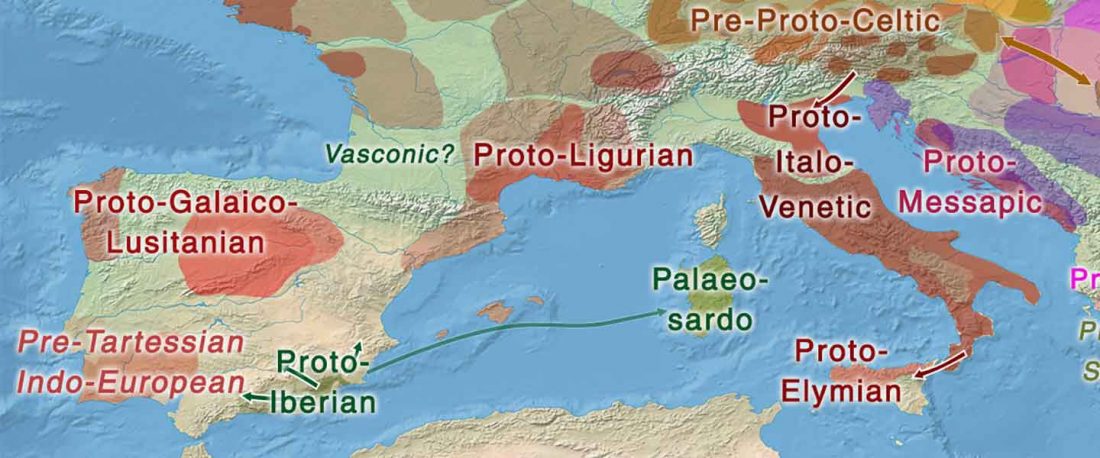
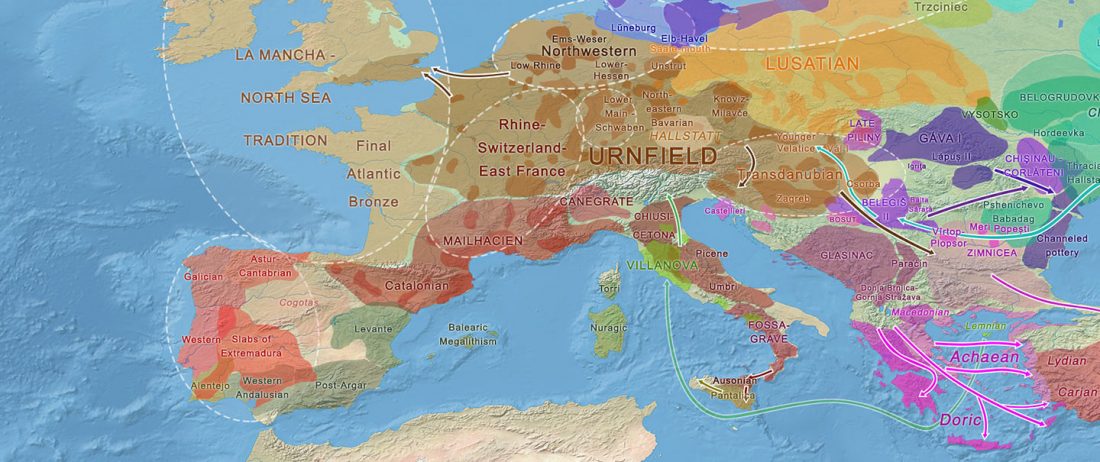
The first layer in hydrotoponymy of Iberia is clearly Indo-European, in territories that were occupied by Indo-Europeans when Romans arrived, but also in most of those occupied by non-Indo-Europeans.
Among Indo-European peoples, the traditional paradigm – carried around in Wikipedia-like texts until our days – has been to classify their languages as “Pre-Celtic” despite the non-Celtic phonetics (especially the initial -p-), because the same toponyms appear in areas occupied by Celts (e.g. Parisii, Pictones, Pelendones, Palantia); or – even worse – just as “Celtic”, because of the famous -briga and related components. This was evidently not tenable at the … Read the rest “European hydrotoponymy (II): Basques and Iberians after Lusitanians and “Ligurians””