Brexit forces relocation of one of today’s main Yamna research projects to Finland
Archaeologist Volker Heyd is bringing his ERC Advanced Grant to Helsinki. So has proudly reported the University of Helskinki.
Some interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
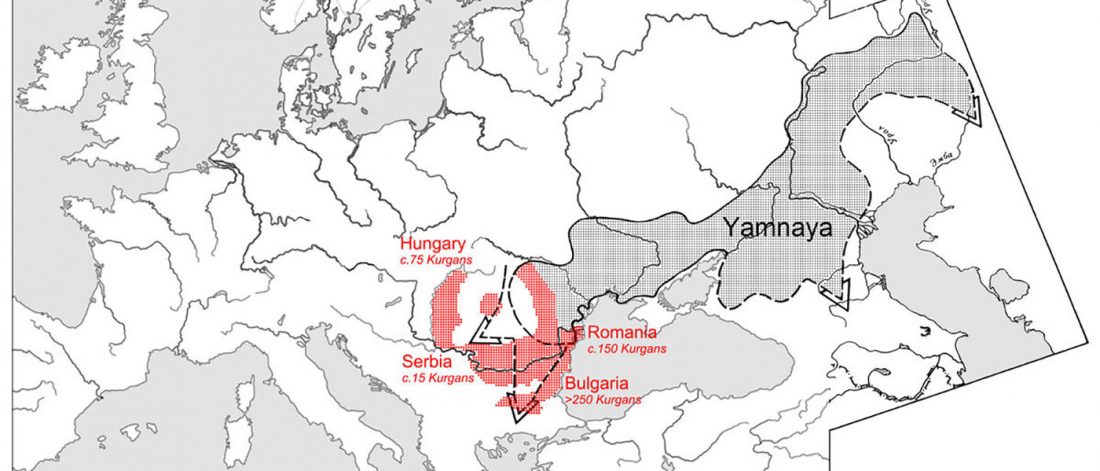
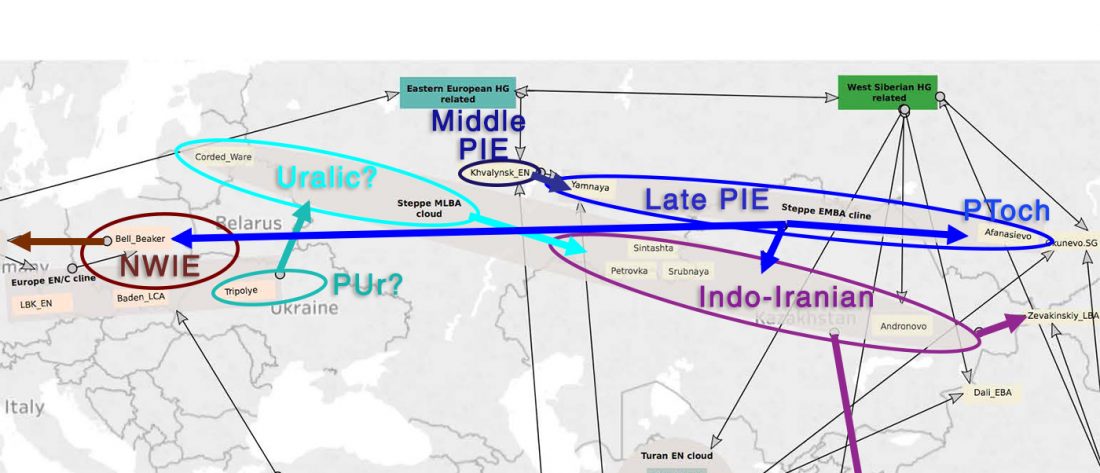
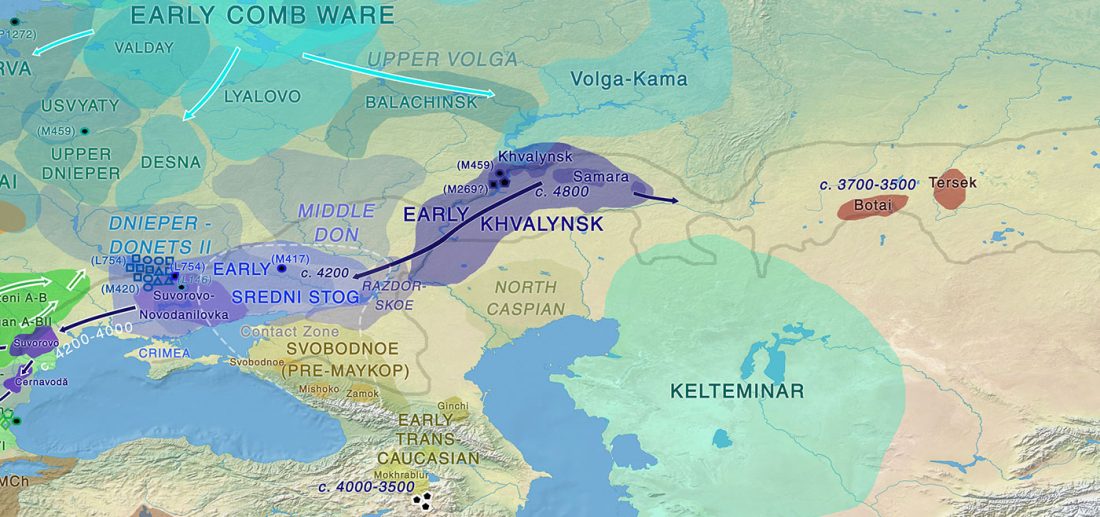
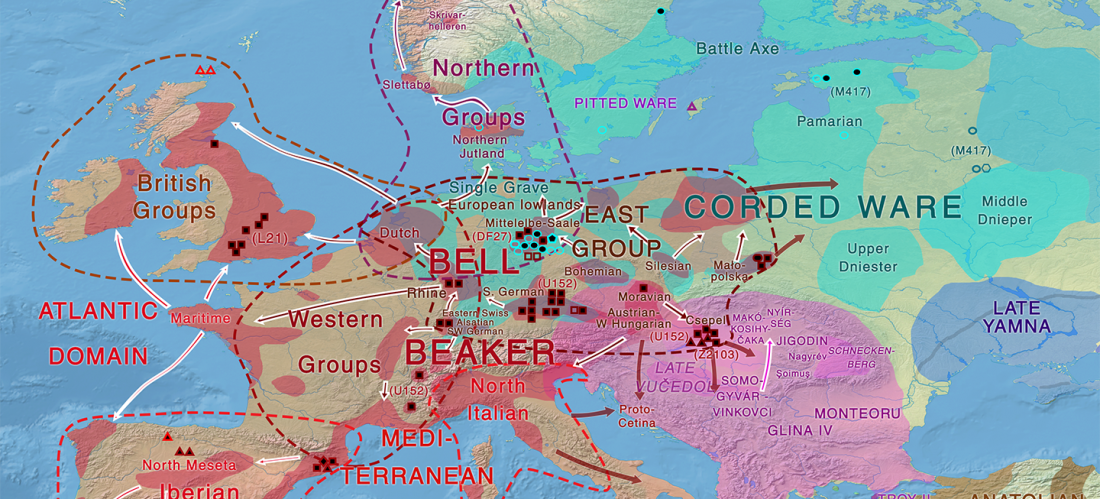
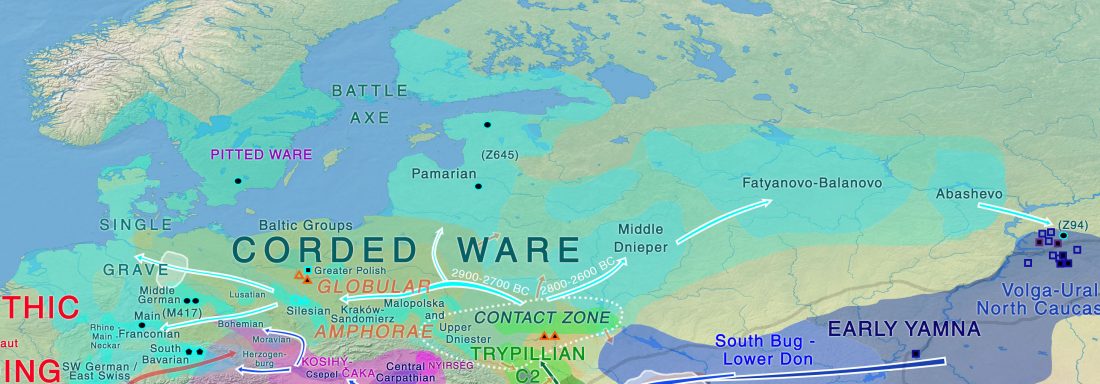
… Read the rest “Brexit forces relocation of one of today’s main Yamna research projects to Finland”With his research group, Heyd wants to map out how the Yamnaya culture, also known as the Pit Grave culture, migrated from the Eurasian steppes to prehistoric south-eastern Europe approximately 3,000 years BCE. Most of the burial mounds typical of the Yamnaya culture have already been destroyed, but new techniques enable their identification and study.
The project is using multidisciplinary methods to solve the mystery. Archaeologists are collaborating with scholars of biological and environmental