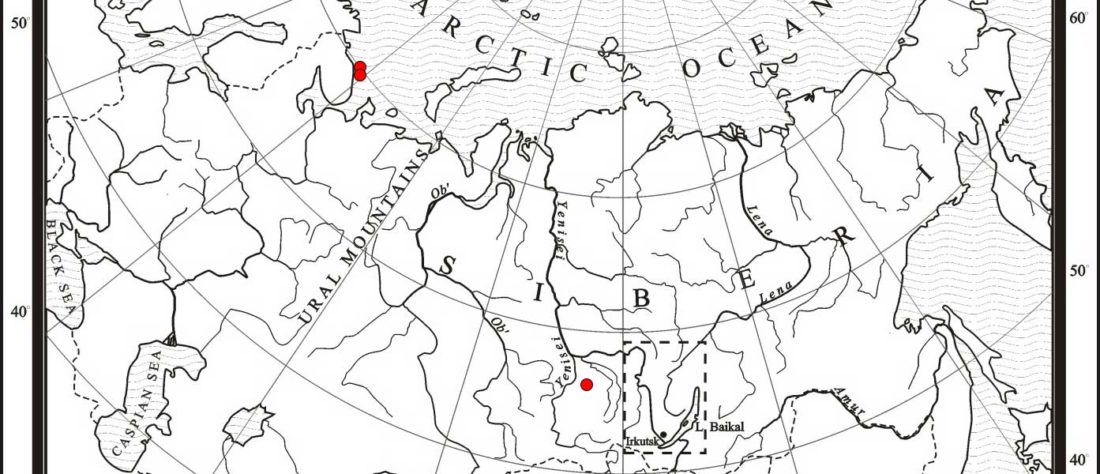
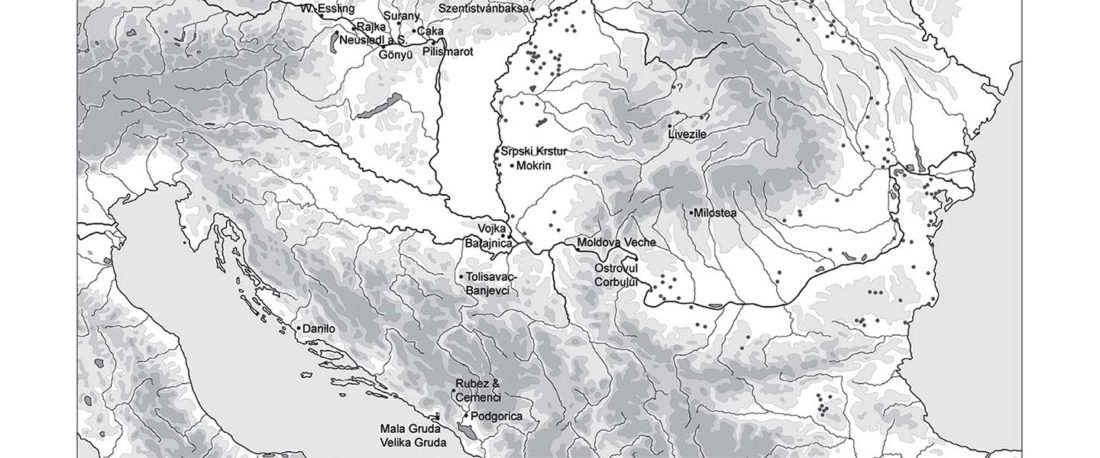
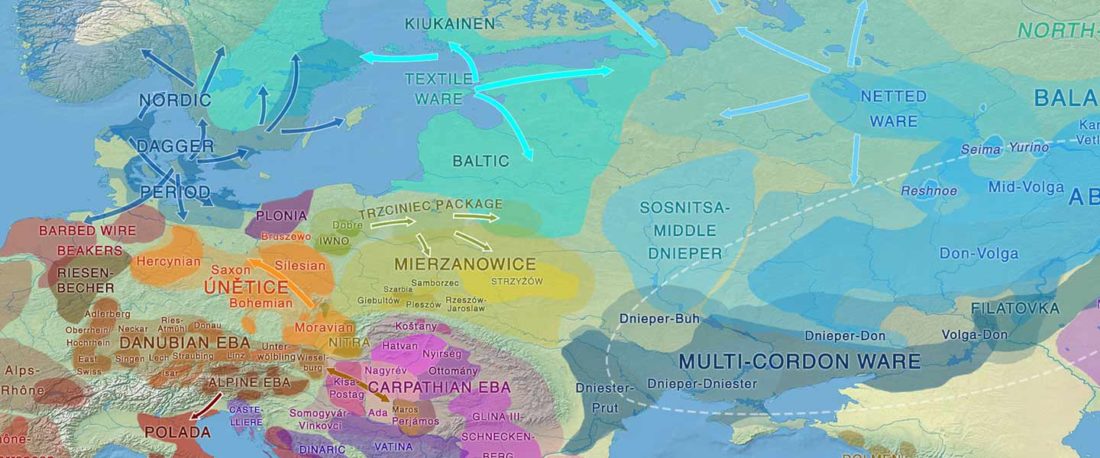
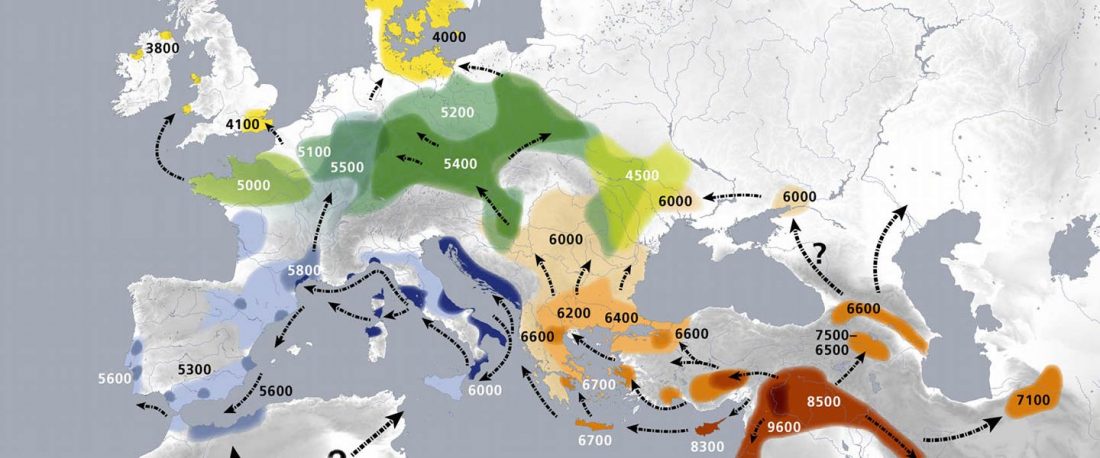
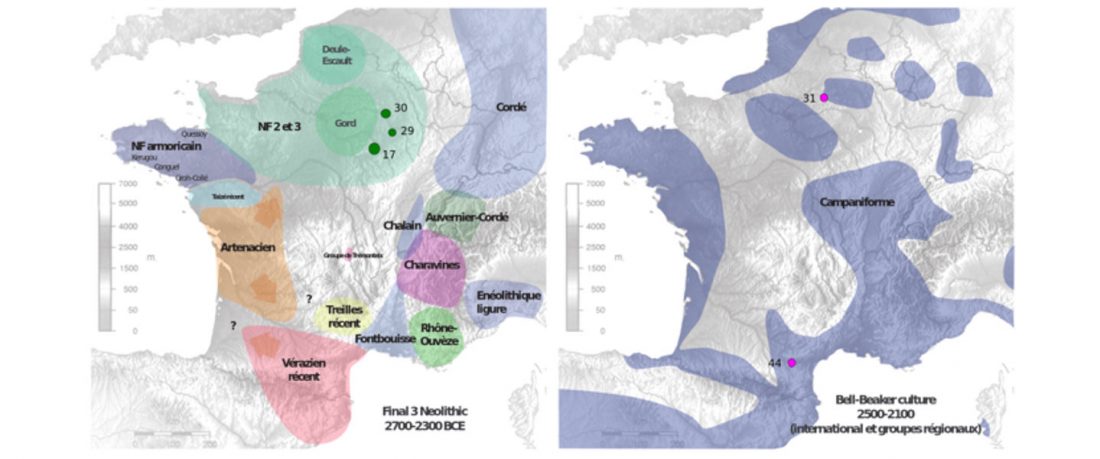
Earliest (and basal) haplogroup N-L1026, from East Siberia
This is an update to the data from Human population dynamics and Yersinia pestis in ancient northeast Asia, by Kılınç et al. Science Advances (2021).
Files have been released, and some of them are huge, so it might take me some time to analyze them all and include specific subclades in the Ancient DNA Dataset.
For the moment, the sample I highlighted in the previous post, kra001 (2336-2135 calBCE), mtDNA C4b1, from burial Nº1 of Nefteprovod-2, is of very good quality, and it would not be surprising if it made its way to YFull’s tree. It can be … Read the rest “Earliest (and basal) haplogroup N-L1026, from East Siberia”