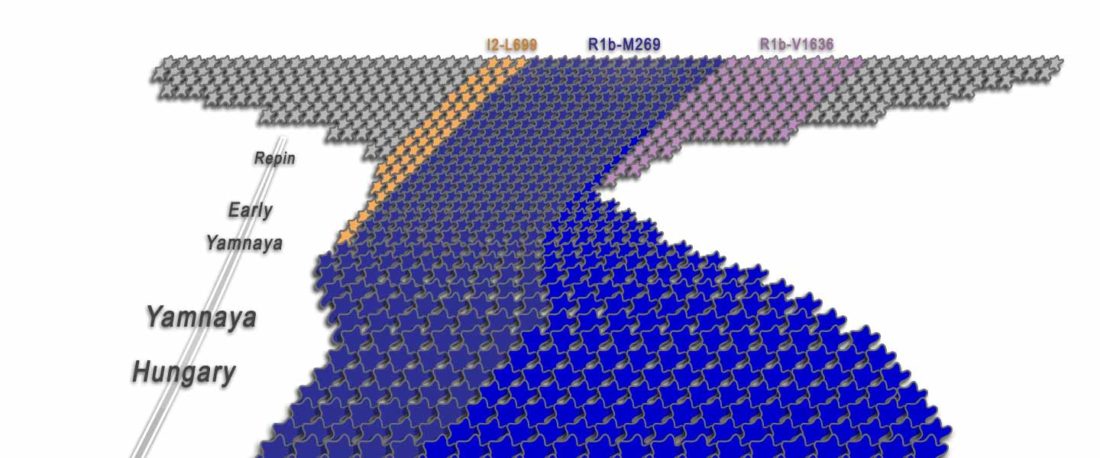
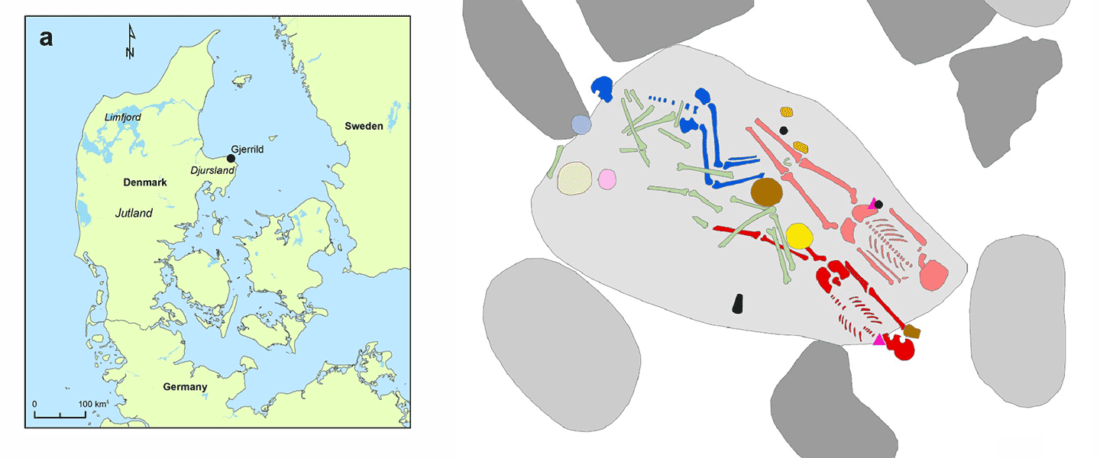
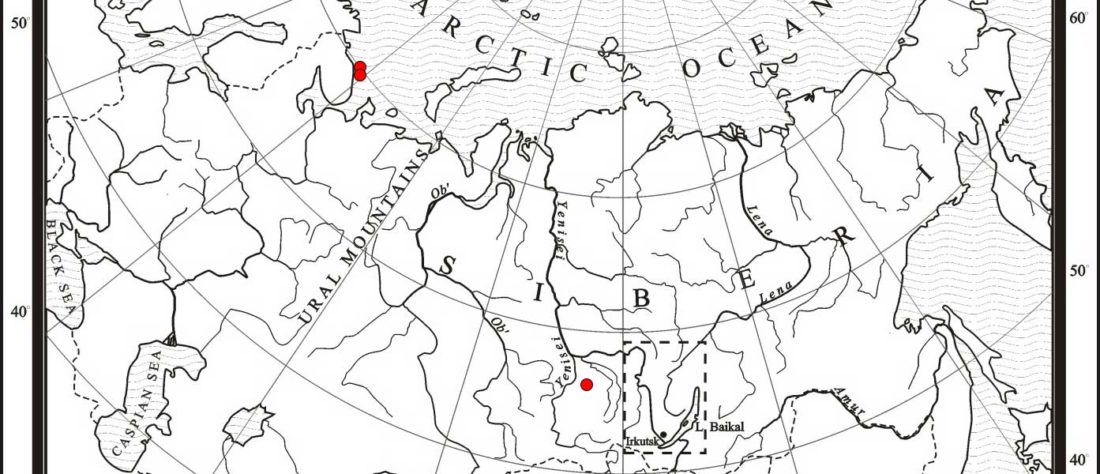
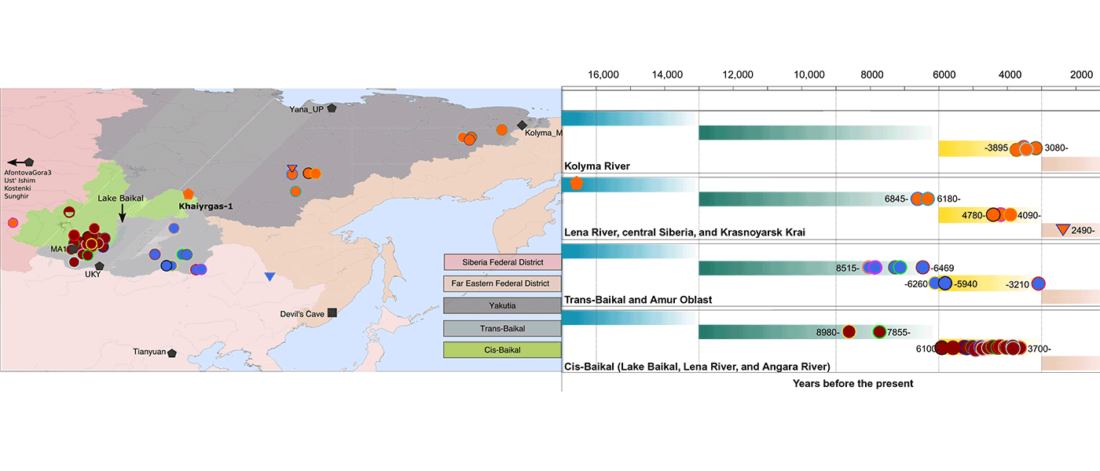
Proto-Indo-Europeans: A family business
I have been updating the Ancient DNA Dataset with date estimates published in the recent preprint by Sedig, Olalde, Patterson & Reich bioRxiv (2020), and it had a reference to some interesting new samples from Khvalynsk, showing tight family connections.
Information below is taken from the preprint and from the latest version of the Reich Lab’s Allen Ancient DNA Resource (AADR). Information about the three published Khvalynsk samples is taken from Mathieson et al. Nature (2015) supplementary materials, and each ID features a different font color in the text below for clarity’s sake.
Khvalynsk Family A
I0434, … Read the rest “Proto-Indo-Europeans: A family business”