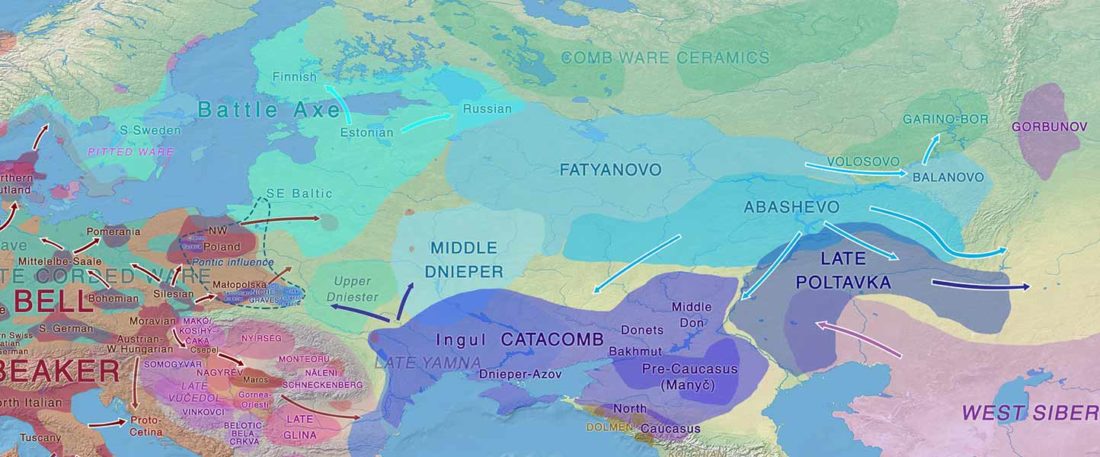
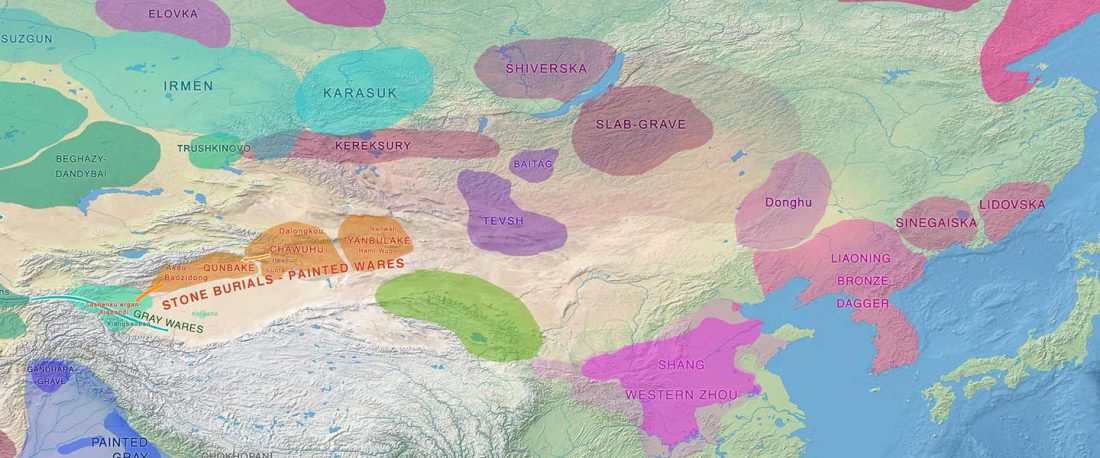
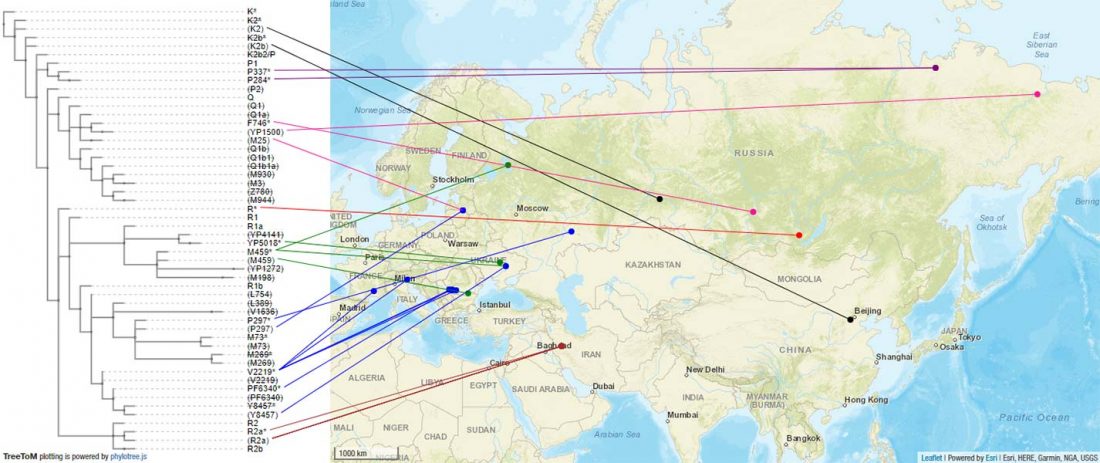
… Read the rest “The complexities of 3rd millennium Steppe-related migrations”This detailed picture of Caucasian population history shows that the initial assertion in the 2015 papers, namely of a one-way migration from east to west, was a simplification supported by a variant of admixture analyses that featured Yamnaya as one unified genetic element (e.g., Haak et al. 2015, fig. 3), which led to calculations of Corded Ware individuals showing 75% Yamnaya ancestry. This