This post is part of a draft on South Siberian language homelands and Sprachbünde.
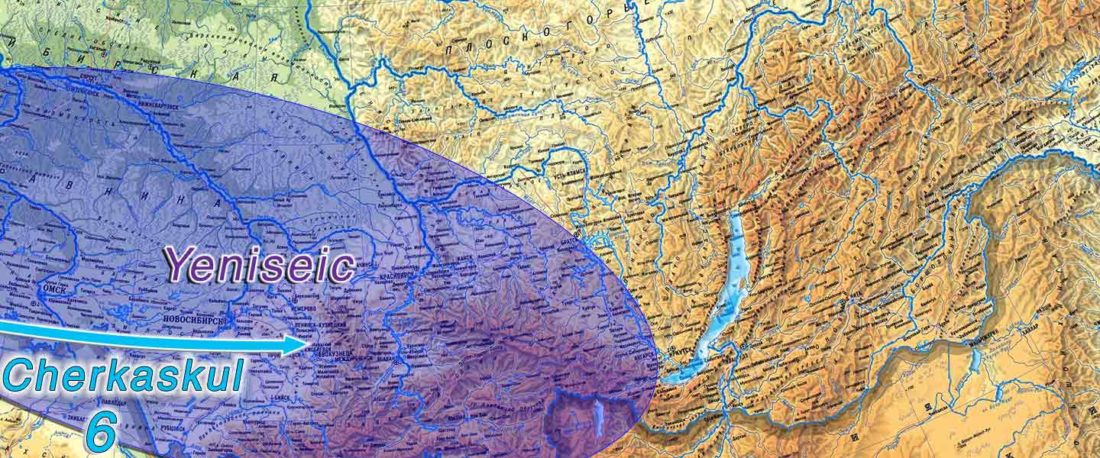
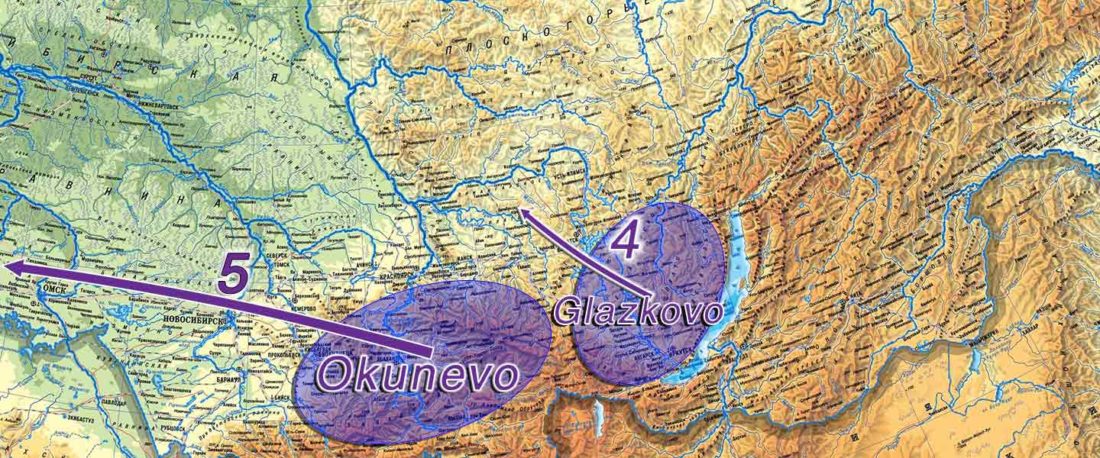
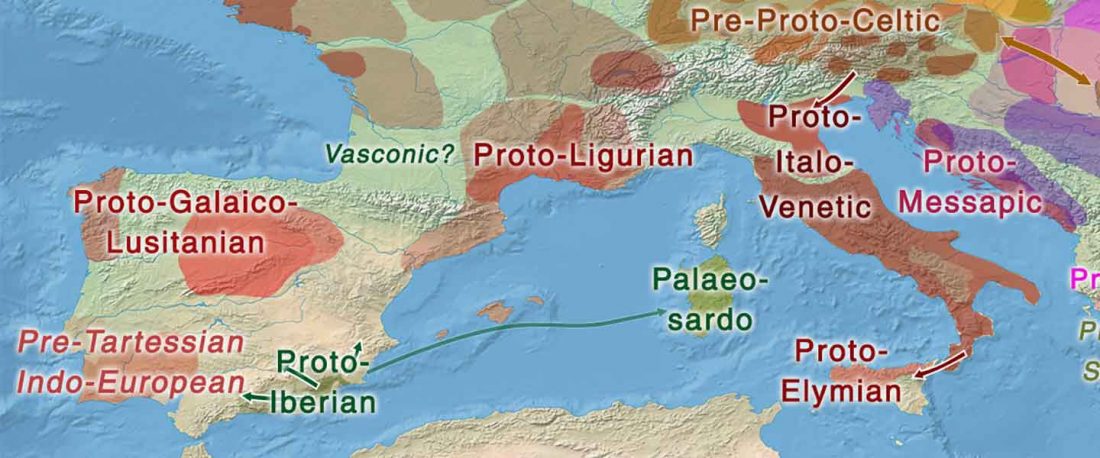
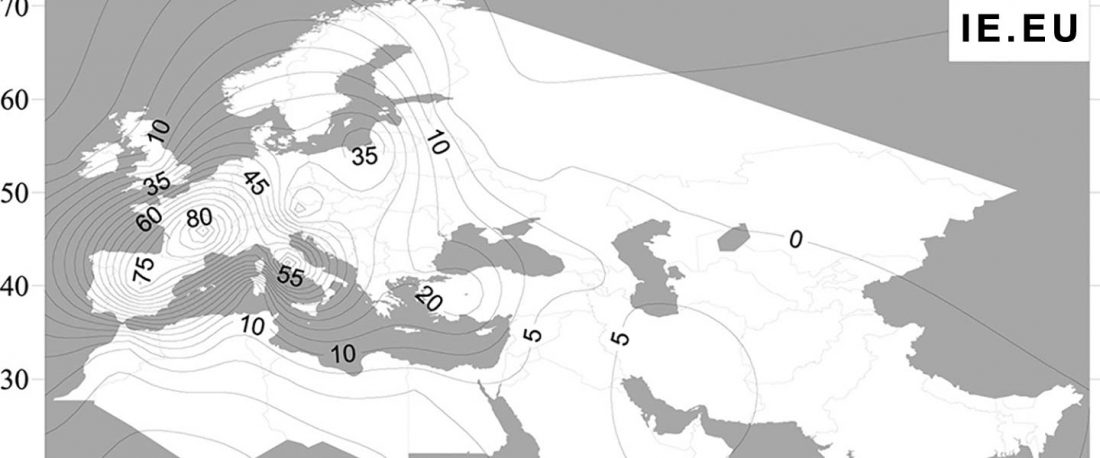
The following text contains a description of Ob-Ugric languages and their connection within an Ugric Sprachbund. Special emphasis is placed on their evolution among surrounding ethnolinguistic groups before they were first documented, and on their most likely connection with archaeological cultures succeeding the Seima-Turbino phenomenon in the Southern Urals and the Trans-Urals. The archaeological-archaeogenetic discussion is therefore focused on the Middle Bronze Age Cherkaskul and Late Bronze Age Andronovo-like cultures, as well as on the formation of the “Scythian” Sargat … Read the rest “Ob-Ugric Homeland”