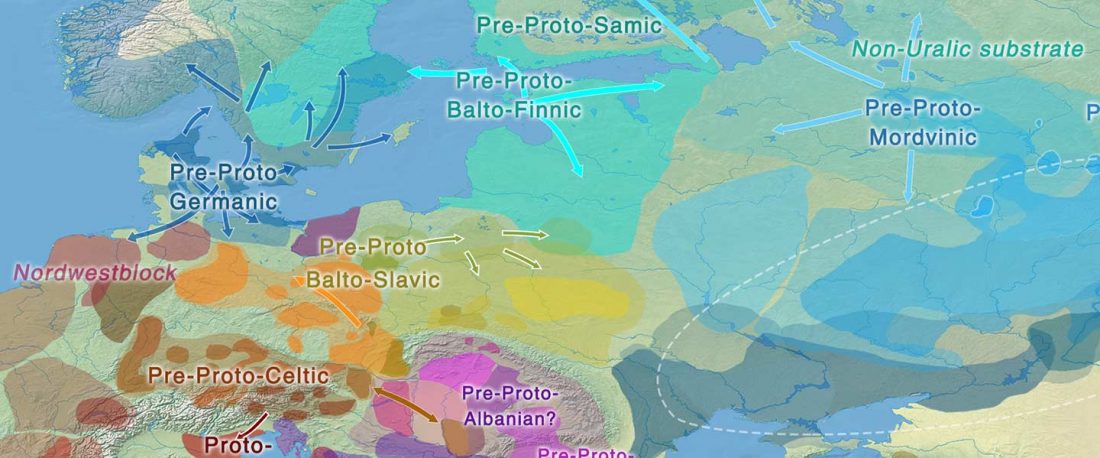
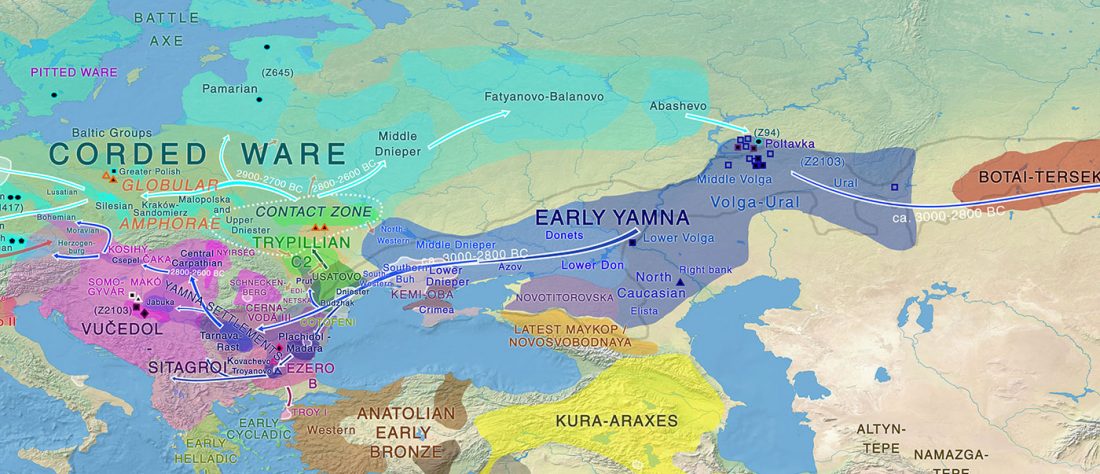
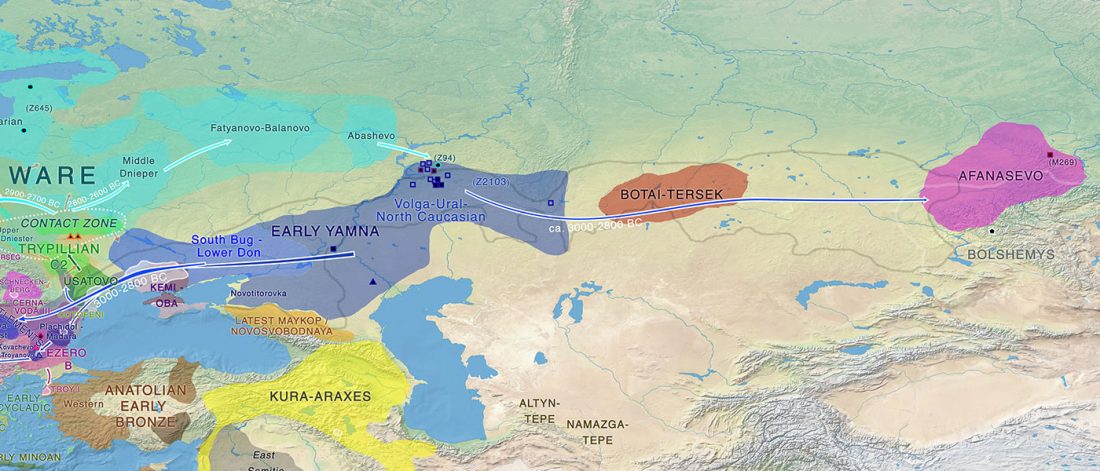
Some very specific prosodic innovations affected the Balto-Slavic linguistic community, probably at a time when it already showed internal dialectal differences. Whether those innovations were related to archaic remnants stemming from the parent Proto-Indo-European language, and whether that disintegrating community included different dialects, remains an object of active debate.
“Archaic” Balto-Slavic?
The main question about Balto-Slavic is whether this concept represents a single community, or it was rather a continuum formed by two (Baltic and Slavic) or possibly three (East Baltic, West Baltic, Slavic) neighbouring communities, speaking closely related Northern European dialects, which just happened to evolve very close … Read the rest “Balto-Slavic accentual mobility: an innovation in contact with Balto-Finnic”