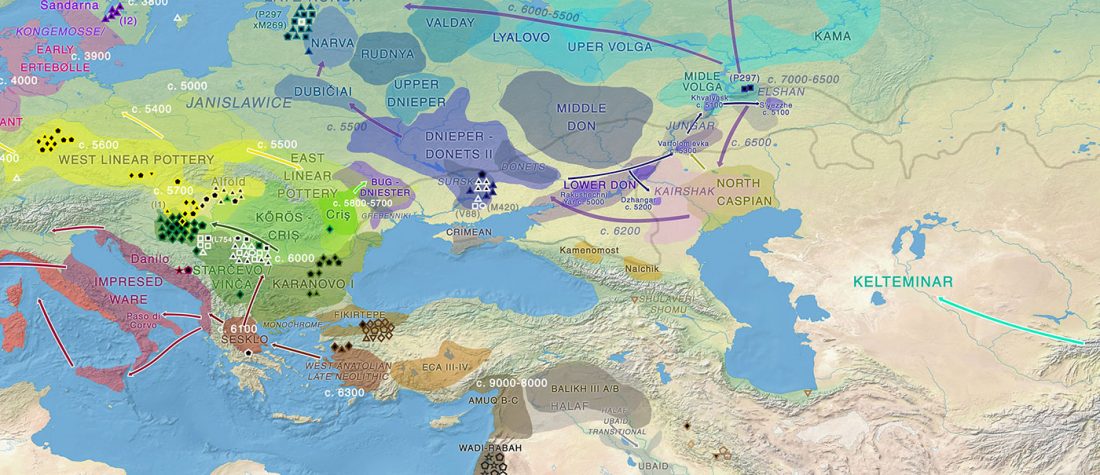
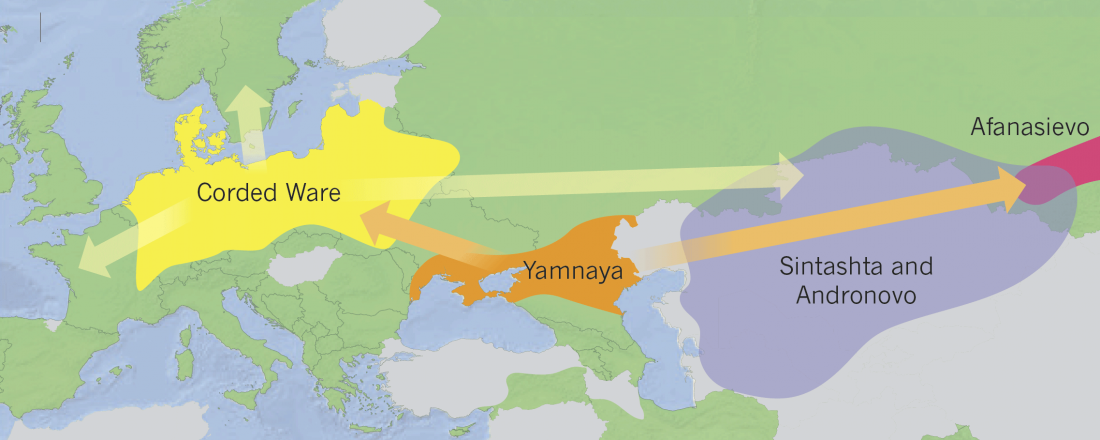
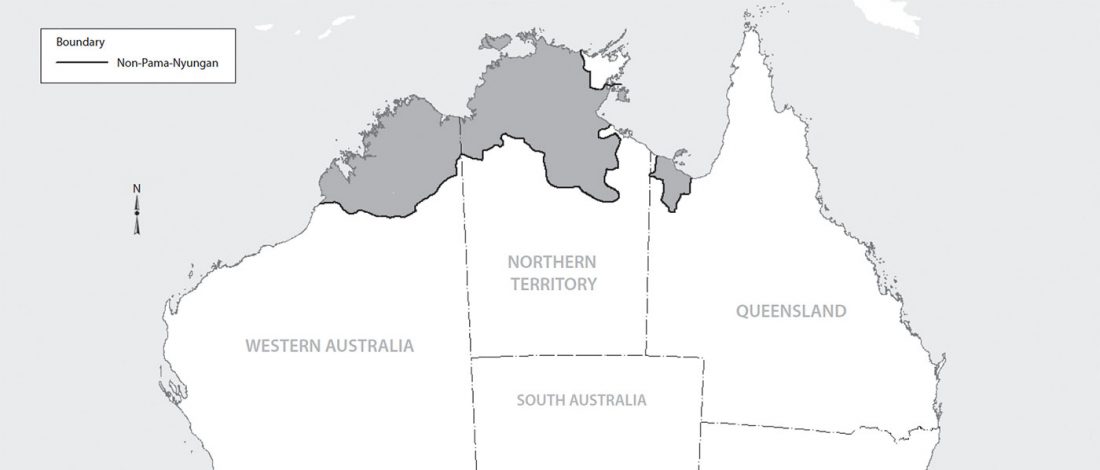
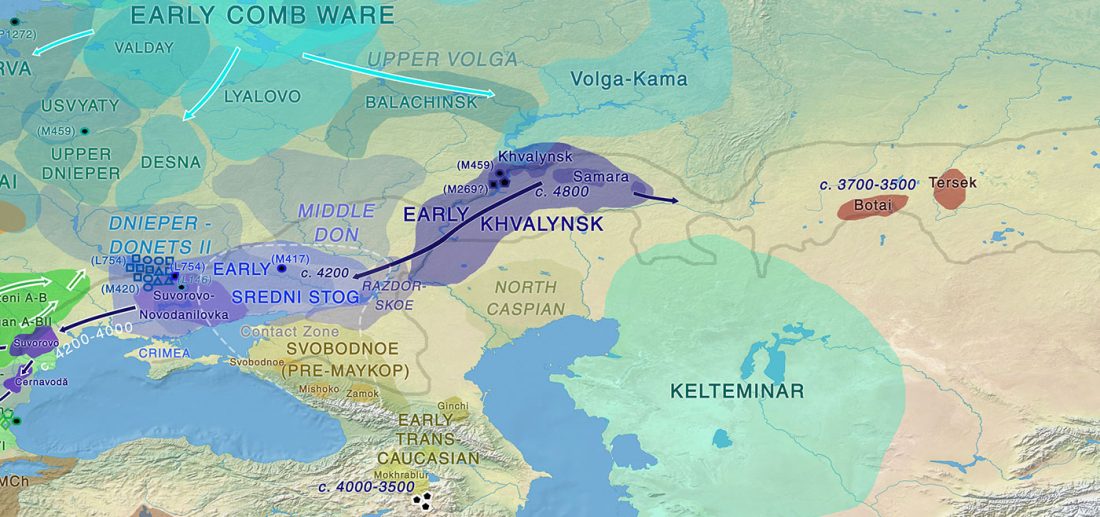
Proto-Indo-European homeland south of the Caucasus?
User Camulogène Rix at Anthrogenica posted an interesting excerpt of Reich’s new book in a thread on ancient DNA studies in the news (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Proto-Indo-European homeland south of the Caucasus?”Ancient DNA available from this time in Anatolia shows no evidence of steppe ancestry similar to that in the Yamnaya (although the evidence here is circumstantial as no ancient DNA from the Hittites themselves has yet been published). This suggests to me that the most likely location of the population that first spoke an Indo-European language was south of the Caucasus Mountains, perhaps in present-day Iran or Armenia, because ancient DNA from people who