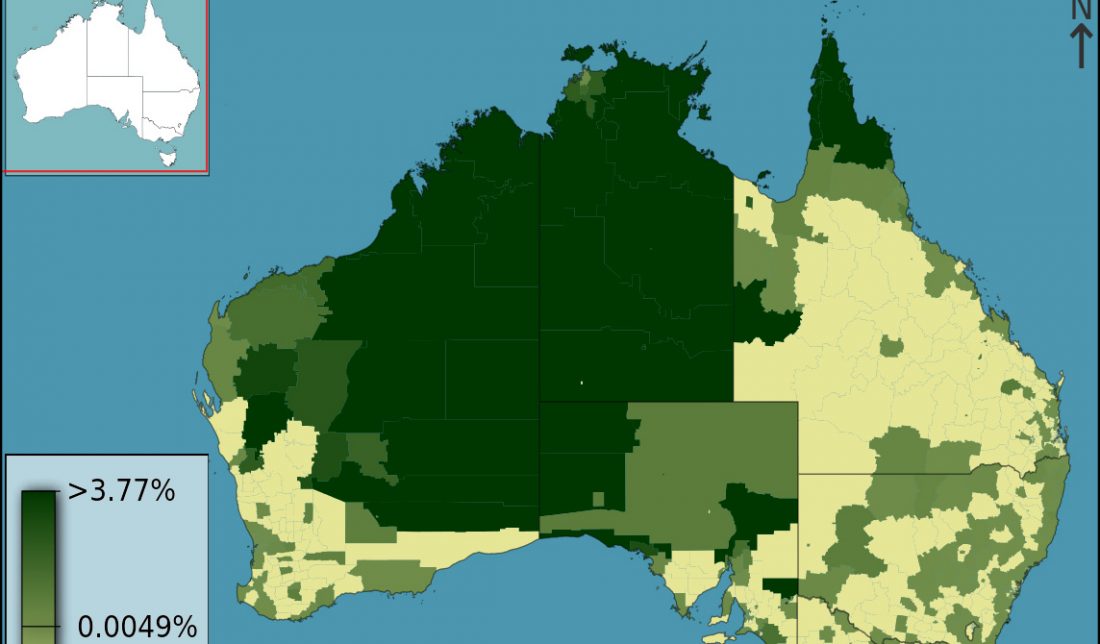
The origin and expansion of Pama–Nyungan languages across Australia
Yet another questionable paper by Nature, The origin and expansion of Pama–Nyungan languages across Australia, by Bouckaert, Bowern & Atkinson, Nat Ecol Evol (2018).
Abstract:
… Read the rest “The origin and expansion of Pama–Nyungan languages across Australia”It remains a mystery how Pama–Nyungan, the world’s largest hunter-gatherer language family, came to dominate the Australian continent. Some argue that social or technological advantages allowed rapid language replacement from the Gulf Plains region during the mid-Holocene. Others have proposed expansions from refugia linked to climatic changes after the last ice age or, more controversially, during the initial colonization of Australia. Here, we combine basic vocabulary data from 306 Pama–Nyungan languages with Bayesian phylogeographic