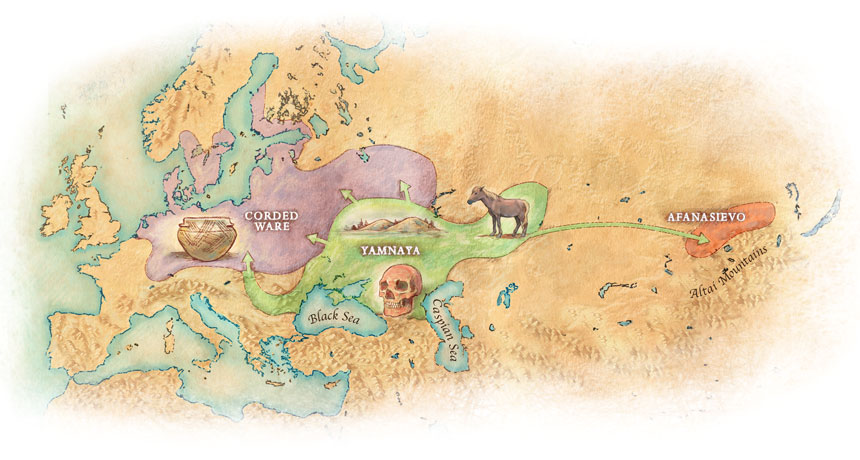
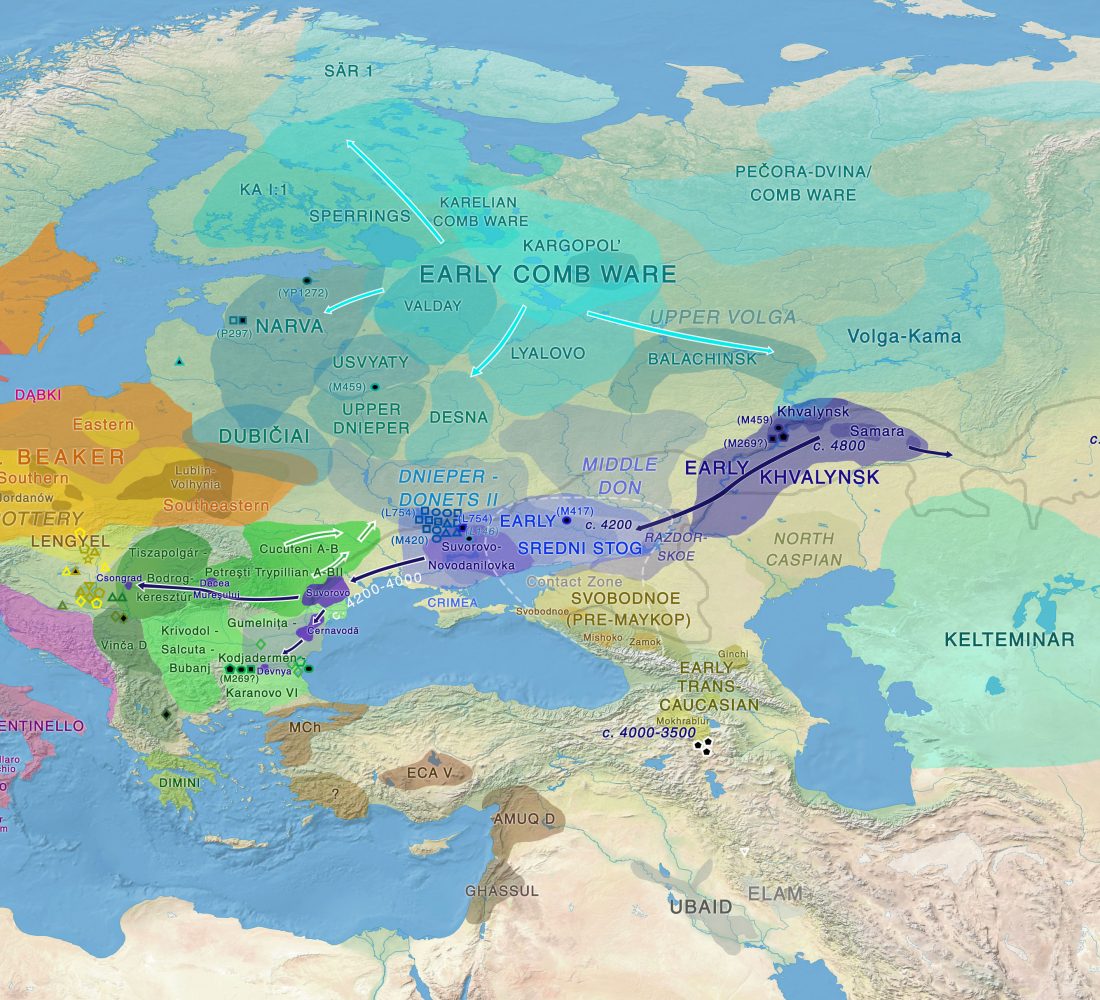
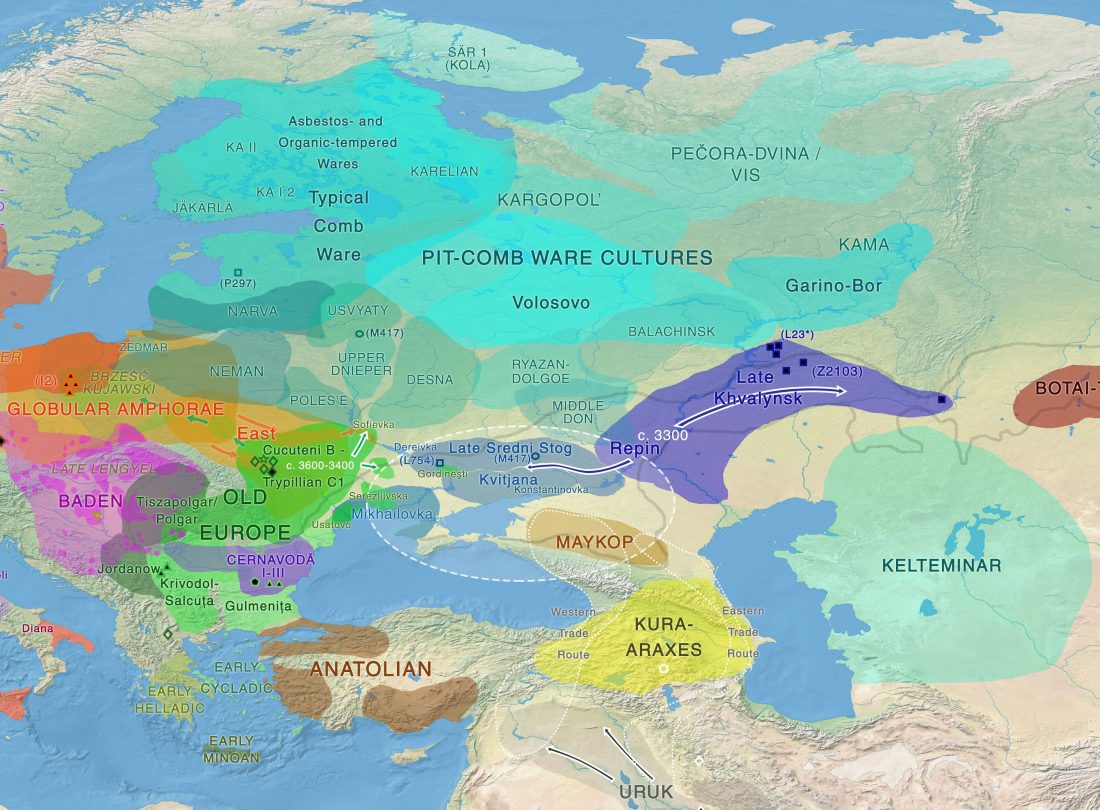
The concept of “Outlier” in Human Ancestry (III): Late Neolithic samples from the Baltic region and origins of the Corded Ware culture
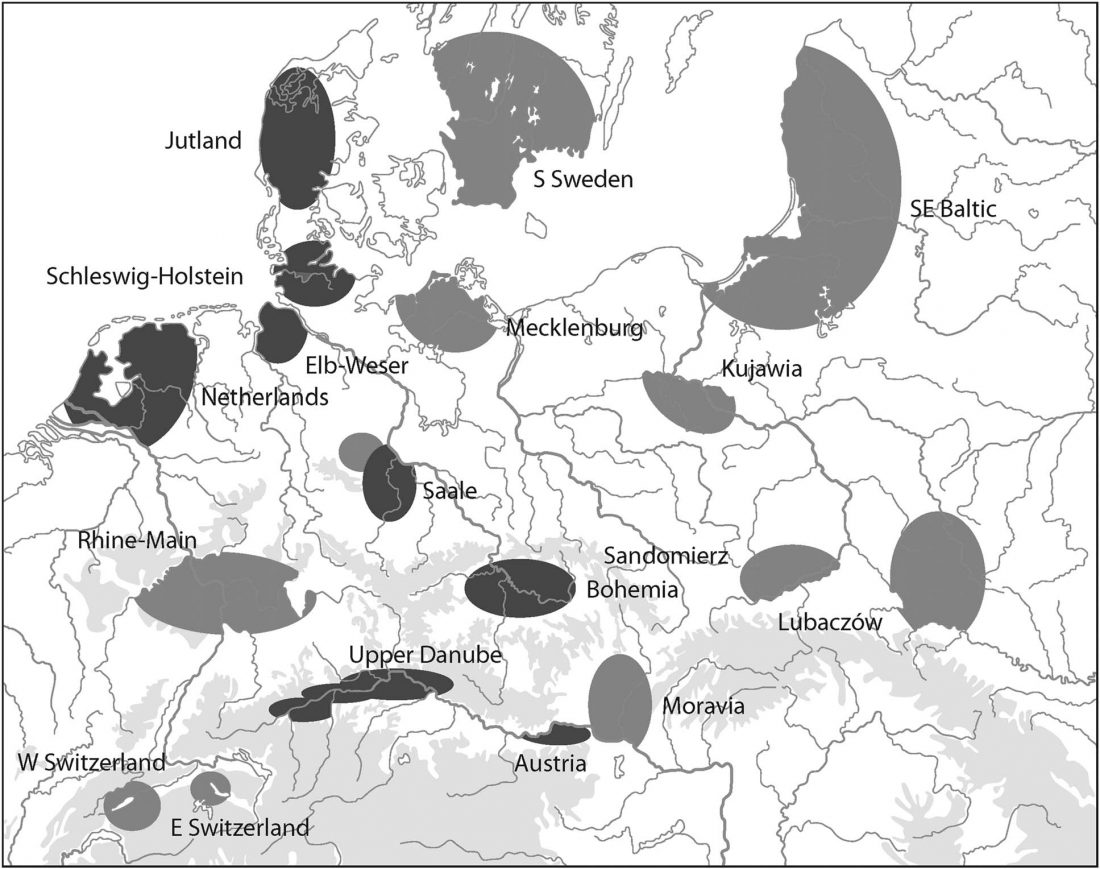
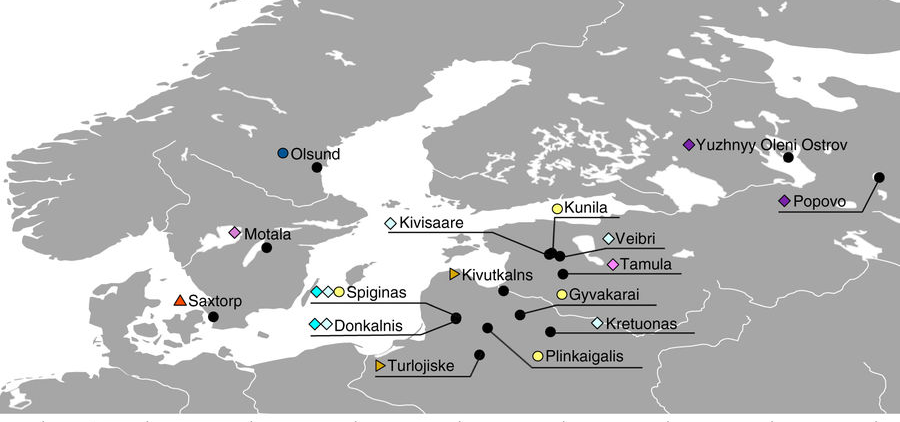
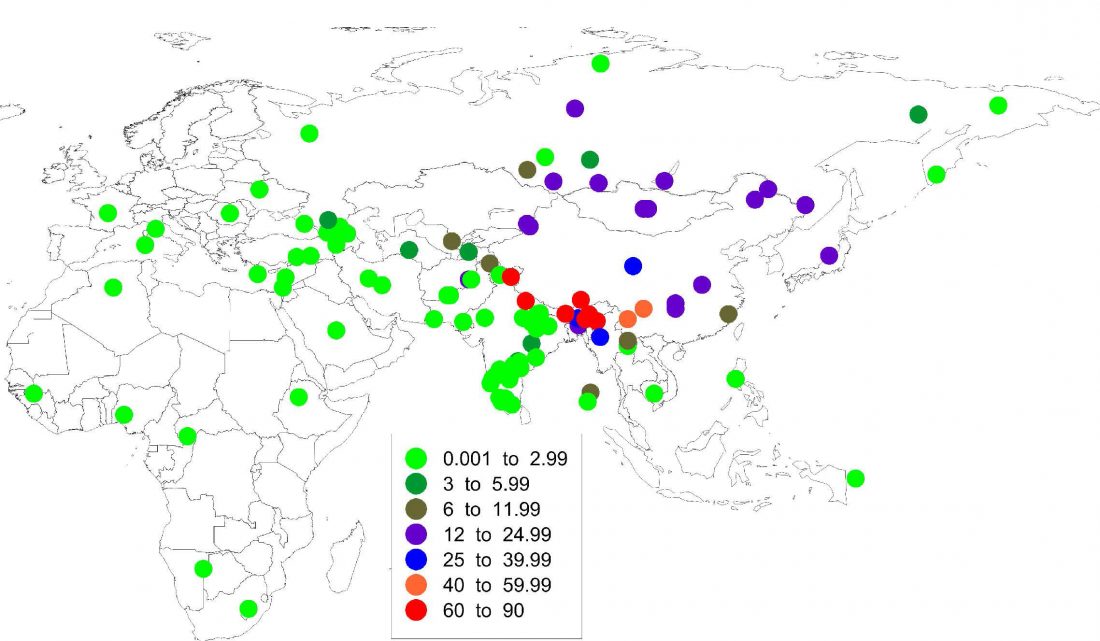
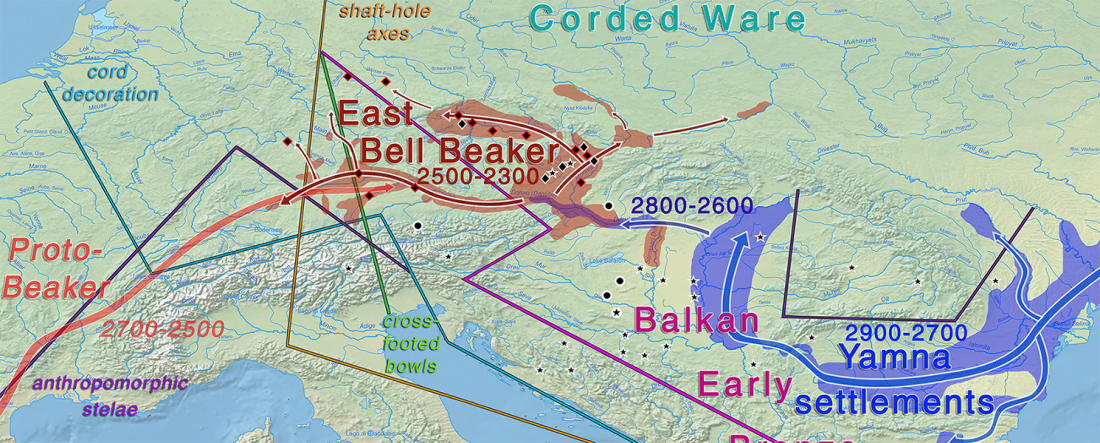
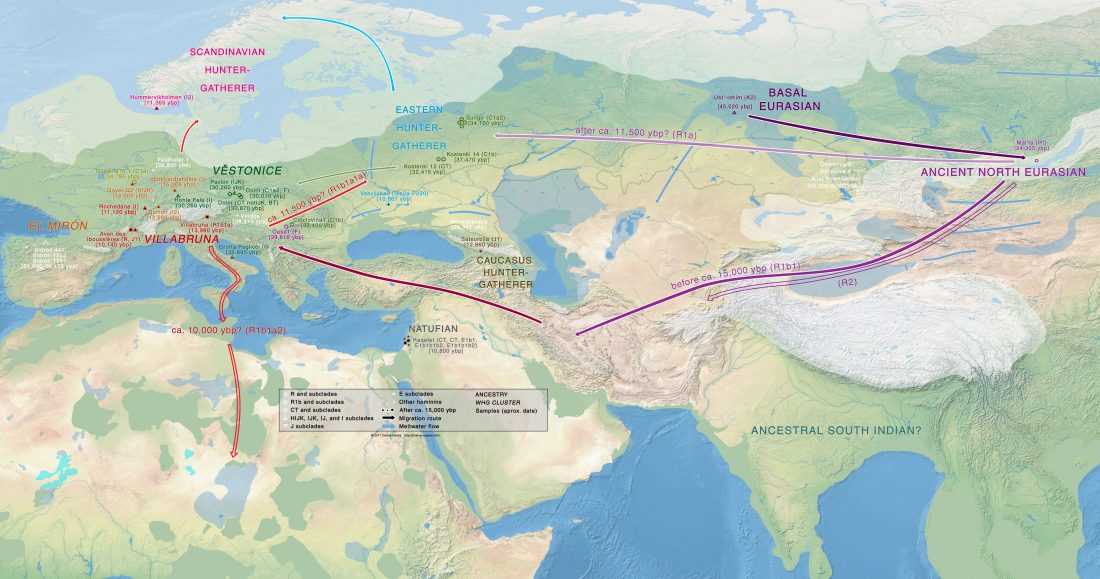
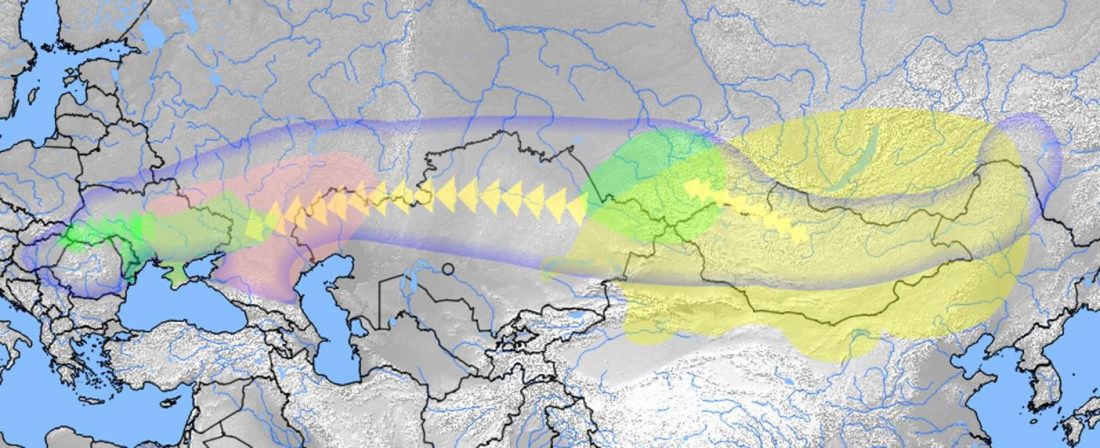
I have written before about how the Late Neolithic sample from Zvejnieki seemed to be an outlier among Corded Ware samples (read also the Admixture analysis section on the IEDDM), due to its position in PCA, even more than its admixture components or statistical comparison might show.
In the recent update to Northern European samples in Mittnik et al. (2018), an evaluation of events similar to the previous preprint (2017) is given:
… Read the rest “The concept of “Outlier” in Human Ancestry (III): Late Neolithic samples from the Baltic region and origins of the Corded Ware culture”Computing D-statistics for each individual of the form D(Baltic LN, Yamnaya; X, Mbuti), we find that the two individuals from the early phase of the