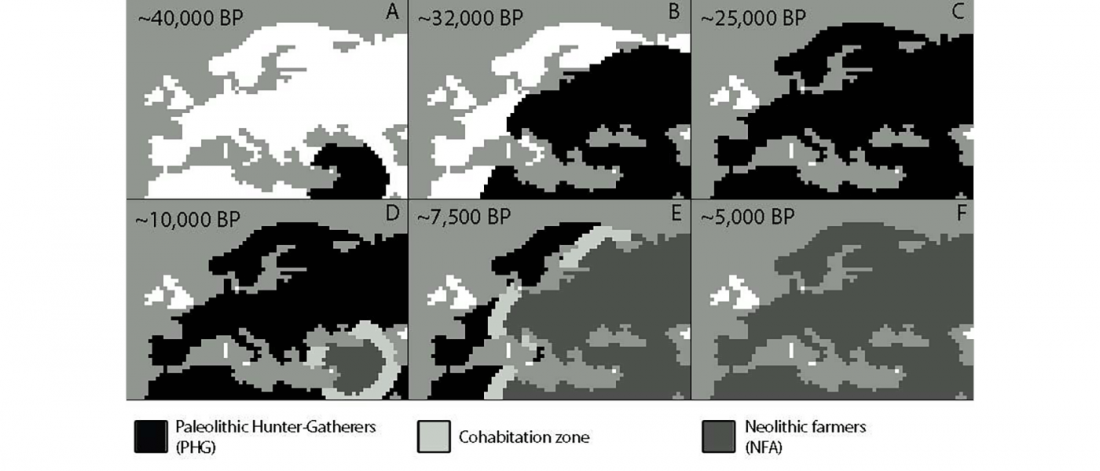
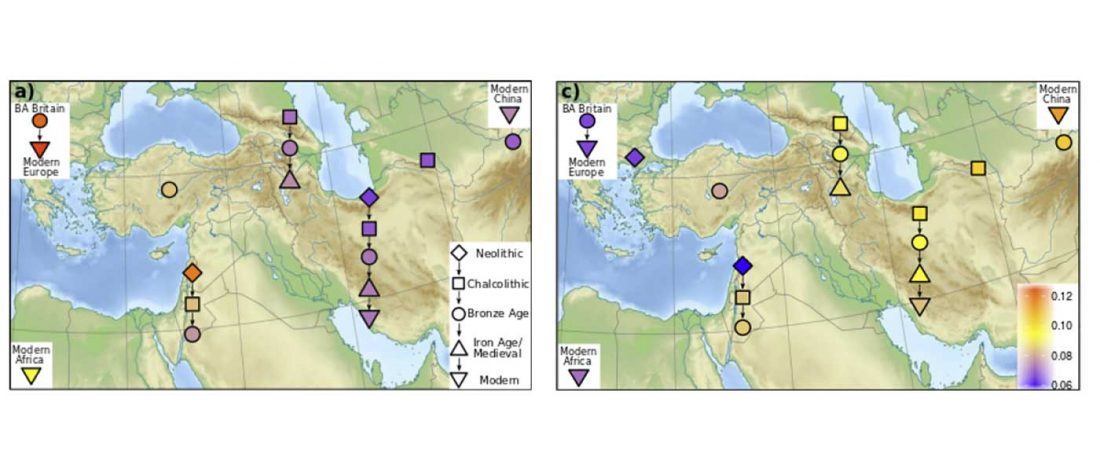
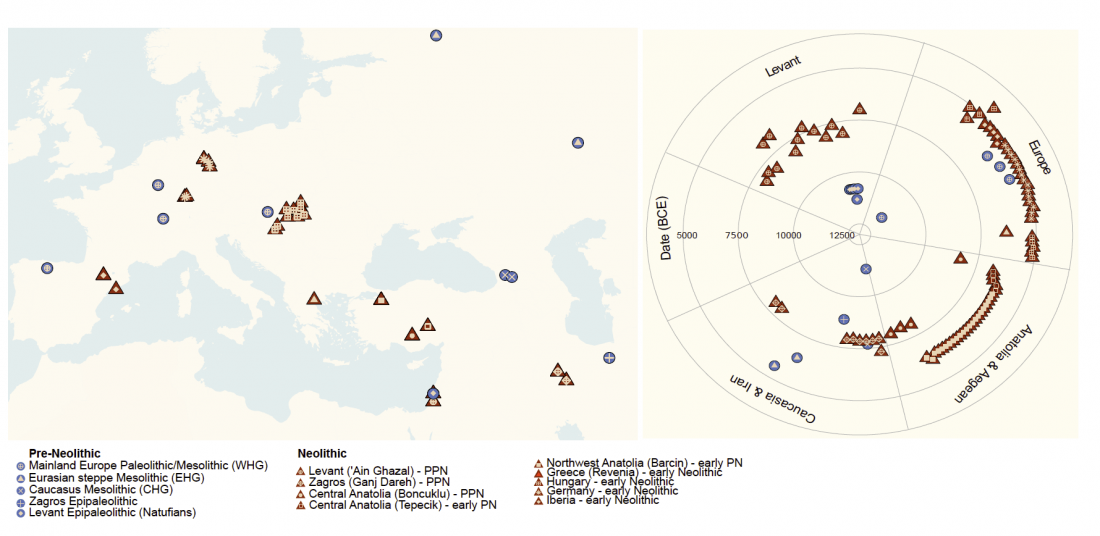
New paper (behind paywall) Ancient goat genomes reveal mosaic domestication in the Fertile Crescent, by Daly et al. Science (2018) 361(6397):85-88.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Expansion of domesticated goat echoes expansion of early farmers”Thus, our data favor a process of Near Eastern animal domestication that is dispersed in space and time, rather than radiating from a central core (3, 11). This resonates with archaeozoological evidence for disparate early management strategies from early Anatolian, Iranian, and Levantine Neolithic sites (12, 13). Interestingly, our finding of divergent goat genomes within the Neolithic echoes genetic investigation of early farmers. Northwestern Anatolian and Iranian human Neolithic genomes are also divergent (14–16),