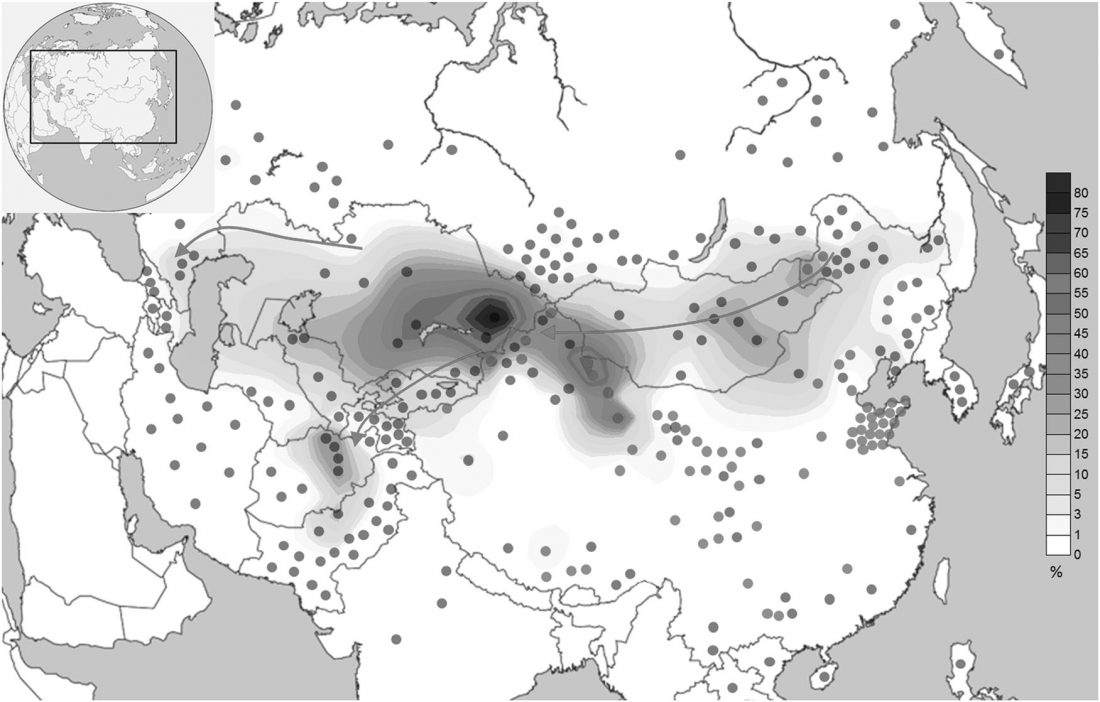
Ancient DNA upends the horse family tree
New paper, behind paywall, Ancient genomes revisit the ancestry of domestic and Przewalski’s horses, by Gaunitz et al., Science (2018)
Abstract:
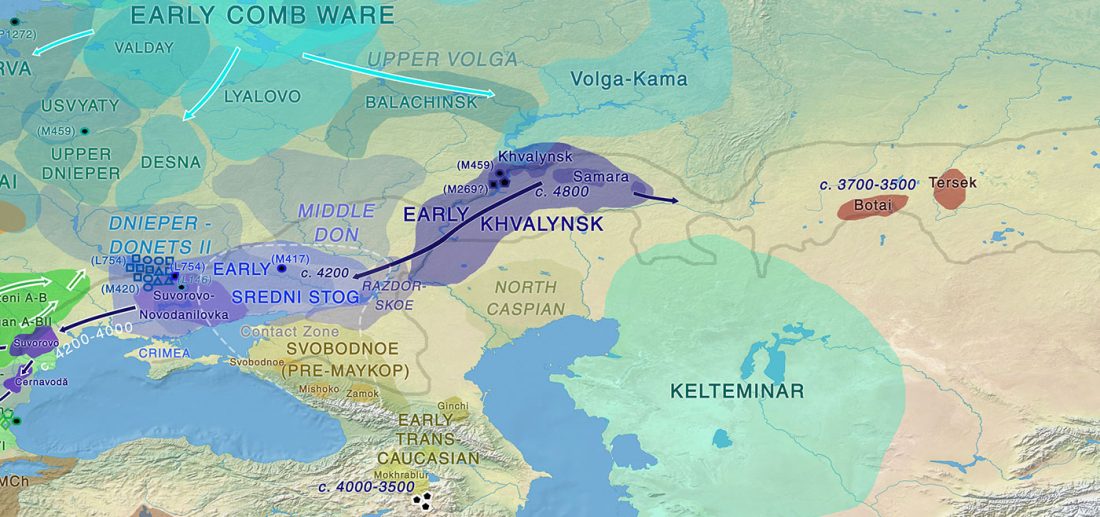
… Read the rest “Ancient DNA upends the horse family tree”The Eneolithic Botai culture of the Central Asian steppes provides the earliest archaeological evidence for horse husbandry, ~5,500 ya, but the exact nature of early horse domestication remains controversial. We generated 42 ancient horse genomes, including 20 from Botai. Compared to 46 published ancient and modern horse genomes, our data indicate that Przewalski’s horses are the feral descendants of horses herded at Botai and not truly wild horses. All domestic horses dated from ~4,000 ya to present only